Rooftop Solar Could Meet Around Two-Thirds of Global Electricity Demand, Study Finds
A recent study by the University of Sussex suggests that fully utilizing rooftop solar panel installations worldwide could theoretically meet approximately 65% of global electricity demand.
The study, published in Nature Climate Change under the title “The Potential of Global Rooftop Photovoltaics for Climate Change Mitigation”, leverages geospatial data mining techniques and artificial intelligence models to analyze the global rooftop area, estimated at approximately 286,000 square kilometers—comparable to the land area of Italy. The findings indicate that if all suitable rooftops were fully utilized for solar photovoltaic (PV) installations, they could generate approximately 19,500 TWh of electricity annually. When combined with load shifting and battery storage technologies, rooftop PV systems could effectively replace fossil fuel-based power generation.
Furthermore, researchers employed advanced climate models to simulate the impact of large-scale rooftop PV deployment. Results suggest that by 2050, global temperatures could be reduced by 0.05 to 0.13°C as a direct consequence.
Professor Felix Creutzig, an expert in climate and policy at the University of Sussex, stated: “Beyond reducing carbon emissions, decreasing reliance on fossil fuels will also improve air quality and enhance energy security. At present, solar energy surpasses nuclear power in terms of cost, deployment speed, and environmental risk control.” He further emphasized that given the immense potential of solar energy, governments should carefully evaluate the rationale for investing in nuclear power or underdeveloped carbon capture projects.
The research also provides an in-depth analysis of regional PV deployment potential, highlighting the necessity of adapting rooftop solar implementation to local conditions. Priority should be given to regions with high solar irradiation or rapid urbanization. For instance, East Asia, characterized by high carbon emission intensity and extensive building stock, is identified as a key area where rooftop PV could significantly contribute to climate change mitigation. Additionally, North America and Europe possess substantial building infrastructure, theoretically capable of accommodating over 4,300 GW of rooftop PV capacity—accounting for one-quarter of the global potential.
The study calls for strengthened international cooperation to accelerate rooftop PV adoption in regions with the highest potential, particularly in Africa. Currently, Africa accounts for only 1% of the global installed rooftop solar capacity, yet it holds vast untapped potential for future expansion.

S&P Global: Power Market Reforms May Drive China’s Solar Demand and Module Prices Up
S&P Global’s latest analysis suggests that China’s upcoming electricity pricing reforms could drive short-term growth in both domestic and international demand for solar modules, potentially leading to price increases. In February, China’s National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) announced plans to replace the current feed-in tariff (FIT) policy with a fully market-based renewable energy pricing system. Under this new framework, renewable energy generation will be traded directly in the market.
In its impact assessment report, S&P Global notes that while this policy shift will enhance market competitiveness in China’s renewable energy sector, it will also introduce greater volatility. According to the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA), the new mechanism is set to take effect on June 1, which may result in an uptick in solar installations ahead of the deadline. At present, solar developers still have the opportunity to sign fixed-price contracts.
Qi Qin, an analyst at CREA China, stated: “Due to the revenue uncertainty introduced by the new policy, developers may accelerate their procurement to mitigate future risks. This could lead to a short-term increase in solar panel demand and drive up prices.” S&P Global further highlights that given the scale of China’s solar market, any rise in module prices could have ripple effects on the global market.
Jessica Jin, Principal Research Analyst for Clean Energy Technology at S&P Global Commodity Insights, commented: “If demand surges, solar module prices may rebound.” She added that while global price adjustments may lag behind, the overall trend will likely align with developments in China. However, due to high tariffs, markets such as the U.S. and India may experience distinct supply and demand dynamics.
S&P Global’s report also suggests that price increases could further stimulate market demand. Some developers might opt for early procurement at current price levels to hedge against potential future hikes. However, some industry experts believe that the current price surge is temporary and unlikely to persist beyond the third quarter of this year.
Additionally, S&P Global emphasizes that the long-term growth of China’s solar module demand will depend on “the optimization and refinement of the entire photovoltaic industry ecosystem.” Qin Gang, a researcher at CREA, pointed out that the rapid expansion of solar installations over the past two years has exposed challenges related to grid integration. He warned: “If these issues—particularly those concerning grid flexibility and power market reforms—are not effectively addressed, they could constrain future solar deployment and, in turn, impact domestic demand for solar panels.”

