Table of Contents
Can Solar Panels be Recycled?
Yes, solar panels can be recycled.
Recycling solar panels comes with several advantages and a few challenges. On the positive side, it helps conserve valuable resources, promotes environmental sustainability by reducing waste and the carbon footprint, opens up economic opportunities, and ensures compliance with environmental regulations where required. However, there are also some downsides, including the technical complexity of recycling, initial high costs, limited recycling infrastructure in some areas, and potential risks associated with handling hazardous materials. Overall, the benefits of solar panel recycling far outweigh the drawbacks, making it a crucial practice for a greener and more sustainable energy future.
Obsolete solar panels can be disassembled to extract various valuable materials, such as silicon, aluminum, silver, copper, and more, which can undergo secondary utilization for the production of new solar panels and electronic components. In terms of the composition of photovoltaic modules, the primary components typically include photovoltaic glass, aluminum frames, solar cells, EVA film, junction boxes, and a photovoltaic backsheet. The approximate weight distribution of each component is roughly as follows: glass accounts for about 70%, aluminum for 10%, adhesive sealing materials for 10%, silicon for 5%, and rare metals like silver, indium, gallium, and others make up approximately 1% of the total weight. When examining the composition of these solar panels, the majority of an obsolete solar panel can be effectively utilized as recyclable materials for remanufacturing. Furthermore, despite metals comprising a smaller proportion of the solar panel’s weight, they still hold significant recycling value. This article will detail the material recycling value of the various components of solar panels.
When to Consider Recycling Solar Panels?
Solar panel recycling should be considered when the panels reach the end of their useful life, are damaged beyond repair, or when upgrading to more efficient panels. In general, here are some instances when you should consider recycling solar panels:
End of Life: Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25-30 years, after which their efficiency declines. At this point, recycling is a viable option.
Technical Failures: If your solar panels develop significant technical faults, such as extensive cell damage or electrical issues, recycling may be more practical than repairs.
Upgrades: When you decide to replace your existing solar panels with more advanced and efficient models, recycling ensures proper disposal of the old ones.
Storm Damage: After natural disasters or severe storms, damaged panels that cannot be restored should be recycled to minimize environmental impact.
Environmental Regulations: In some regions, there are regulations and requirements for proper solar panel disposal and recycling. Compliance with these regulations is essential.
Recycling solar panels in these scenarios is not only environmentally responsible but also helps recover valuable materials for use in new panels and reduces waste.

Why Recycle Solar Panels?
In the electronic waste market, the quantity and scale of discarded solar panels may currently be unimpressive, but their growth rate is the most rapid. The industry is concerned that as the global transition to green energy accelerates and deepens, and as solar energy applications become increasingly widespread, the management of a vast number of retired solar panels will become an unsustainable burden for the solar energy sector. Therefore, this topic of recycling solar panels is being thought and discussed by more and more people, and the recycling of solar panels has become a necessity to protect the environment. Recycling solar panels offers several significant benefits, aligning with environmental protection and potential cost savings:
Environmental Conservation: Recycling solar panels is an environmentally conscious practice that safeguards against landfill disposal, which could lead to environmental contamination. Additionally, recycling solar panels requires less energy compared to mining and refining raw materials. By using recycled materials, energy consumption in the production of solar panels is reduced, contributing to overall energy efficiency and a reduced carbon footprint. In the long run, recycling can be more cost-effective than disposing of solar panels. As recycling technologies improve and demand for recycled materials increases, the economic benefits of recycling become more substantial.
Resource Recovery: Solar panels contain valuable materials, such as silicon, aluminum, silver, copper, and rare metals. Recycling these materials provides an economically viable source for manufacturing new panels and electronic components, saving on production costs. Recycling solar panels contributes to a circular economy where materials are continually reused and repurposed, creating a sustainable supply chain.
Generating Additional Income: Apart from the environmental and economic advantages, solar panel recycling can create opportunities for generating extra income. As the demand for clean energy grows, the recycling industry is set to expand. Entrepreneurs and individuals can explore the collection and recycling of end-of-life solar panels, contributing to the sustainable energy ecosystem while benefiting financially. This extra income stream can be a significant incentive for those considering solar panel recycling as a worthwhile venture.
