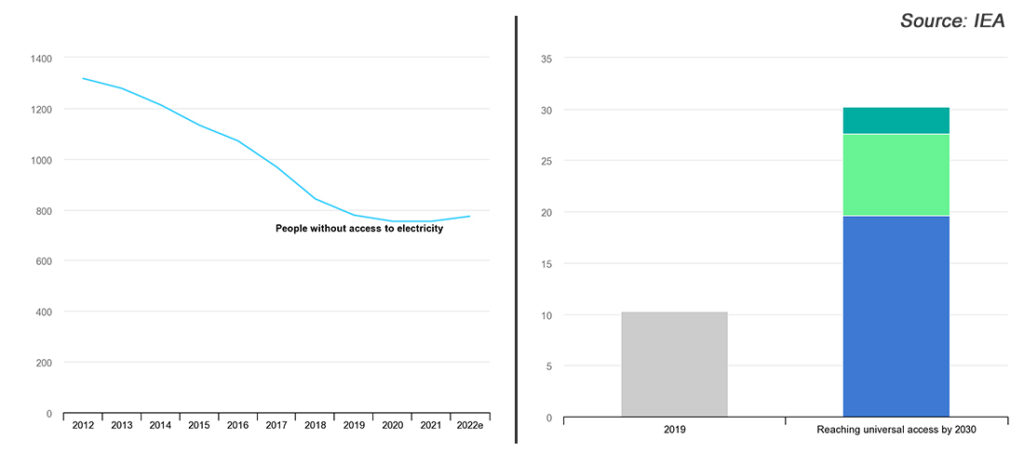
For those of you reading this article in front of a screen, you may not know that nearly 10% of the people on this planet still do not have access to electricity. Electricity, a basic necessity of modern human life. Lack of electricity supply or energy poverty will seriously hinder the development of economic and social development and the progress of human civilization. According to the latest IEA data, the number of people around the world who live without electricity is set to rise by nearly 20 million in 2022, reaching nearly 775 million, the first global increase since the IEA began tracking the numbers 20 years ago. The rise is mostly in sub-Saharan Africa, where the number of people without access is nearly back to its 2013 peak.
COVID-19 Pandemic, the energy crisis, inflation, and a combination of factors hitting consumer demand are holding back the process of solving the problem of powerless zones in some regions. Prices of key components used to manufacture solar PV modules, cells and inverters have risen this year, further exacerbated by the depreciation of local currencies against the U.S. dollar. By 2022, the cost of building off-grid PV plants has increased by at least 20% from pre-2019 levels. Since 2020, the average market price of new solar home systems (SHS) has increased by about 30%, leading households to choose smaller or lower quality systems. This is the main reason for the increase in the number of people without electricity this year.
Thanks to the development of new energy technologies, in the past decade, people have extended the power grid, new wind farms, hydroelectric plants, photovoltaic plants, etc., so that 530 million people around the world have access to electricity. And according to the IEA estimates, to achieve global electricity access by 2030 will require an annual investment of $30 billion from now until 2030. Among them, photovoltaic power system is the first choice to solve the problem of power supply in areas without electricity.

Photovoltaic power
Far from the grid, small loads and wide dispersion are the main characteristics of the powerless areas. For example, in China in 1996, there were still 76.56 million people without electricity, distributed in the vast northwest region. It would have taken at least 20 years to solve the power supply problem in the powerless areas by extending the power grid. This would have been too time-consuming and costly. And photovoltaic power generation can reverse all this.
Photovoltaic off-grid power generation system can operate independently of the grid and can be “stored and used” or “stored first and used later”. The system consists of a photovoltaic array, solar controller, inverter, battery bank, load, etc. The PV array converts solar energy into electricity when there is light, and supplies power to the load through the solar controller and inverter, while charging the battery bank; when there is no light, the battery supplies power to the AC load through the inverter.

Compared with wind power, hydropower, biomass power generation, PV power has the following advantages.
1, More flexible investment. Suitable for small-scale construction, from small to household use, to large-scale energy base construction can be used, easy to promote the construction of villages and counties as a unit.
2, BOS cost is lower. Each accessory of PV system is small, easy to transport and assemble, which can significantly reduce the construction cost and time cost during the construction of electric field, and the project is less difficult to promote.
3, More friendly to the environment. PV farms do not produce waste and noise, which has less impact on the ecological environment and residential environment, and also has the effect of sand control and water consolidation in desert areas, which helps local greening.

The Chinese Experience
As early as 2001, China launched the “Brightness Project” to use wind power, photovoltaic and other renewable energy sources to solve the electricity problem of 23 million people in remote areas without electricity. 2007, the state began to formally levy renewable energy surcharge, photovoltaic power industry subsidies have a guaranteed source of funding, greatly enhancing the investment incentives of photovoltaic enterprises. From 2009 to 2010, the state launched the “Golden Sun Project” to develop the construction of PV power plants in remote areas.
By the end of 2012, there were still 2.73 million people without electricity nationwide, mainly located in remote minority areas in Xinjiang, Tibet, Sichuan, Qinghai and other provinces (districts).From 2013 to 2015, the Chinese government arranged for the construction of additional substations and other infrastructures in the power grid to expand the power grid system and electrify 1.545 million people without electricity; in addition, it arranged for investment in the construction of independent photovoltaic power supply projects, which were implemented by central enterprise companies In December 2015, the National Energy Administration of China announced the successful completion of the task of comprehensively solving the electricity problem of people without electricity nationwide.
Maysun Solar was founded in 2008 and has followed the growth of PV in China. We are committed to bringing green energy to more homes. We have 8 offices and 23 warehouses worldwide and sell our products to more than 80 countries and regions, including energy-poor areas in South Asia and Africa. Let’s join hands and work together to reduce the number of people without electricity worldwide.



