Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are the core component of solar modules. There are two common types of photovoltaic cells in production: full-cell and half-cell.
① Full-Cell
Full-cell refers to a photovoltaic cell made entirely from a single crystalline silicon wafer. The manufacturing process is relatively simple, which makes the cost lower.
② Half-Cell
Half-cell refers to a single crystalline silicon wafer that is cut in half, and then the two halves are connected to form the photovoltaic cell.
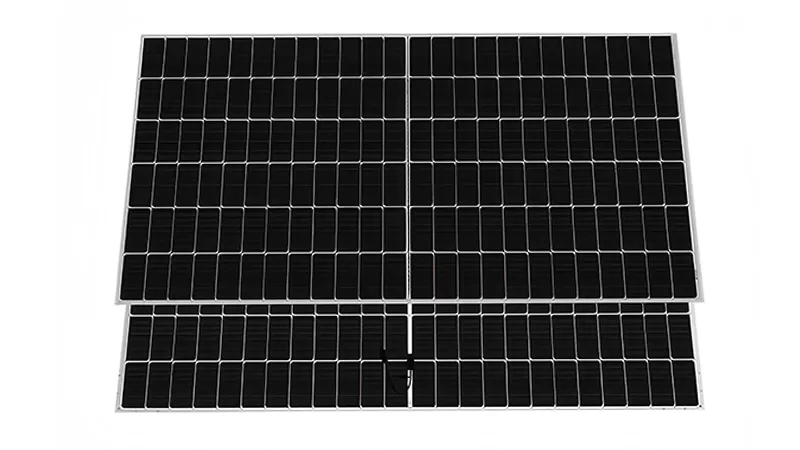
Half-Cell Technology
Half-cell technology involves cutting the standard photovoltaic cells in half. Unlike typical photovoltaic modules with 60 or 72 cells, these modules have 120 or 144 half-cells, while maintaining the same design and dimensions as conventional modules.
The half-cell technology generally uses laser cutting to cut standard-sized photovoltaic cells in half, along a direction perpendicular to the cell’s main grid lines, then welding the two halves together in series.
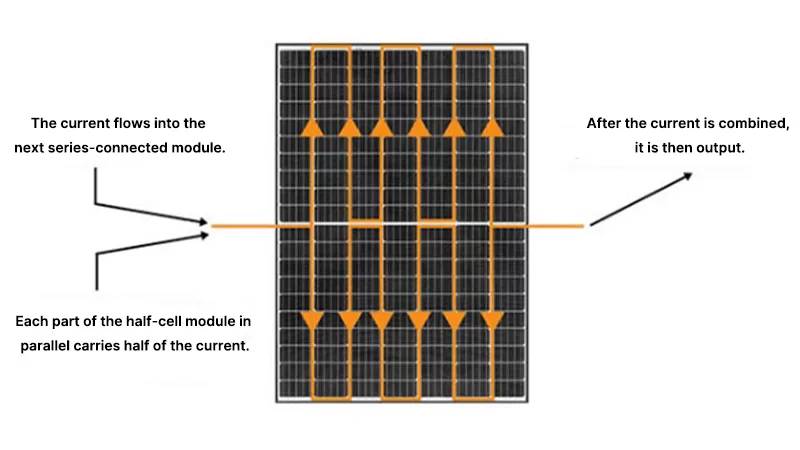
Like conventional modules, the half-cell modules are encapsulated using tempered glass, EVA, and backsheet. Conventional solar modules typically contain 60 series-connected solar cells, with each cell having a voltage of 0.5-0.6V. The voltage increases when cells are connected in series, resulting in an operating voltage of 30-35V for a 60-cell module. When half-cells are connected like those in standard modules, they produce half the current and double the voltage, with resistance remaining unchanged (as shown in the figure below).

