Table of Contents
Risks of Thunderstorms to PV Systems
PV systems face multiple risks during thunderstorms. This article introduces the threats posed by thunderstorms to PV systems and the protection measures for different types of PV systems to ensure safe operation.
1. Direct Lightning Strikes
Direct lightning strikes pose the most immediate threat to PV systems. When lightning directly strikes PV modules or nearby structures, it can cause catastrophic damage. The high-energy surge from a lightning strike can damage critical electronic components of PV modules, such as inverters, battery management systems, and connecting cables. This damage can not only stop the system from functioning but also potentially cause fires or explosions, severely affecting the equipment’s lifespan and safety.
2. Induced Lightning
Induced lightning is another common form of damage to PV systems, especially in regions with frequent thunderstorms. Even if lightning does not directly strike the PV modules, electromagnetic induction can cause overvoltage within the system. This overvoltage may exceed the rated working voltage of the modules and electronic devices, leading to component damage or performance degradation. The cumulative damage from induced lightning can shorten the system’s lifespan and reliability.
3. Ground Potential Rise
Ground potential rise occurs when lightning strikes the ground or nearby conductors, transmitting overvoltage through the grounding system to the PV system. Although the grounding system is designed to safely direct lightning currents into the ground, ground potential rise can cause the grounding system to fail to effectively eliminate the overvoltage. In this situation, the overvoltage may enter the PV system’s circuits, damaging or even completely destroying critical equipment.
Do PV Systems Attract Lightning During Thunderstorms?
PV systems do not actively attract lightning during thunderstorms, but taking preventive measures to reduce the risk is advisable.
Should I Turn Off My PV System During Thunderstorms?
Turning off the PV system can reduce the likelihood of equipment being affected by lightning, especially when there are no dedicated lightning protection facilities. This is an effective safety measure.
Necessity of Installing Lightning Protection
In most countries and regions, installing lightning protection facilities is a necessary measure to protect equipment and user safety. Electrical safety codes usually require PV systems to be equipped with suitable lightning protection measures to ensure long-term stable operation.
Key Components of PV System Lightning Protection Design
1.Grounding System
A good grounding system is the first line of defense against lightning damage. Ensure the grounding resistance is below safety standards to effectively dissipate lightning overvoltage.
2.Lightning Rods and Conductors
Installing lightning rods or conductors near PV arrays can reduce the likelihood of lightning striking PV modules and safely direct the lightning energy into the ground.
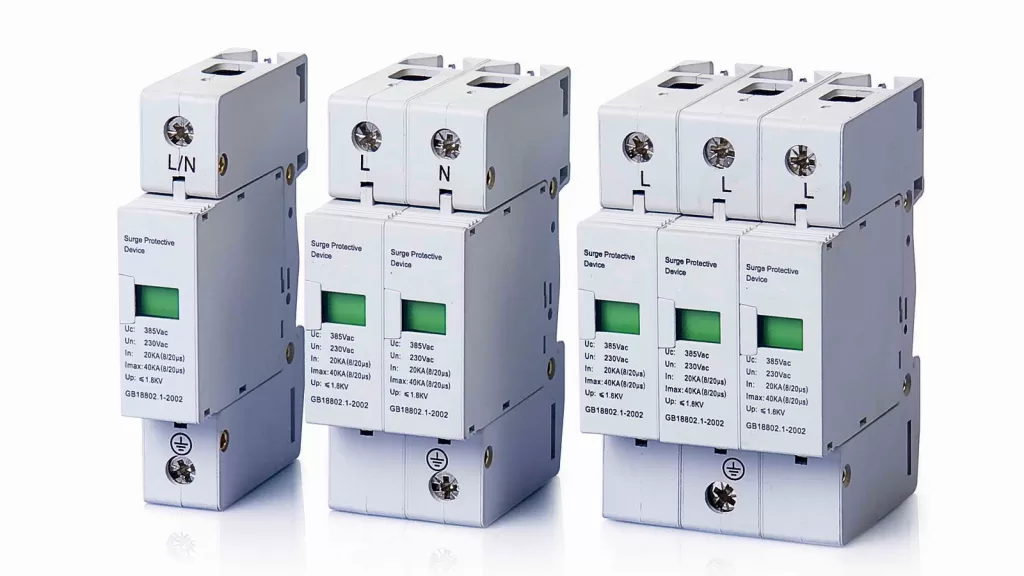
3.Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
Photovoltaic systems’ sensitive electrical equipment, such as AC/DC inverters, monitoring devices, and photovoltaic arrays, must be protected using surge protection devices (SPDs). SPDs are mainly divided into three types:
Type 1: Installed at the main distribution board or meter location, used with lightning rods and other lightning protection systems to dissipate the strong currents from direct lightning strikes.
