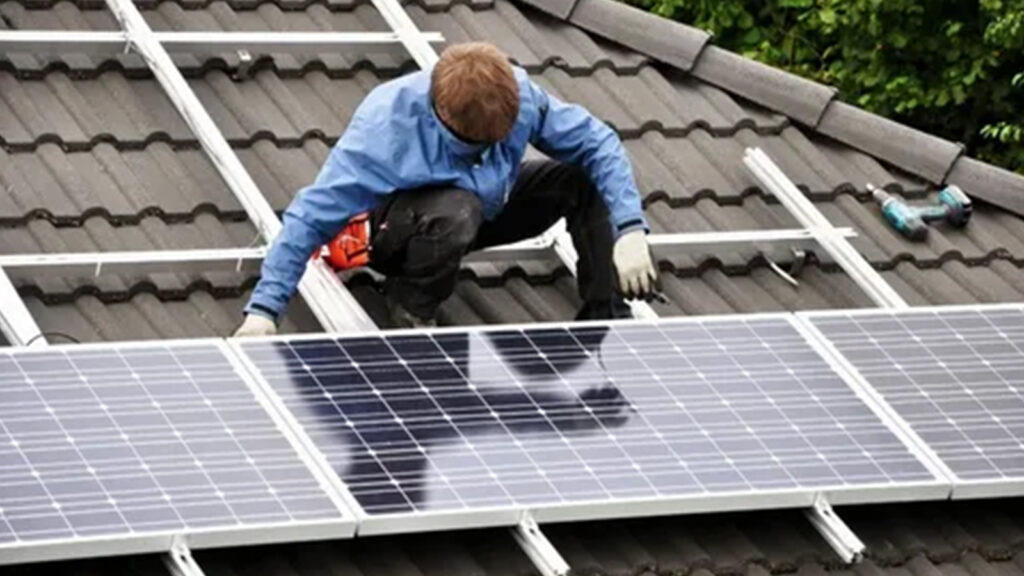
To achieve optimum performance, safety, and lifespan, photovoltaic (PV) system installation involves meticulous design and execution. Regardless of the type of roof you have, it is crucial to comprehend the installation method and steer clear of common blunders.
Flat roofs, in-roof integrations, and pitched roofs all need unique installation methods. The optimal procedures for PV installation are outlined in this article. These consist of flat roofs, in-roof mounting, and installation on pitched roofs.
Use these instructions to install your PV system quickly and effectively. By doing this, you’ll be able to maximize your system’s capacity for energy production. Let’s look at the specific steps to follow and common mistakes to avoid before starting your PV installation journey.

This Is What You Are About To View:
- How Can A PV System Be Installed On A Pitched Roof?
- Alternative Option: In-Roof Mounting
- Installation Of A PV System On A Flat Roof
- Avoiding The Most Common Mistakes In PV Installation
How Can a PV System Be Installed on a Pitched Roof?
When installing a photovoltaic (PV) system on a sloped roof, safety measures are crucial. Additionally, it is crucial to confirm that the weather is dry before moving on. The steps for on-roof mounting are as follows:
1. Secure the roof hooks:
Roof hooks should first be fastened to the roof truss. Typically, these hooks are affixed to the rafters.
Roof hook quantities and types vary depending on elements including the weight of the system, wind, and snow. The quantity and kind of roof hooks required must be determined in light of these loads.