To ensure consistent output voltage and current with conventional modules, half-cell modules generally adopt a series-parallel configuration design, effectively creating two smaller modules connected in parallel.
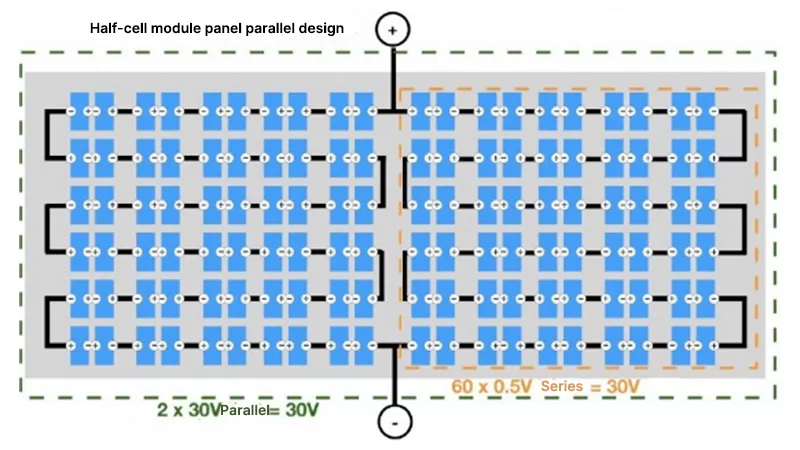
As shown in the diagram above, the open-circuit voltage of a half-cell is the same as that of a full-cell. When the number of half-cells is doubled, each part of the module contains the same number of cells as a full-cell module. After connecting the two parts in parallel, the voltage remains the same as that of each individual part, meaning the total output voltage remains unchanged compared to the full-cell module.
Because half-cell modules are only half the size of conventional cells, each half-cell carries half the current of a full-cell. By designing the module with two halves in parallel, the output current is restored to the same value as that of a full-cell module.
The resistance of a half-cell is half that of a full-cell, so each part in parallel has only half the resistance of the full-cell module. When the two parts, each with half the resistance, are connected in parallel, the total loop resistance is reduced to one-quarter of the full-cell resistance.
Advantages of Half-Cell Design
i) Lower Packaging Losses
The internal current and line resistance are reduced, leading to lower internal power losses. Since power loss is proportional to current, half the current and one-quarter of the resistance in half-cell modules lead to a 4x reduction in power loss, thereby increasing the output power and energy generation.
b. As internal losses decrease, the operating temperature of the module and junction box also drops. Under outdoor conditions, the temperature of half-cell modules is about 1.6°C lower than that of conventional full-cell modules, which improves the module’s photovoltaic conversion efficiency.
c. Even if the two halves are not connected in parallel and all half-cells are connected to operate like a standard solar panel, the current would be half, but the resistance remains the same, reducing power consumption to one-quarter.
ii) Reduced Shading Tolerance and Hotspot Risk
Half-cell modules offer better resistance to shading effects compared to standard solar modules.
b. Unlike standard modules, which have 3 cell strings, half-cell modules have 6 cell strings, effectively creating a 6-string panel. Even if a small part of the module is shaded (e.g., by tree leaves, bird droppings, etc.), it would cause only one string to fail. However, thanks to the bypass diode design (highlighted in red in the diagram below), this failure does not affect the other cell strings, thus minimizing the impact of shading.
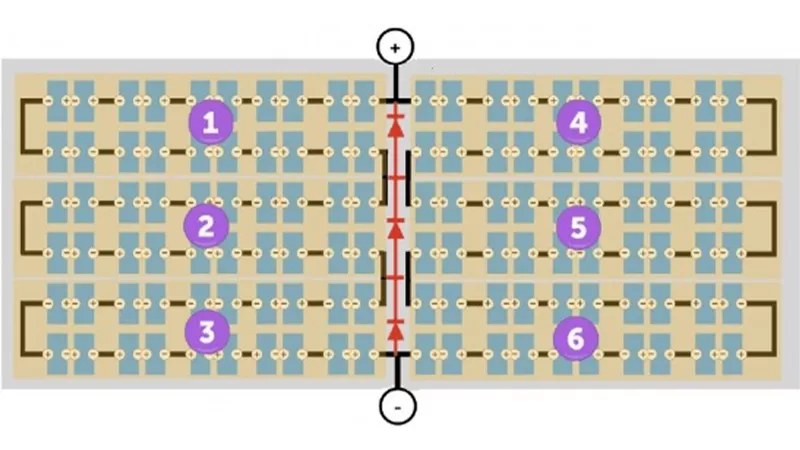
The 6 independent cell strings in half-cell modules are equipped with 3 bypass diodes, providing better local shading tolerance. Even if half of the module is shaded, the other half can still operate.
iii) Lower Current Reduces Hotspot Temperature
a. Half-cell modules distribute internal current more evenly within the system, improving their performance, lifespan, and shading tolerance.
b. When one cell in a string is shaded, that specific cell forms a hotspot in the circuit. The prolonged high temperature caused by this hotspot can potentially damage the module. Since half-cell modules have twice as many strings as conventional modules, the heat at the hotspot is divided across more strings. As a result, the temperature at the hotspot is reduced by half, which minimizes the damage to the module. This enhances the module’s ability to resist hotspot damage and ultimately improves its overall lifespan.
iv) Reduced Shading Tolerance Decreases Power Loss
a. In a photovoltaic array, multiple modules are typically connected in series, and these series strings are then connected in parallel. Current flows sequentially through each module in the series string.
b. In traditional module designs, if one module experiences power loss due to shading, it will affect all the modules in that series string. However, in the half-cell module design (as shown in the diagram above), the bypass diodes limit the power loss to only the shaded portion of the module, rather than the entire module. These diodes create an alternative path for the current to flow through the unshaded parts of the module, thereby preventing the current from flowing through the shaded sections. This reduces the impact of shading and improves the overall performance of the module.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has been dedicated to producing high-quality photovoltaic modules, including advanced IBC, HJT and TOPCon panels, and innovative solutions like balcony solar stations. As solar carports become an increasingly popular choice for renewable energy generation across Europe, Maysun Solar’s products offer excellent performance and guaranteed quality for these applications. Whether you’re looking to integrate solar panels into a carport system or any other energy solution, Maysun Solar provides reliable, cutting-edge technology to meet your needs. With offices and warehouses established worldwide, we are committed to long-term partnerships with top installers to bring sustainable energy solutions to homes and businesses. For the latest quotes on solar panels or any photovoltaic-related inquiries, please contact us—we are here to help you make the most of your solar energy investment.

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!




It’s interesting how half-cell tech not only boosts efficiency but also reduces the risk of damage during installation. I’m curious, though, if there are any long-term durability studies comparing full-cell vs. half-cell modules.
Thank you for your comment! Half-cell technology indeed enhances efficiency and reduces the risk of damage during installation. Additionally, its design minimizes internal resistance and heat accumulation, which can contribute to long-term stability. If you’re interested, we can explore further insights on durability comparisons.