French Government Launches Final Public Consultation on PPE 3, Solar Targets Revised Downward
The French government has officially launched the final public consultation on the third Multiannual Energy Plan (PPE 3), a key strategic document guiding the country’s energy transition from 2025 to 2035. The consultation will remain open until April 5. Concerns previously raised by industry stakeholders have now been confirmed, as the revised PPE 3 sets lower solar power targets. Compared to the draft released in November 2024, which proposed a target range of 75 GW to 100 GW, the latest version from March 2025 has been adjusted to 65 GW to 90 GW. By 2030, the solar capacity target is set at 54 GW (compared to the current installed capacity of approximately 25 GW), aligning more closely with the lower end of the 54 GW to 60 GW range suggested during the consultation process at the end of 2024.
Furthermore, as highlighted in an analysis by Gossement Law Firm, the revised targets are now broken down into different categories of solar installations: 41% will come from small to medium-sized rooftop projects, 5% from small-scale ground-mounted installations, and 54% from large-scale projects—of which 38% will be ground-mounted and 16% rooftop installations. However, PPE 3 does not specify any development targets for agrivoltaics or photovoltaic projects integrated with agricultural operations.
The revised plan also includes objectives to strengthen France’s industrial solar manufacturing sector, aiming to establish up to 10 GW of production capacity across key segments of the photovoltaic value chain by 2035. The targets for specific segments include 3 GW to 5 GW for silicon materials, 3 GW to 5 GW for ingots and wafers, and 5 GW to 10 GW for solar cells and modules. However, the latest draft does not explicitly address long-term public support for renewable energy production, nor does it set specific targets for self-consumption of renewable electricity.
In the appendix titled “Changes Following the 2024 Consultation”, the rationale for adjusting solar targets is provided. The document states that “some stakeholders believe that, given the slower-than-expected electrification process, the original 2035 targets were overly ambitious.” However, several organizations—including the renewable energy industry coalition that signed the 2024 Solar Pact—advocate for maintaining or even increasing the initial targets. Additionally, France’s transmission system operator RTE, in its 2035 electricity adequacy report, outlined two possible development trajectories: a high scenario targeting 90 GW (requiring annual growth of 7 GW) and a low scenario targeting 65 GW (requiring annual growth of 4 GW). The revised PPE 3 ultimately references RTE’s projections and states that solar deployment speed may be further adjusted before 2030 based on actual electricity demand growth.
In response to these revisions, the French solar energy association Enerplan commented: “At a time when solar power is readily available, economically competitive, and rapidly deployable, lowering the target sends a contradictory signal to the market. This adjustment does not align with the current energy landscape. France’s low-carbon energy supply is far from excessive, as 60% of the country’s energy consumption still relies on fossil fuels.”