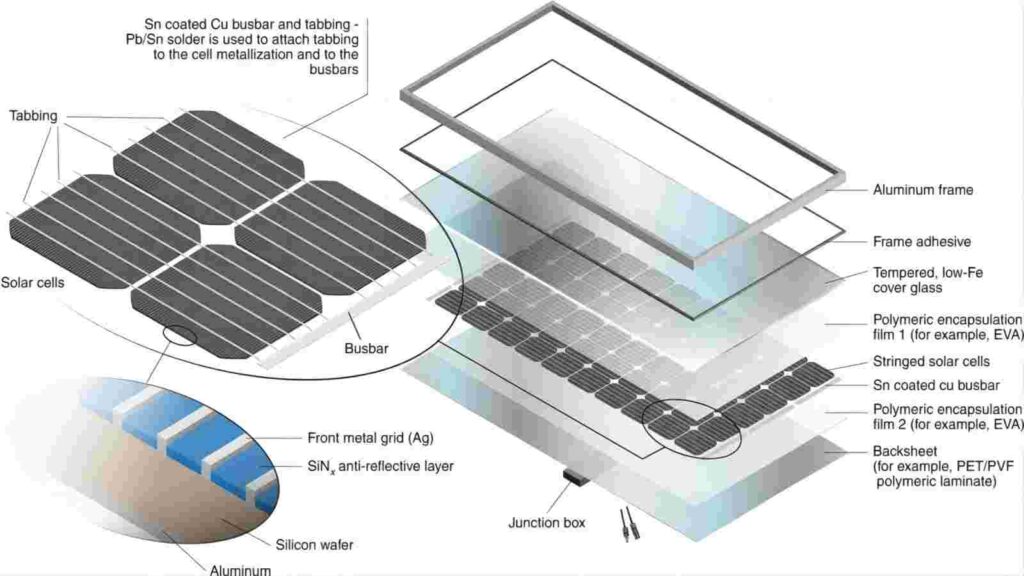
Recycling Value of Solar Panel Components
Solar panels, as a cornerstone of the renewable energy sector, possess a complex composition of materials, many of which offer a significantly high recyclable value. Monocrystalline solar panels are one of the most common types of solar panels available in the market today. Below is an analysis of the various parts of a monocrystalline silicon solar panel:
Silicon wafers:
Silicon wafers are the essence of solar panels, fabricated from either polycrystalline or monocrystalline silicon. Their high purity allows for efficient recycling and subsequent utilization in the production of new solar panels, reducing dependence on limited silicon resources.
Percentage: About 5-10% of the module weight.
Value: Higher. The recycling value of silicon wafers depends on the market price of silicon, which usually ranges from a few dollars to a dozen dollars per kilogram.
Difficulty of recycling: Medium. Requires technology to separate the wafers from the EVA and further refine the silicon.
Frame ( Usually made of aluminium):
Solar panel frames are usually made of aluminium, whose mechanical loads and properties are perfectly suited to support and protect PV modules. After recycling, they can undergo the smelting process, leading to the manufacture of new aluminum products such as frames, mounts, or other aluminum components.
Percentage: About 5-10% of module weight.
Value: High. The recycling value of aluminium is typically in the range of a few hundred to a few thousand dollars per tonne.
Recycling difficulty: Low. Aluminium recycling technology is mature.
Glass:
Glass is a very important part of solar panels, it enables the collection of sunlight, directs the light to the cells to produce electricity and effectively protects the cells inside the solar panel from external physical damage. Single glass solar panels generally use fully tempered glass, while glass-glass solar panels use semi-tempered glass. Recycled glass can be remelted or reprocessed for the manufacture of new glass products, reducing reliance on primary glass resources.
Percentage: About 75-80% of the module weight.
Value: The recycling value of glass is relatively low, usually in the range of tens to hundreds of dollars per tonne.
Recycling Difficulty: Moderate. Glass recycling technology is well established, but it is necessary to ensure that the glass is completely separated from other materials.

EVA ( Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Copolymer ):
EVA is an important material for the encapsulation of solar panels and one of the guarantees for the life of the solar module, EVA plays the role of sealing and bonding to protect the cells inside the solar panels. Properly treated EVA films can be reused in the manufacturing of solar panels, decreasing the demand for new materials.
Percentage: About 10% of module weight.
Value: Low. EVA is more difficult to reuse, with the main value being environmental protection.
Difficulty of recycling: High. Effective methods need to be developed to separate and reuse EVA.
Backsheet:
Backsheets are mainly used to protect solar panels against the erosion of light, humidity, heat, frost and other harsh environmental factors on their encapsulation film, cells and other materials. Backsheet materials generally include polymers and aluminum foils. These can be recycled for reuse in the production of solar panel backsheets or other applications, mitigating resource wastage.
Percentage: About 3-5% of module weight.
Value: Depends on the material. Polymer backsheets have a low recycling value, while backsheets made of fibreglass or other materials may have a high recycling value.
Recycling Difficulty: Moderate. Requires technology to separate the backsheet from other materials.