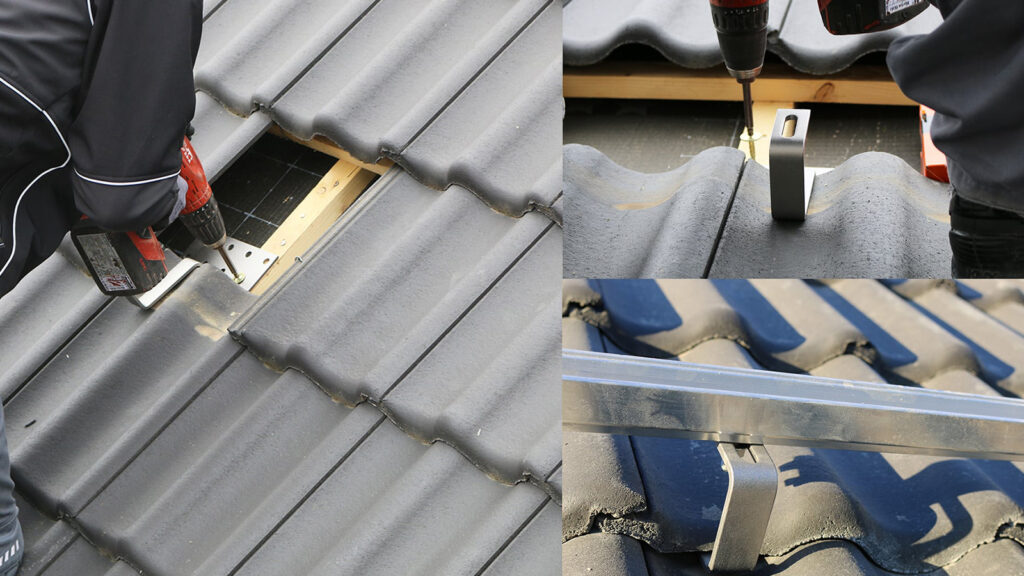

Select roof hooks that are made for the exact roof tile shapes that are used.
The roof covering must be temporarily removed or cut out at the planned hook places in order to attach the roof hooks. Then, it could be reattached.
2. Establish Support Rails:
Install the support rails that will retain the mounting system after the roof hooks are firmly set.
There are numerous techniques to install support rails. They can be positioned on short rails, cross rails, or in a parallel arrangement. This is dependent on the requirements and design.
In order to provide a solid foundation for the mounting system, make sure the support rails are tightly bolted together.
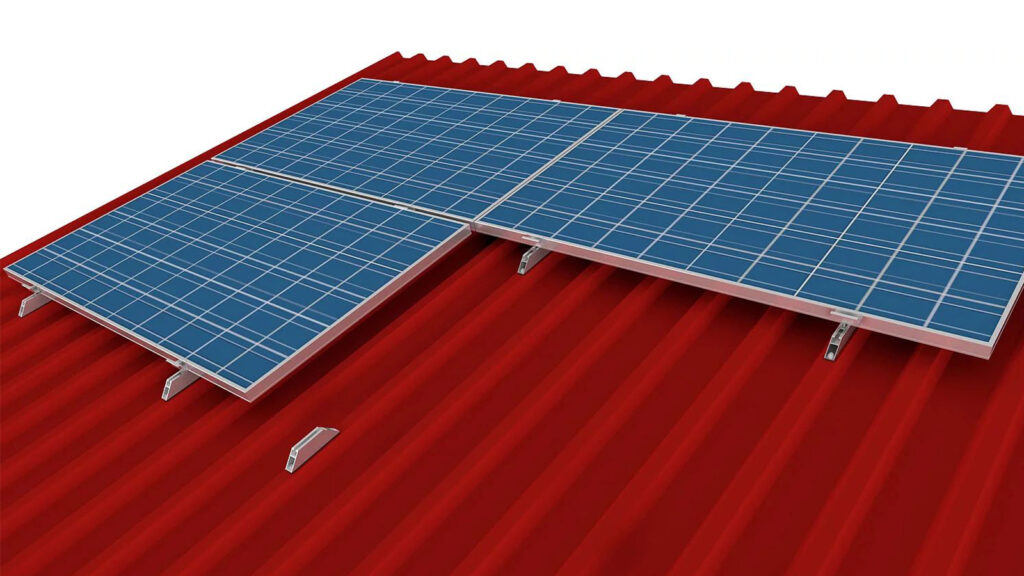
Utilize adjustable roof hooks for height. You can level the roof for the PV modules using these hooks. They make up for any roof irregularities.
3. Mount solar panels:
It’s now time to mount the PV modules onto the installed mounting system with the support rails in place.