Type 2: Installed at the household electrical panel, can be used independently or with lightning rods, protecting against indirect lightning strikes and other overvoltages.
Type 3: Installed near specific electronic devices at the point of use, providing supplementary surge protection for individual devices such as computers, TVs, and peripherals, suitable for devices more than 10 meters away from Type 1 or Type 2 SPDs.
The effectiveness of SPDs depends on correct installation and matching surge current ratings. It is recommended to consult a licensed electrician to assess the lightning risk in your area, determine the most suitable SPD type for your home, and ensure that SPDs have appropriate surge current ratings to protect your electronic devices from damage.


Four Types of PV System Lightning Protection Measures
In PV systems, lightning protection is crucial. Understanding the different types of lightning protection systems and their applications can effectively protect PV systems from lightning strikes and voltage surges. Here are four types of lightning protection measures for different PV systems:
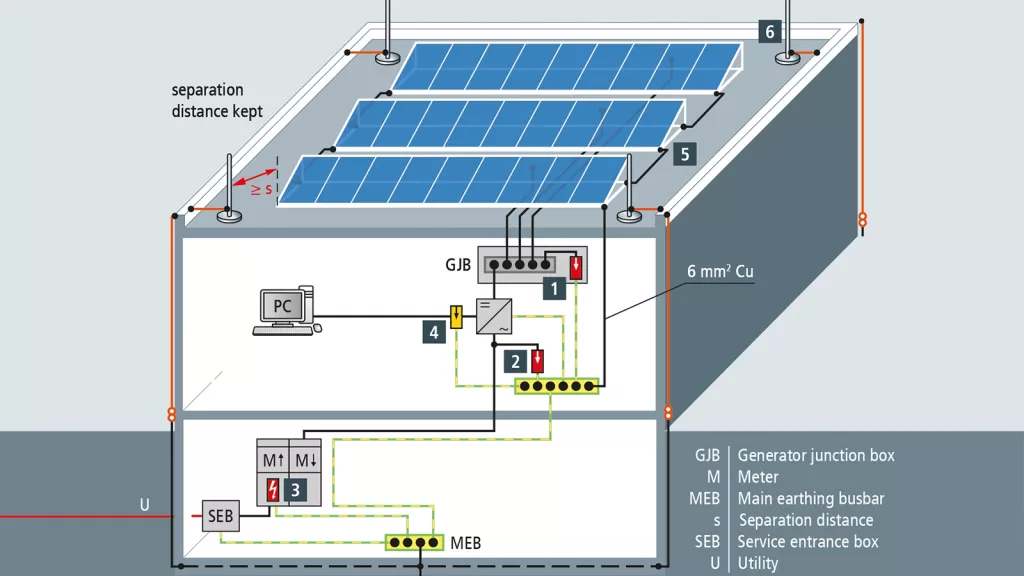
1.PV System with Independent Lightning Protection System
A PV system with an independent lightning protection system means installing and operating a separate lightning protection system for the PV system based on existing buildings. This design ensures that the PV system can safely operate independently of the building’s lightning protection system.