Connectors and wires:
The function of the J-box of the solar panel is to link the power generated by the panel to the outside.
Percentage: Less than 1%.
Value: Higher because they may contain copper and other valuable metals.
Recycling difficulty: Medium.
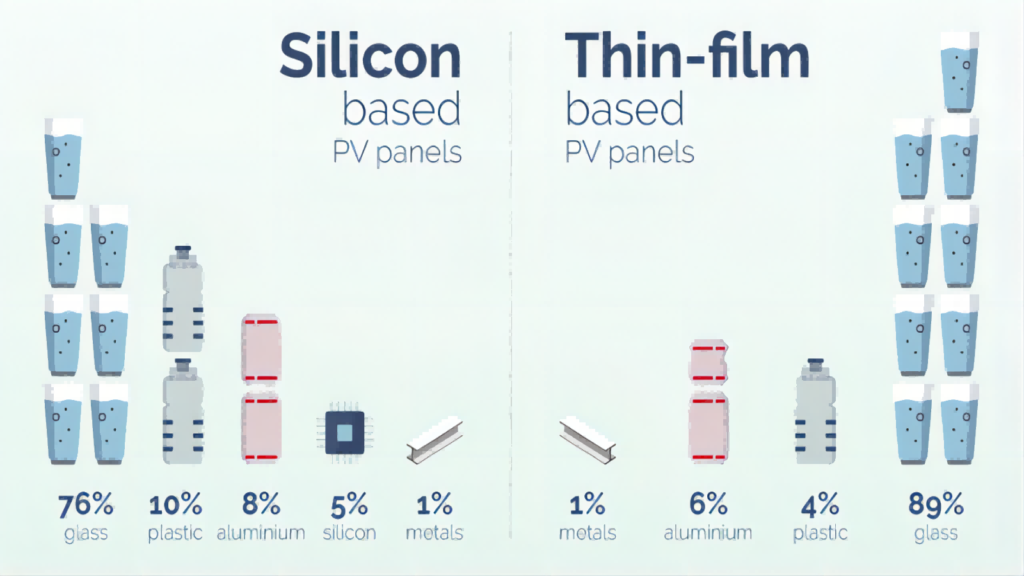
In summary, the constituent materials of solar panels offer exceptionally high recyclable value. Effective recycling and reuse serve to curtail resource consumption, minimize waste production, and propel the sustainable development of the clean energy sector, meeting the ever-growing demand for clean energy. This contributes to the establishment of a more eco-friendly and sustainable energy ecosystem, safeguarding our planet and our future.
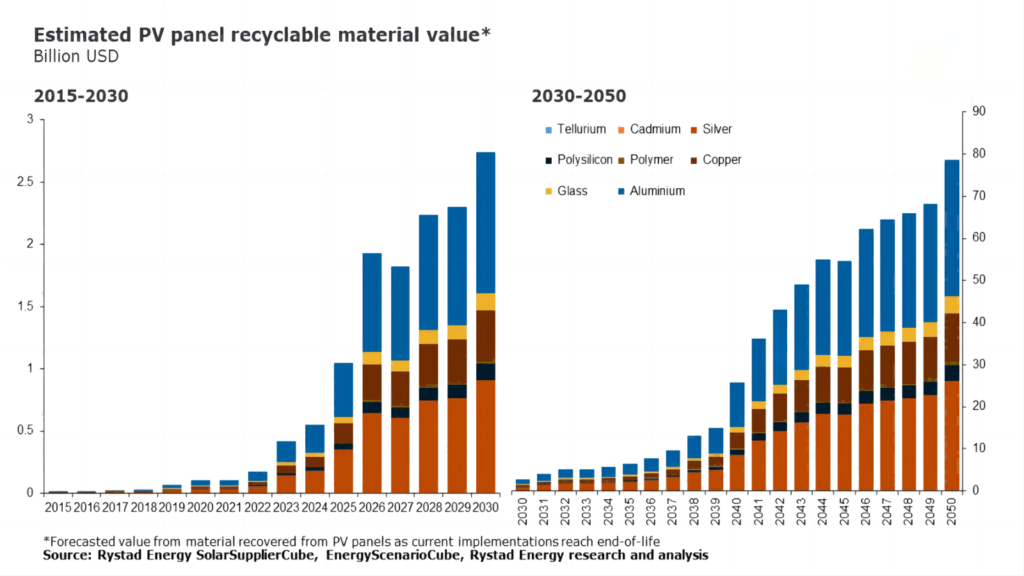
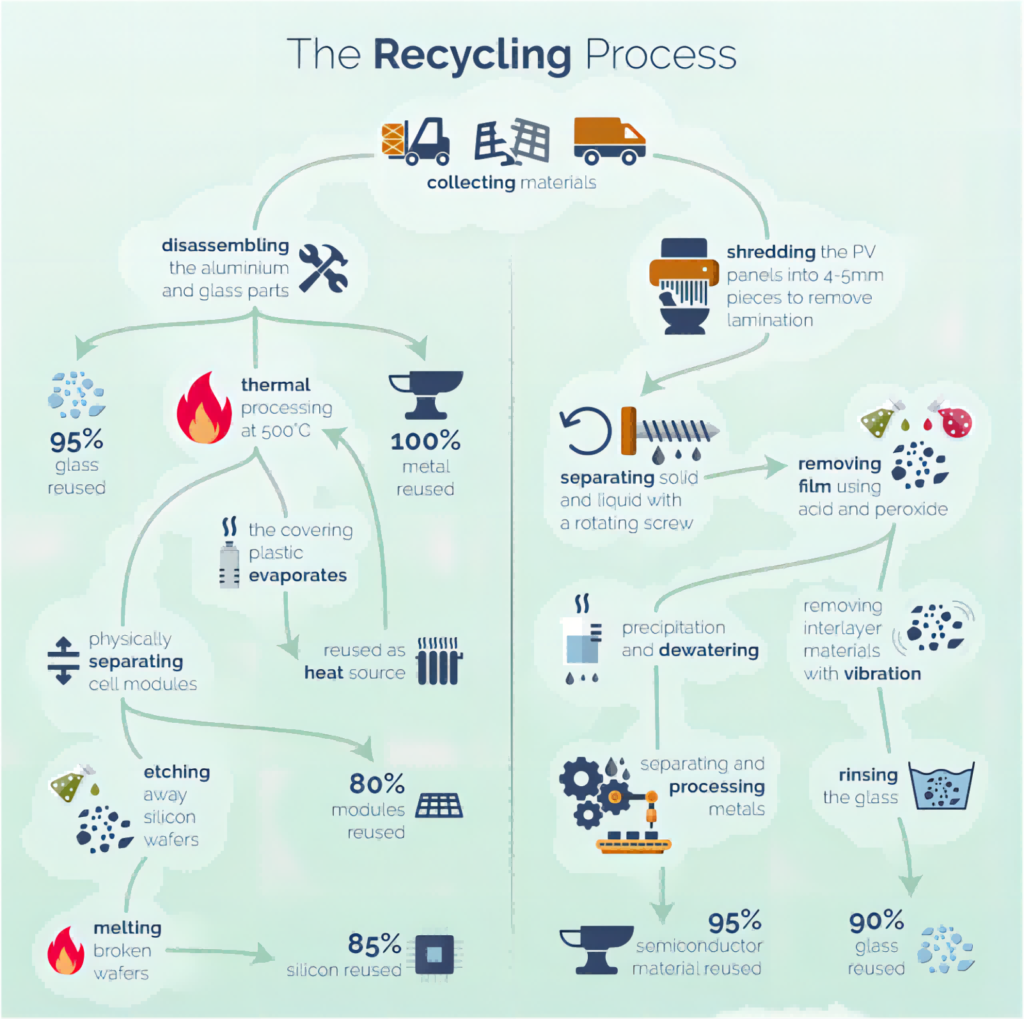
Recycling Processes for Solar Panel Components
There exist two primary categories of solar panels, each necessitating distinctive recycling methods. These categories, namely silicon-based and thin-film-based panels, are amenable to recycling via unique industrial processes. At present, silicon-based panels enjoy broader prevalence, yet the materials within thin-film-based cells retain significant value, underscoring their potential contributions to sustainable recycling practices.
Silicon-Based Panel Recycling:
Frame and Junction Box Removal: This starts with careful disassembly to separate aluminum and glass components. The extracted frames and junction boxes can be repurposed for new panels, reducing the need for raw materials.
Glass and Silicon Wafer Separation: Glass is separated from silicon wafers using thermal, mechanical, or chemical methods. Approximately 95% of glass can be repurposed.
Thermal Treatment: Materials undergo treatment at 500°C, allowing vaporization of encapsulating plastic. Even this waste is repurposed as a heat source.
Silicon and Metal Purification: Chemical and electrical methods refine silicon wafers and metals. Purified silicon can be reused in solar cells, and metals in high-tech industries.

Thin-Film-Based Panel Recycling:
Shredding and Refinement: Panels are fed into a shredder and further refined in a hammermill to ensure particles are 4-5mm or smaller.
Liquid Separation: A rotating screw separates solid and liquid components, with liquids undergoing precipitation and dewatering for purity.