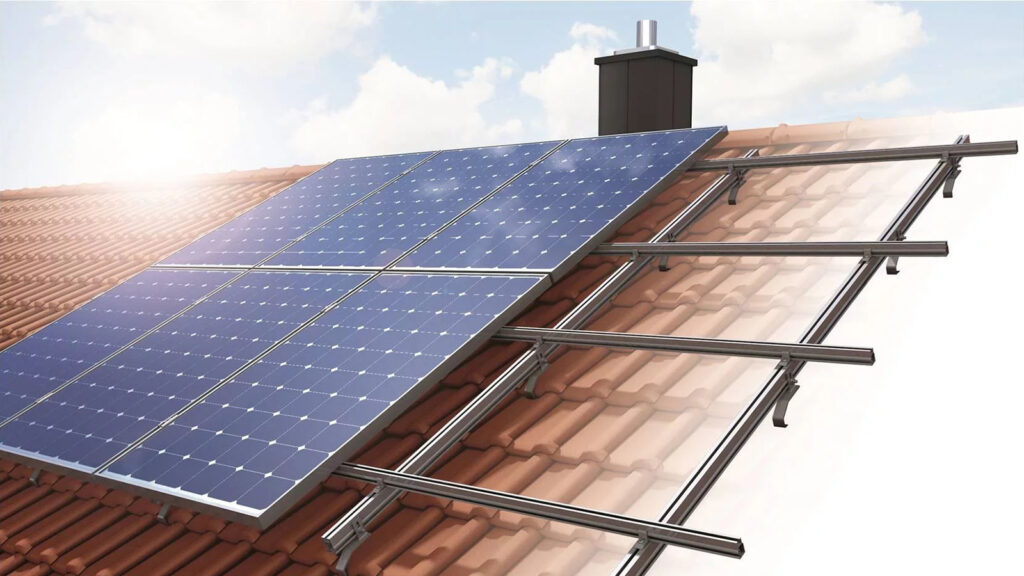

For your system design, you have two choices. Module clamps or rail systems can be used to hold the modules in place. The decision is based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and the system design.
Cable ducts that are already present in some train systems may make it simpler to route and manage the ensuing cable connections.
Alternative option: In-Roof Mounting
A PV system can be installed in two different ways. One possibility is on-roof mounting. In-roof mounting is an additional. Here, portions of the roof covering are replaced by PV modules, which turn into a crucial component of the roof cladding.
Although it is often more difficult and expensive, in-roof mounting enables a more aesthetically pleasing integration. What you should know about in-roof mounting is as follows:

1. Roof construction and rear ventilation:
For cold roofs with rear-ventilated roof constructions, in-roof mounting is preferable. This promotes appropriate airflow and guards against module overheating. It is not appropriate for warm roofs with insulated roof constructions.
In cold roof constructions, rear ventilation aids in preventing heat buildup. The PV modules’ backs or bottoms may experience this heat buildup. This contributes to maintaining the best possible module performance.
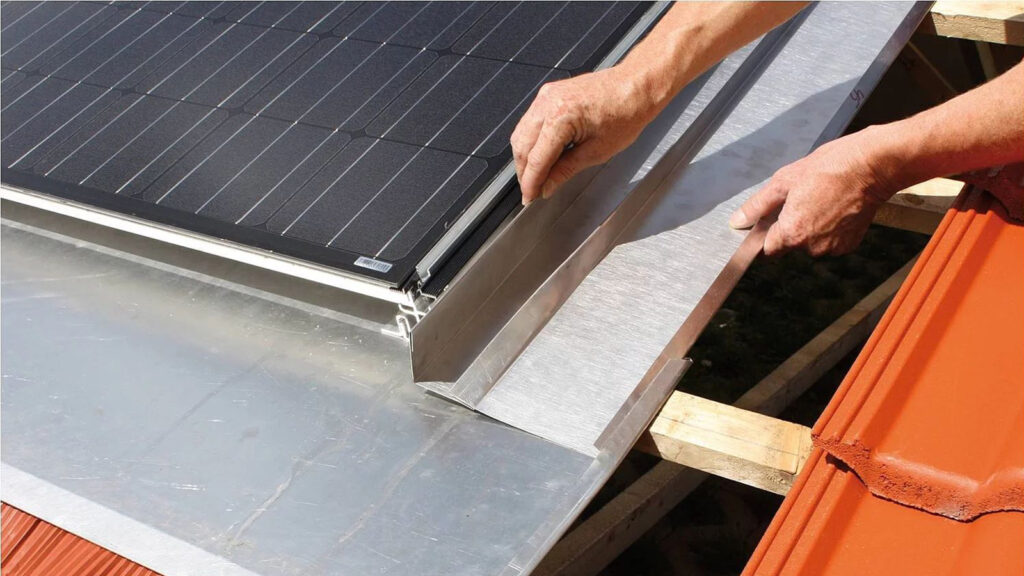

2. Installation Process:
Manufacturers provide complete sets specifically designed for in-roof installations, including all the necessary components for the installation process.
