Table of Contents
N-TOPCon Technology Penetration Expected to Exceed 40% by 2024
In recent years, the new energy industry has thrived, with a multitude of emerging technologies in photovoltaics (like HJT, TOPCon, BC, and perovskite) and energy storage (including sodium-ion, solid-state, liquid flow, composite flow, and manganese iron phosphate).
However, at this critical juncture of the new energy boom, very few technologies have overcome challenges, achieved industrial validation, and achieved large-scale market adoption. N-type TOPCon stands out with a predicted penetration rate exceeding 20% this year and expected to surpass 40% next year, becoming the dominant technology.
While other technologies face limitations and controversies, TOPCon is leading the way. However, it’s worth noting that TOPCon is different from previous technologies, with higher barriers and more significant differentiation, affecting the competitive landscape.
As component prices decrease, N-type solar panels are replacing P-type ones, with TOPCon leading the transition. Major players are investing heavily in TOPCon, accelerating its adoption. In contrast, technologies like HJT and BC face challenges in cost reduction and market penetration. Perovskite and other emerging technologies require further breakthroughs for large-scale industrialization.
This time, the industry focuses on technology more than capital, with TOPCon’s sustained technological barriers driving differentiation and technological advancement. It encourages R&D and efficiency improvements, positioning TOPCon as the main battlefield for photovoltaic cell technology evolution.
Given that TOPCon is the main battleground and has higher barriers, it is destined to become the driving force behind the differentiation of the photovoltaic industry. As solar cell technology continually advances and approaches the theoretical limits of crystalline silicon, competition is increasingly determined by minute differences in technology. TOPCon’s high technological barriers will continue to amplify through factors such as climb rate, yield rate, conversion efficiency, capacity utilization, and profit margin. As the market size continues to expand, it will influence the industry landscape. TOPCon’s technical barriers are high, differentiating companies significantly. It is poised to reshape the photovoltaic industry.
As the market size grows, TOPCon’s influence will increase, reshaping the industry landscape and market competition. The future awaits with anticipation.
Maysun Solar’s N-TOPCon bifacial solar cells are characterized by their high conversion efficiency and reliability. These advanced cells can generate electricity from both the front and rear sides, maximizing energy capture even in challenging lighting conditions. With meticulous quality control processes, they maintain uniform performance and exhibit low mismatches during encapsulation, ensuring seamless system operation. These solar panels excel in low irradiation conditions, making them suitable for regions with variable weather patterns. Additionally, their low hot spot effect enhances safety and durability, making them a dependable choice for efficient and sustainable solar energy solutions. Below is the N-TOPCon 430W full black solar panel installed by Maysun Solar’s customer in Germany, click the button below to learn more about the related products!