Dynamics of the European Solar and Wind Energy Markets: Impact of Declining Capture Rates and Price Volatility
Solar and wind energy have gradually become the backbone of Europe’s electricity supply, steadily replacing traditional fossil fuel-based power generation. Enervis, in its latest report, “2025 Renewable Energy Electricity Market Report: Navigating Volatility and Erosion,” provides an in-depth analysis of the impact of this shift on the market. A notable finding from the report is that, compared to 2023, the average market electricity price has decreased in 2024. However, due to rising natural gas prices, overall power generation in Europe remains higher than pre-crisis levels.
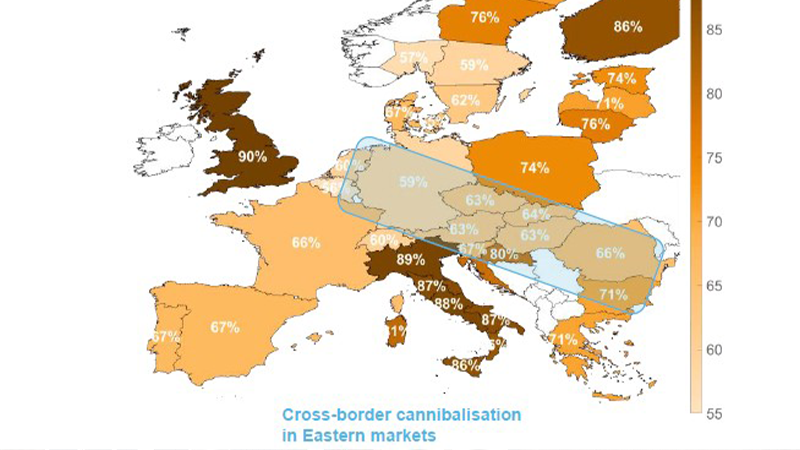
Image: Enervis “2025 Renewable Energy Electricity Market Report: Navigating Volatility and Erosion”
Renewable Energy Development and Seasonal Power Market Volatility
The report highlights that as renewable energy’s share in the electricity market continues to grow, the seasonal volatility of the market has become more pronounced. For instance, during spring, when renewable energy supply is abundant, market electricity prices reached their lowest in nearly three years. However, the “dark period” from November to December 2024 had a significant impact on the market, with electricity prices during this period noticeably higher than in the same months of the previous year.
Sharp Decline in Solar Capture Rates, Germany Most Affected
Enervis’ analysis reveals that almost all markets have experienced a persistent decline in solar system capture rates, with Germany being the most affected. The study estimates that in 2024, Germany’s solar capture rate will drop to 59%, the lowest in Europe. Capture rate is an indicator that measures the relationship between renewable energy project revenues and base-load electricity prices, influenced by technology and geographic location. Within Europe, countries such as the UK (90%), Italy (86%-89%), and Finland (86%) have relatively high capture rates. However, in Southeast European countries, including Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, and Romania, solar system capture rates have also declined significantly, maintaining only between 63% and 66%.
Cross-Border Power Flow and Market Erosion Phenomenon
The study identifies a phenomenon called “cross-border erosion” that is affecting markets in Southeast Europe. For instance, Germany’s peak solar power generation leads to large amounts of electricity flowing to neighboring countries, thereby lowering their domestic capture rates. This trend has caused some markets’ solar electricity prices to decline at a rate faster than the historical average.
Frequent Negative Electricity Prices, Increasing Pressure on PPA Prices
Enervis’ research further indicates that while base-load electricity prices in 2024 remain higher than pre-crisis levels, the market erosion of solar electricity has resulted in further revenue reduction. In Germany, the capture price for solar power is only €47 per megawatt-hour, lower than in France, Spain, Portugal, and some Nordic countries. Additionally, negative electricity price periods have significantly increased in multiple European markets in 2024, with the Netherlands and Germany experiencing the highest frequency of negative prices, while Spain encountered negative prices for the first time. This situation has triggered a chain reaction in the power purchase agreement (PPA) market, with buyers increasingly inclined to share market risks with producers, putting additional pressure on PPA prices.
Impact of Negative Prices on Solar Operators
In Germany, around 20% of solar power generation was affected by negative price periods in 2024. According to market regulations, when electricity prices remain negative for at least three consecutive hours, solar power plants will be unable to receive subsidies, affecting 16% of solar generation. In contrast, wind power generation is only 6% affected by similar conditions.
Storage and Grid Flexibility Development Lagging, Future Market Will See High Volatility
Theoretically, additional storage capacity or more flexible grids could help mitigate these issues, but the current growth rates of energy storage and grid adjustments are far slower than the expansion of solar and wind power. Enervis predicts that between 2025 and 2030, renewable energy generation capacity will increase by 390 GW, while storage expansion will only reach about 93 GW. Due to insufficient growth in storage capacity, future peak solar generation during midday will be hard to buffer effectively, meaning negative price issues will persist.
The study concludes: “In the coming years, electricity market volatility is expected to remain high, with the frequency of zero, negative, and scarce electricity prices likely to increase further. During this transitional phase, assets that enhance system flexibility will hold higher economic value.”
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has been dedicated to producing high-quality photovoltaic modules. Our range of solar panels, including IBC, HJT and TOPCon panels, and balcony solar stations, are manufactured using advanced technology and offer excellent performance and guaranteed quality. Maysun Solar has successfully established offices and warehouses in many countries and built long-term partnerships with top installers! For the latest quotes on solar panels or any photovoltaic-related inquiries, please contact us. We are committed to serving you, and our products provide reliable assurance.
Reference:
Enkhardt, S. (2025, February 27). Enervis: Photovoltaik-Ausbau führt zu grenzüberschreitenden Kannibalisierungseffekten in Europa. Pv Magazine Deutschland. https://www.pv-magazine.de/2025/02/27/enervis-photovoltaik-ausbau-fuehrt-zu-grenzueberschreitenden-kannibalisierungseffekten-in-europa/
Jowett, P. (2025, March 11). S&P Global: Chinas Strommarktreform könnte die Nachfrage nach Solarmodulen und die Preise ankurbeln. Pv Magazine Deutschland. https://www.pv-magazine.de/2025/03/11/sp-global-chinas-strommarktreform-koennte-die-nachfrage-nach-solarmodulen-und-die-preise-ankurbeln/
Deboutte, G. (2025, March 13). France sharply reduces PV targets in draft energy program. Pv Magazine International. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2025/03/13/france-sharply-reduces-pv-targets-in-draft-energy-program/
Jowett, P. (2025b, March 13). Rooftop solar could supply two-thirds of global power, study finds. Pv Magazine International. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2025/03/13/rooftop-pv-could-cover-almost-two-thirds-of-the-worlds-electricity-study-says/
You may also like:

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!

What’s New in Solar Energy (March 2025)
March’s solar news highlights include rooftop solar meeting two-thirds of global demand, China’s market reforms potentially boosting solar demand and module prices, France revising solar targets in PPE 3, and challenges in Europe with declining capture rates and price volatility.