PV modules are typically mounted directly onto the roof battens, providing a sturdy base for the system.
To ensure a watertight connection, the module array is integrated into the roofing. One row or column of roof tiles is used for each side.
3. Complete Roof Replacement:
It is possible for photovoltaic systems to replace roof cladding entirely. This is known as a solar or energy roof. Additionally, PV modules can be integrated into the roof cladding.
Solar roof tiles are a special type of in-roof installation. They can be integrated into the existing roof cladding without any extra mounting systems. This makes for a seamless installation. However, it’s important to note that solar roof tiles are typically more expensive than conventional in-roof systems.
4. Mounting and Homogeneous Surface:
The PV system can be integrated directly into the roof cladding through in-roof mounting. The PV modules replace the roof covering in this process.
PV modules are mounted on fastening rails, creating a uniform and homogeneous surface with the roof.
The process of installing PV modules begins by removing the existing roof tiles. This creates space for the modules. Aluminum rails are then used to mount the modules directly onto the roof beams. It’s important to note that the inclination of these rails cannot be adjusted once securely screwed onto the roof beams.
Mounting PV modules in the roof offers an aesthetically pleasing solution. They blend with the roof cladding for a seamless look. This provides both energy generation and preserves the roof’s protective function.
Careful planning and consideration of rear ventilation is essential for successful in-roof installation. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines will help ensure a visually appealing integration of the PV system into the roof structure.
Installation of a PV System on a Flat Roof
Installing a photovoltaic system on a flat roof requires careful planning and execution to ensure optimal performance and stability. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the installation process:
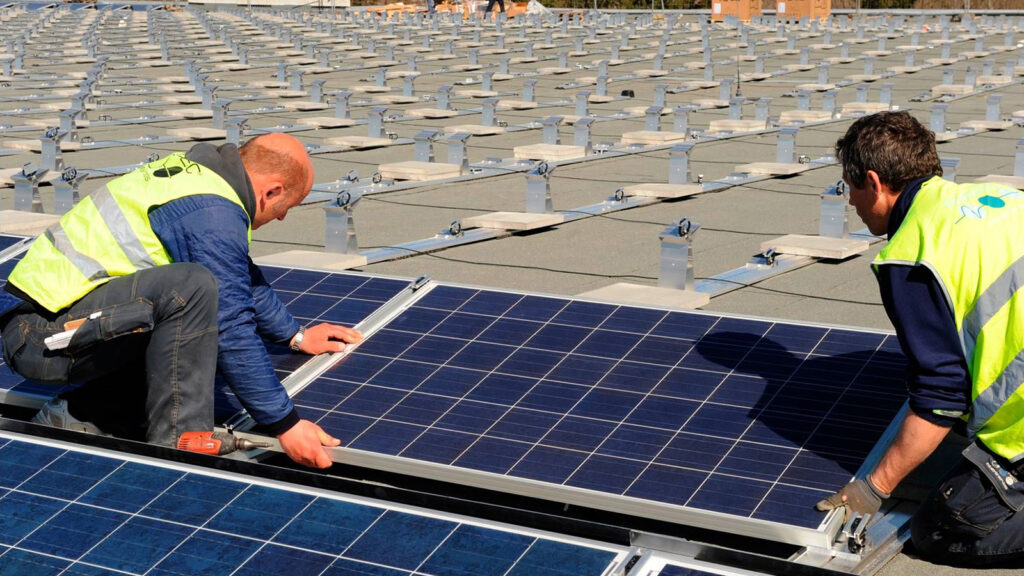

1. Frame and Mounting Considerations:
To mount the PV modules, a sturdy frame, often made of lightweight aluminum, is utilized.