Germany’s cumulative solar power generation capacity surpasses 80 GW
Germany has achieved a significant milestone by reaching 80 GW of cumulative solar capacity. In November alone, the country added approximately 1.18 GW of new PV systems, and it has the potential to install over 14 GW of PV capacity by the end of this year, according to data released by the national network operator.
The Federal Network Agency (Bundesnetzagentur) reported that Germany’s new PV capacity installations for November amounted to 1,183 MW, slightly lower than the 1,231 MW recorded in October but significantly higher than the 675 MW installed in November 2022.
In the first 11 months of this year, solar developers connected a total of 13.18 GW of solar power to the grid, a substantial increase compared to the 6.8 GW installed during the same period the previous year. This achievement pushed Germany’s cumulative solar capacity to 80.74 GW by the end of November.
However, to meet the nation’s target of reaching 215 GW of solar capacity by 2030, there is still a need to accelerate the pace, requiring an average installation of 1.58 GW per month.
Of the newly registered capacity in November, nearly 413 MW came from projects selected through tenders, while nearly 628 MW were from rooftop PV systems operating under the feed-in tariff scheme or direct marketing. An additional 128 MW was contributed by ground-mounted projects, with the remaining 15 MW coming from other system typologies.
Expected 20% Decline in Solar LCOE in Europe by 2023
Over the past decade, there has been a significant reduction in the cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. Market prices for PV modules, when adjusted for inflation, have dropped by approximately 95% since 2011. In most countries, PV has achieved price parity with both retail and wholesale electricity.
To conduct a comprehensive analysis of the PV market and pricing trends, the European Technology and Innovation Platform for Photovoltaics (ETIP-PV) recently published levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) calculations spanning from 2023 to 2050. These LCOE assessments focused on five European locations (Helsinki, Munich, Toulouse, Rome, and Malaga) and four PV system categories (residential 5 kW, commercial 50 kW, industrial 1 MW, and utility-scale 100 MW).
The PV LCOE is influenced by generation costs, encompassing all expenses associated with delivering PV-generated electricity to the grid connection point. It is also contingent on both the capital (CAPEX) and operational (OPEX) costs of PV systems. OPEX includes costs and profit margins across the entire value chain, encompassing financing, project development, manufacturing, installation, operation, and maintenance.
Historically, module prices have closely adhered to the learning curve, which means that with each doubling of global cumulative PV generation capacity, module prices have typically decreased by approximately 25%. The projections for future module price reductions are based on this historical learning rate (LR). These reductions are expected due to improved manufacturing processes, more efficient material usage, and continuous enhancements in module efficiency. Additionally, the calculations factored in a 2% annual inflation rate, a 30-year system lifetime for rooftop installations (or 35 years for ground-mounted installations), and an annual degradation rate of 0.5% across all cases.
Key Findings:
According to ETIP PV’s base scenario, global cumulative PV capacity is anticipated to increase from 1.5 TW at the end of 2032 to around 5.5 TW by 2030 and further to 30 TW by 2050.
OPEX for utility-scale PV is projected to decrease from €12.5 ($13.6)/W/year at the end of 2023 to €9/kW/year by 2050, while for rooftop solar, it amounts to €10/kW/year. CAPEX for utility-scale PV is expected to drop from €0.46/W at the end of the current year to €0.23/W by 2050. For residential (5 kW), commercial (50 kW), and industrial (1 MW) installations, prices may reach €0.81, €0.48, and €0.33, respectively. Across all sectors, CAPEX is approximately halved between January 2024 and 2050.
In comparison to current values, the PV LCOE is forecasted to decrease by roughly 20% by 2030 and by 50% by 2050. When compared to the average wholesale electricity prices from 2019 to 2021, utility-scale PV is already competitive across all countries, even with a nominal Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) rate well above 10%. During the 2022 energy crisis in Europe, elevated spot-market prices further enhanced the competitiveness of PV.
ETIP PV anticipates a decline in LCOE for all locations, with particularly significant reductions in Rome and Malaga. For example, in Malaga, the LCOE for utility-scale PV, assuming a 7% nominal WACC, is projected to be €24/MWh in 2024, but is expected to decrease to €19/MWh by 2030 and €13/MWh by 2050. Nonetheless, LCOE predictions for all locations are extremely positive, indicating that PV-generated electricity is already more cost-effective in all five locations across various WACC rates and consumer segments.
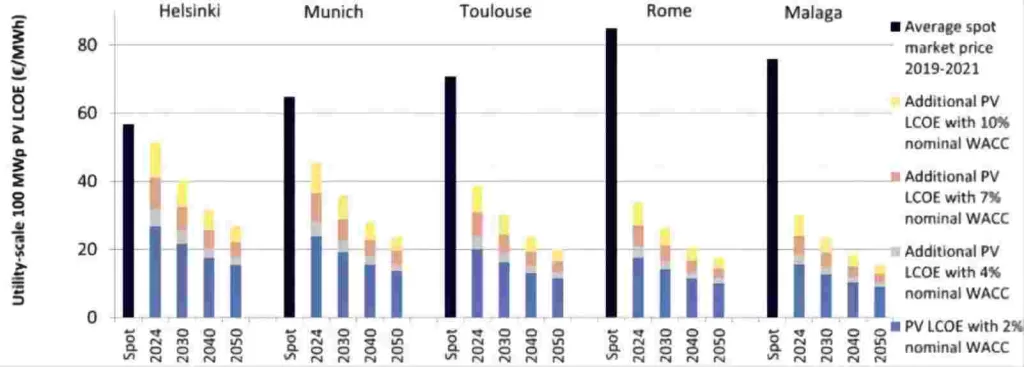
The figures above illustrate the PV LCOE for 100 MWp utility-scale PV in five European locations under different nominal WACCs, comparing them to the average spot market electricity price.
European Commission Greenlights €5.7 Billion Italian Initiative for Energy Communities
The European Commission has recently granted approval for a €5.7 billion program aimed at advancing energy communities in Italy. According to recent data provided by the Polytechnic University of Milan, Italy currently operates 104 energy communities. With ongoing projects considered, this number is expected to increase to 191. The report notes that municipalities are the primary promoters of these energy communities in 44% of cases, while private companies are the main promoters in the remaining instances. Over 70% of the analyzed energy communities utilize systems with a total capacity of less than 200 kW, and all of them rely on photovoltaic energy sources. This initiative seeks to facilitate the expansion of small-scale existing renewable energy projects and the development of new projects not exceeding 1 MW in size, as outlined in an official press release.
The program comprises two distinct funding components:
- The first component, with a total budget of €3.5 billion, involves a 20-year tariff system based on the electricity consumption of self-consumers and renewable energy communities. This is funded through a levy imposed on the electricity bills of all consumers. In this context, a renewable energy community is defined as a “legal entity that empowers citizens, small businesses, and local authorities to produce, manage, and consume their electricity.”
- The second component, with a total funding allocation of €2.2 billion, consists of investment grants covering up to 40% of a project’s total costs. These projects must be located in municipalities with populations of 5,000 residents or fewer and must become operational by June 30, 2026.
The funding for the second component is sourced from the €723.8 billion Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF), an instrument established by the European Commission to reinforce the European Union (EU) in the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic.
This allocation follows the European Commission’s approval of Italy’s Recovery and Resilience Plan on July 31, 2021, which outlined an €11.2 billion investment in enhancing and advancing Italy’s renewable energy technologies, circular economy initiatives, water waste management facilities, and more.