Semiconductor Material: A metal processing stage segregates semiconductor materials, reclaiming around 95% of the material.
Final Glass Recovery: Through rinsing and vibration, up to 90% of glass elements are preserved for reintroduction into the manufacturing cycle, minimizing waste and conserving resources.
Where can We Go to Recycle Solar Panels?
Manufacturer and Retailer Programs: Many solar panel manufacturers and retailers have established recycling programs. Check with the company from which you purchased your solar panels to inquire about their recycling initiatives.
Local E-Waste Recycling Centers: Electronic waste recycling centers may accept end-of-life solar panels as part of their services. Contact your local recycling centers or electronic waste facilities to inquire about their solar panel recycling capabilities.
Government Programs: In some regions, there are government-sponsored programs for recycling solar panels. These programs may offer collection points or guidelines for proper disposal.
Recycling Companies: Some recycling companies specialize in the recycling of electronic waste, including solar panels. You can search for such companies in your area and inquire about their services.
Trade-In Programs: Some organizations and solar panel providers offer trade-in programs where you can exchange your old panels for newer, more efficient ones. They often handle the recycling of the old panels.
Industry Associations: Solar industry associations may provide resources and information on solar panel recycling. They can guide you to reputable recycling facilities.
Before recycling your solar panels, it’s advisable to contact the recycling facility or program to understand their specific requirements and procedures. Proper recycling ensures that valuable materials are recovered while minimizing environmental impact.
In some countries in Europe where PV modules are popular, France, Germany and Italy take solar panel recycling seriously.
France
France set up Europe’s first solar panel recycling plant in 2018 in a joint effort by PV CYCLE and waste organisation Veolia. At the end of June 2023, the world’s first factory dedicated to the fully recycling of solar panels has officially opened in France. ROSI, the company specialising in solar recycling, owns the facility, which is located in the Alpine city of Grenoble, and hopes to eventually be able to extract and reuse 99% of the unit’s components. This signifies that the recycling of solar panels is becoming more and more important, as well as more standardised and efficient.
Germany
Recycling of solar panels in Germany usually involves specialised recycling organisations and companies. A major organisation is the German office of PV Cycle. PV CYCLE is a non-profit organisation, created by the European solar industry. It is active in Germany and other European countries. PV Cycle coordinates the recovery, disposal and material recycling of solar panels to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. If you require specific solar panel recycling services or more information, we recommend contacting your local solar panel manufacturer, installer or consulting a specialist organisation such as PV Cycle for detailed information and guidance.
If you would like more information, please click on the link below:
Italy
The Italian Government has introduced relevant policies. The financing of PV module waste is subject to its categorization:
Waste derived from PV modules categorized as household (B2C) waste (i.e., those installed in PV plants with a nominal power below 10 kW) is funded by the Producers present in the market during the year in which the expenses are incurred, in proportion to their respective market shares.
For waste originating from PV modules classified as non-household (B2B) waste (i.e., those installed in PV plants with a nominal power equal to or exceeding 10 kW) placed on the market before 12/04/2014, Producers are responsible for financing the recycling when selling new PV modules to replace the old ones. In all other scenarios, the financial responsibility falls on the users. However, for waste stemming from B2B PV modules introduced to the market after 12/04/2014, the financial burden lies with the Producers of the modules they placed on the market.
Besides that, Italian startup Tialpi is pioneering an innovative process for recycling end-of-life solar panels, with the potential to recover 100% of a PV module’s weight. The novel plant design is currently undergoing testing at Tialpi’s facility in the northern Italian province of Biella.
Now that we understand the feasibility of recycling solar panels, the pertinent question pertains to the potential economic advantages. The establishment of a robust solar panel recycling infrastructure is essential to effectively manage the imminent surge in discarded PV modules. Once this framework is in place, it will give rise to several favorable factors and new economic prospects. Rising energy costs, advancements in recycling technologies, and government regulations are likely to pave the way for a market where more obsolete solar panels are directed towards recycling rather than being relegated to landfills. This transition to recycling PV panels not only promises cost savings for operators but also offers a means to mitigate supply chain challenges, thus enhancing the prospects of nations achieving their solar capacity objectives.
Maysun Solar has been specialising in producing high quality photovoltaic modules since 2008. Choose from our wide variety of full black, black frame, silver, and glass-glass solar panels that utilise half-cut, MBB, IBC, and Shingled technologies. These panels offer superior performance and stylish designs that seamlessly blend in with any building. Maysun Solar successfully established offices, warehouses, and long-term relationships with excellent installers in numerous countries! Please contact us for the latest module quotations or any PV-related inquiries. We are excited to assist you.

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!