Two common options for flat roof mounting are available:
The frame is firmly attached to the roof. This ensures a watertight and energy-efficient installation that won’t reduce the roof’s insulation. This method allows for proper ventilation behind the modules, promoting their cooling and increasing overall system efficiency.
Ballast Installation: Alternatively, the modules can be placed on frames that rest in designated troughs on the flat roof. These troughs are weighted down according to regulations, typically using stones or gravel. It’s important to consider the additional weight and its potential impact on the roof’s structural integrity
2. Elevation and Module Placement:
The elevation system is carefully set up on the flat roof to provide optimal module alignment and tilt towards the sun.
Ensuring sufficient distance between module rows is crucial to prevent shading. A general rule of thumb is to calculate row spacing by multiplying the height of the module edge by three.
The installation angle of the modules must be set according to the midday position of the sun on the winter solstice. This day is December 21st at 12 noon. This angle maximizes energy production and minimizes shading. Utilizing a solar orbit indicator can assist in accurately determining the optimal installation angle.
3. Mounting Options:
In areas prone to strong winds, a fixed installation method using rails and module attachments is recommended. However, this approach necessitates drilling into the roof cladding, requiring meticulous sealing to prevent water damage.
For regions with calmer climates, a ballast system with weighted frames provides stability without the need for roof penetration.
4. Support and Row Spacing:
Adequate support should be provided on the side facing away from the sun. This can be achieved using metal sheets or by positioning opposing solar modules.
The installation angle of the modules, typically ranging from 10 to 35 degrees, determines the appropriate row spacing. Lower angles impede self-cleaning, while higher angles necessitate increased row spacing.
Some systems incorporate motorized tracking mechanisms to adapt to the sun’s position. Single-axis tracking systems adjust module tilt based on the time of year or sensor feedback. Two-axis tracking systems also align modules throughout the day. However, these advanced tracking technologies are primarily recommended for large-scale outdoor installations due to their complexity and maintenance requirements.
Installing a PV system on a flat roof requires thorough consideration of the roof’s structure and specific mounting requirements. Adhere to safety protocols to establish a reliable and efficient photovoltaic system on your flat roof. Perform accurate calculations for the best results. Ensure professional installation for a successful system.
Avoiding the Most Common Mistakes in PV Installation
When installing photovoltaic (PV) systems, common mistakes can have serious consequences. Poor performance, safety risks, and overall failure are all possible outcomes. By understanding and avoiding these errors, you can ensure a seamless and efficient PV installation. Let’s explore the most common mistakes and how to steer clear of them.
Mistake #1: Poor Alignment of PV Modules
Proper alignment of PV modules is crucial for an aesthetically pleasing and efficient installation. Misalignment can lead to a crooked or wavy appearance, impacting both the visual appeal and overall performance of the system. Take great care to align the modules accurately, ensuring an even and seamless arrangement.