Recommended Measures:
(1)Lightning Arrestor Installation: Install dedicated lightning arrestors on PV panels or mounting structures to provide a preferential path for lightning currents, safely directing them to the ground.
(2)Surge Protection Devices (SPDs): Install SPDs near electrical components to detect and safely dissipate surge currents, preventing damage.
(3)Potential Equalization: Establish good potential equalization, connecting all electrical components to the grounding system to ensure a unified ground reference.
(4)Effective Grounding System: Install an effective grounding system to safely guide lightning currents and reduce harmful currents to components.
2. PV System with Shielded Lightning Protection System
If spatial constraints do not allow sufficient separation distance between the lightning protection system and the PV system wiring, these usually independent systems are interconnected. This design includes traditional lightning protection measures and shielding measures for electromagnetic interference (EMI) to enhance the system’s electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).
Recommended Measures:
(1)Shielded Cables: Use shielded cables (with a conductive material layer) to protect cables from external electromagnetic field interference and prevent electromagnetic interference generated by cables.
(2)Shielded Electronic Components: Use shielded electronic components to reduce sensitivity to electromagnetic interference, improving system performance and reliability.
(3)EMC Optimization: Optimize the layout and shielding of system components and cables to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure system and surrounding environment stability.
3.PV System with Lightning Protection but No Shielding
In this configuration, the PV system has lightning protection measures but no additional shielding to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). The system focuses primarily on preventing lightning strikes and voltage surge damage.
Recommended Measures:
(1)Lightning Arrestors and SPDs: Install lightning arrestors and SPDs to ensure lightning currents and voltage surges are safely dissipated, protecting system components.
(2)Effective Grounding: Ensure all metal components (such as module frames and mounting racks) are well connected to the grounding system to guide lightning currents and reduce damage risk.
4. PV System Without Lightning Protection
PV systems without lightning protection systems are at extremely high risk, easily suffering damage from lightning strikes and voltage surges.
Potential Risks:
(1)Lightning Damage: PV systems, usually installed on roofs or high places, are prone to lightning strikes, causing severe damage.
(2)Voltage Surges: Lightning-induced voltage surges may enter the system, damaging electrical components.
(3)Fire Risk: Lightning strikes may cause fires, especially in the absence of lightning protection measures.
(4)Building and Electrical System Damage: Lightning and surges may spread to building structures and power networks, causing extensive damage.
(5)Safety Risks: Lightning strikes pose potential safety threats to people near PV systems.
Conclusion
PV systems face various potential risks during thunderstorms, including direct lightning strikes, induced lightning, and ground potential rise. To ensure the safe operation of the system, appropriate lightning protection measures, such as lightning rods, good grounding systems, and SPDs, must be installed. By adopting the appropriate lightning protection measures for different types of PV systems, you can effectively protect the system from lightning strikes and voltage surges. Regular maintenance and inspection of these lightning protection facilities, and consulting professional advice, will ensure that the PV system can operate safely under all weather conditions.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has been dedicated to producing high-quality photovoltaic modules. Maysun Solar offers TOPCon,IBC and HJT solar panels, as well as balcony solar power stations. These solar panels boast excellent performance and stylish design, seamlessly integrating with any building. Maysun Solar has successfully established offices and warehouses in many European countries and has long-term partnerships with excellent installers! Please feel free to contact us for the latest module quotes or any photovoltaic inquiries. We are happy to assist you.
Reference:
Blitzschutz von Photovoltaik-Anlagen. (n.d.). VDE Blitzschutz. https://www.vde.com/de/blitzschutz/infos/pv-anlagen
Steffen, C. (2024, May 19). Blitzschutz für PV-Anlagen – wirklich notwendig? 

Zagorac, A. (2024b, May 29). Are you protected against power surge damage? Schneider Electric Blog. https://blog.se.com/homes/2017/12/22/protected-power-surge-damage/
You may also like:

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!