Maysun Solar has been dedicated to manufacturing top-tier photovoltaic modules since 2008. Explore our extensive range of solar panels, including full black, black frame, silver, and glass-glass options, all incorporating cutting-edge technologies such as half-cut, MBB, IBC, HJT, and Shingled. These panels are designed for superior performance and boast stylish aesthetics that seamlessly integrate with any architectural setting. Maysun Solar has successfully established offices, warehouses, and enduring partnerships with skilled installers across numerous countries. For the latest module quotations or any inquiries related to photovoltaics, please feel free to reach out. We are eager to assist you in harnessing the power of solar energy.
Reference:
TOPCon Leading the Transformation of the Photovoltaic Industry – GUANGFU.BJX.COM.CN. (n.d.). https://guangfu.bjx.com.cn/news/20231225/1352106.shtml
Enkhardt, S. (2023, December 21). Germany hits 80 GW milestone. Pv Magazine International. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2023/12/21/germany-hits-80-gw-milestone/
Morandotti, A. S. a. L. (2023, November 27). EU Commission approves €5.7 billion Italian scheme for energy communities. Pv Magazine International. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2023/11/27/eu-commission-approves-e5-7-billion-italian-scheme-for-energy-communities/
Solar LCOE may decrease by up to 20% in Europe by 2030. (2023, December 14). Pv Magazine International. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2023/12/14/solar-lcoe-may-decrease-by-up-to-20-in-europe-by-2030/

How to Effectively Clean and Intelligently Maintain Photovoltaic Systems for Optimal Performance?
Explore how scientific cleaning and intelligent maintenance can ensure the efficient operation of commercial and industrial photovoltaic systems. Practical advice covers module cleaning frequency, monitoring system configuration, and long-term strategies for energy savings and performance enhancement.

2025 European Photovoltaic Policy Map: Deployment Paths and Regional Strategies for Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics
A comprehensive analysis of the 2025 European commercial and industrial photovoltaic policy map, focusing on deployment strategies, incentive comparisons, and zero-investment models to support businesses in achieving an efficient and green transition.

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.