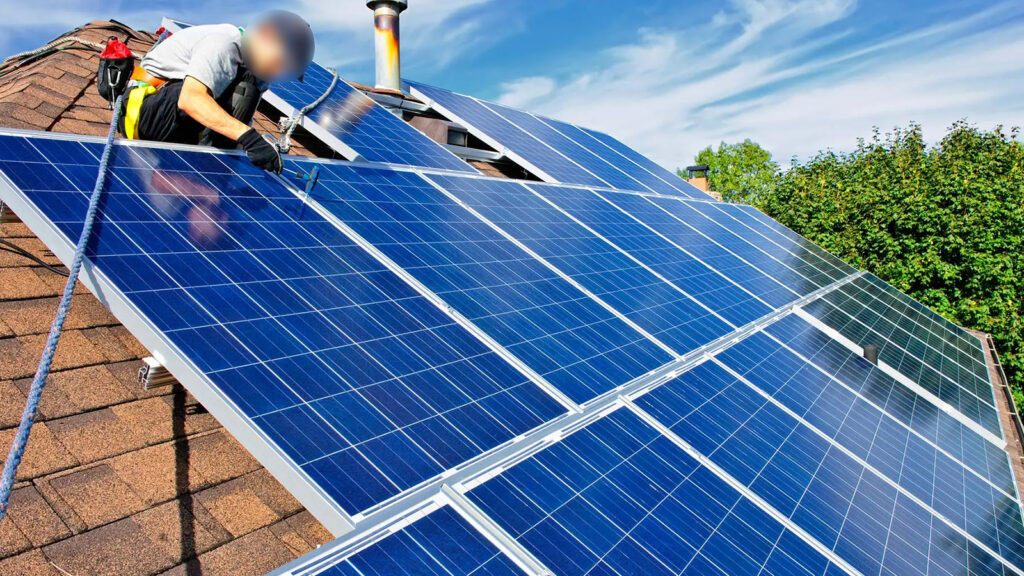

Mistake #2: Unsafe Cable Routing
Cable routing plays a significant role in PV installations. Improper routing can pose safety risks due to high current flow. Sharp corners, tight bends, or rough surfaces can damage cable insulation, leading to insulation faults and reduced system yield. Avoid cable contact with the roof and ensure a smooth, safe routing path to prevent such issues.
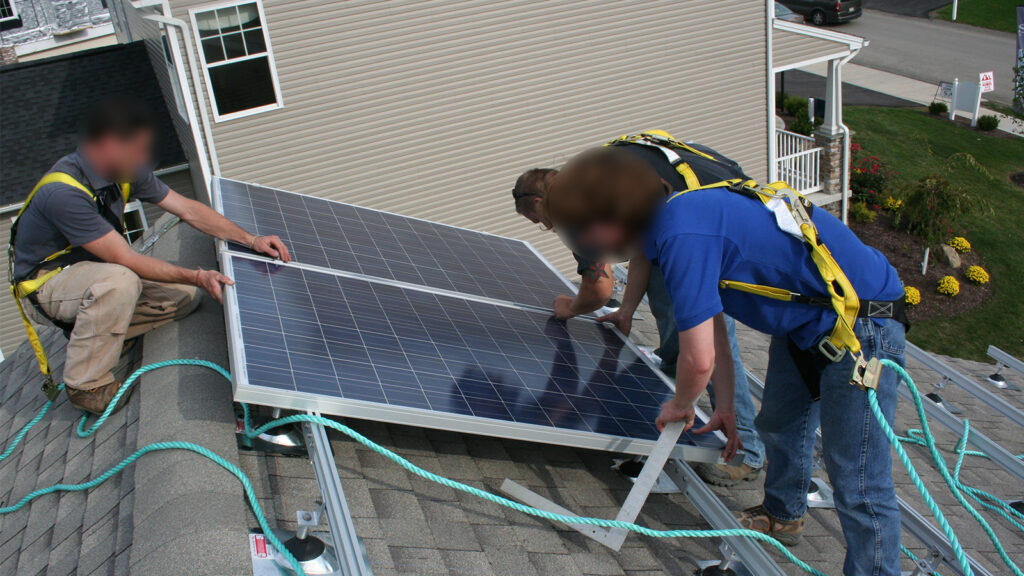

Mistake #3: Inadequate Roof Penetrations
Proper roof penetrations are essential for a secure and watertight PV installation. Inadequate roof penetrations can result in water damage to the building or even module detachment. Pay close attention to sealing and fastening the roof hooks in the rafters, ensuring a sturdy and weather-resistant connection.
Mistake #4: Improper Installation of Roof Hooks
Improper installation of roof hooks can lead to various complications. When installing roof hooks, take care to avoid damaging the roof cladding. Ensure recesses for the hooks are made correctly, avoiding excessive or inadequate material removal. Maintain a sufficient distance between roof hooks and tiles to accommodate potential snow loads and prevent tile damage.
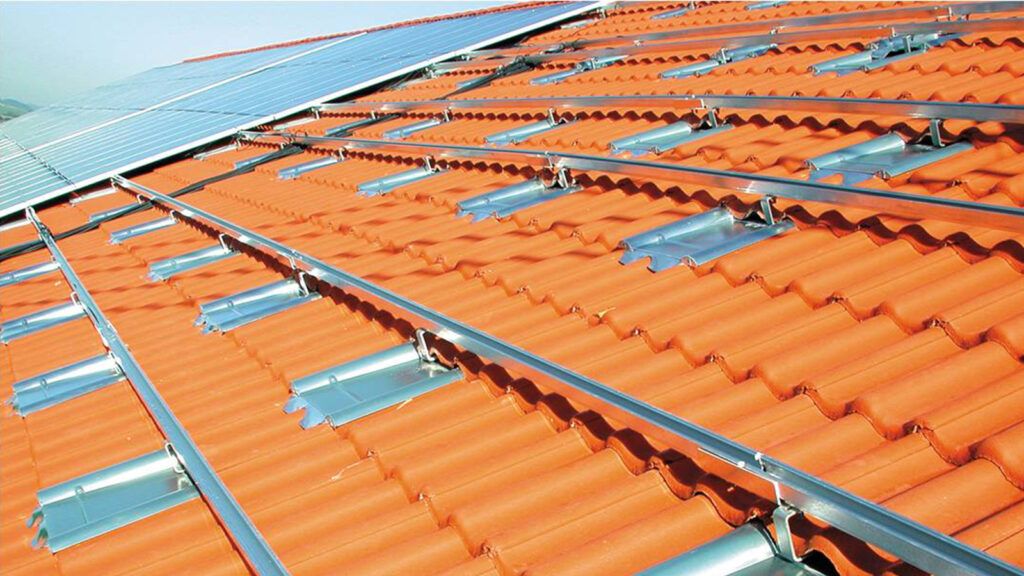

Mistake #5: Insufficient Use of Roof Hooks
Using the wrong number or type of roof hooks can compromise the stability of the PV system. Select roof hooks that match the shape of your roof tiles and consider regional load requirements. Install roof hooks to evenly distribute the load for a stable construction. Pay special attention to edges and corners that are vulnerable to wind turbulence.
Mistake #6: Neglecting to Level Out Unevenness
Uneven surfaces on the roof can pose challenges during PV installation. If your roof exhibits undulations or warping, it is crucial to use adjustable roof hooks that can compensate for these irregularities. Adjustable or variably adjustable roof hooks allow for a level installation, minimizing shading and maximizing system performance.
Mistake #7: Failure to Secure the Installation Environment
Creating a safe work environment is essential during PV installation. Take precautions to protect the installation area. Use flutter tapes to cordon it off.
Display warning signs. Install fences to prevent unauthorized access. Clear driveways and remove potential trip hazards to minimize the risk of accidents.
Avoid common mistakes and follow the recommended guidelines. This will ensure a successful and efficient PV installation. It will also maximize the performance, safety, and longevity of your system.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has specialized on producing premium solar modules. The most frequently suggested solar module is our Twisun X. Its all-black look and exceptional performance are both appealing. Its style fits any architectural environment nicely.
With the Twisun X Series from Maysun Solar, you can rely on the dependability and quality of our products. Join us in using the sun’s energy to make the earth greener. Make contact with Maysun Solar right away, and let’s work to create a sustainable future.

How to Effectively Clean and Intelligently Maintain Photovoltaic Systems for Optimal Performance?
Explore how scientific cleaning and intelligent maintenance can ensure the efficient operation of commercial and industrial photovoltaic systems. Practical advice covers module cleaning frequency, monitoring system configuration, and long-term strategies for energy savings and performance enhancement.

2025 European Photovoltaic Policy Map: Deployment Paths and Regional Strategies for Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics
A comprehensive analysis of the 2025 European commercial and industrial photovoltaic policy map, focusing on deployment strategies, incentive comparisons, and zero-investment models to support businesses in achieving an efficient and green transition.

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.



