As we work to make the planet greener, solar carbon footprints are a hot topic in the field of renewable energy. What is the carbon footprint? The carbon footprint is the amount of carbon dioxide produced during the manufacturing process of solar panels. Even if solar energy reduces carbon emissions in thousands of homes every day, the manufacture of solar panels can have a sizable impact on the environment.
In this article, the carbon footprints of solar panels and the amount of CO2 saved by solar energy will be compared, and benefits of using solar panels to reduce carbon footprint will also be discussed.
Table of Contents

Carbon footprint of solar panels
Solar panels have a carbon footprint, although the life-cycle emissions of solar electricity are around 12 times lower than those of natural gas and 20 times lower than those of coal. Additionally, there is great opportunity to significantly lower the carbon footprint of solar panels, unlike burning fossil fuels.
Some claim that the manufacturing and building of wind, solar, and nuclear power have “hidden” carbon footprints. These carbon debts and the associated energy debts must be “paid off” in order for these forms of alternative energy to be economically feasible and environmentally beneficial.
According to the European Commission’s Product Environmental Footprint methodology, in the life cycle of a PV power plant, the three major carbon emitting segments of a PV module, the upstream process generates between 80% and more than 95% of the emissions, including the production of silicon materials, wafers, batteries, the manufacture of modules, and the manufacture of balance of systems (BoS) such as inverters, which totals about 22 grams of carbon emissions per kilowatt-hour. Emissions from the later operation of the PV plant, such as O&M, are roughly 5-20 per cent of the total emissions.
Many current commercial solar panels can carry a heavy environmental price tag. The relatively high carbon footprint of crystalline silicon modules is the energy-intensive processes such as silicon manufacturing, ingot growing and wafer cutting. As a result these manufacturing processes have shifted away from less carbon-intensive markets to other carbon-rich and cheaper countries and regions.
Similarly, photovoltaic (PV) power plants have a carbon footprint. From a life cycle perspective, the carbon footprint of thin film PV plants ranges from about 12 grams per kWh to a much higher range for crystalline silicon PV plants, and in recent years, with process innovations and technological advances, the carbon emissions of crystalline silicon power generation have declined from 33-50 grams per Kwh ten years ago to about 24 grams per Kwh today.
How much CO2 is reduced when using solar panels?
Many of these dangerous greenhouse gases are discharged into the environment when fossil fuels are utilized to produce electricity. But if we increase the use of solar energy and swap out fossil fuels for it, we can lower these emissions and do our part to stop climate change. According to the NREL, generating power with solar panels that are expected to last 28 years can drastically reduce emissions by more than 100 tons. Over time, this decrease in greenhouse gas emissions may mitigate the effects of global warming.
During the first several years of using a solar panel, around 50g of CO2 per kilowatt-hour is created. The carbon footprint of a solar panel is around 20 times lower than that of a coal-powered electrical source. As a result, as soon as you install solar panels in your home, your carbon footprint will go down. However, in order to become carbon neutral and pay off your carbon debt, you must have solar panels in place for three years. Your overall carbon footprint will then decrease after three years of use because the system will continue to operate at a carbon neutral level for the remainder of its useful life.
A cautious estimate approach is to suppose that gas power plants, which are the most prevalent and frequently utilized to ‘top-up’ supply in order to meet demand at any given time, be replaced by solar energy. According to a recent assessment by National Grid PLC, these large commercial power stations currently release 392g CO2 per kWh.
Thus, based on this cautious estimate, we can state that a typical household solar PV system in southern Britain reduces CO2 emissions by roughly 1.2 tonnes annually just in terms of power generation.
To be truly sustainable energy sources, solar panels must address their possible environmental disadvantages. But with careful planning and effective implementation, solar energy’s advantages vastly outweigh its drawbacks.
Solar power can contribute to the shift to renewable energy sources and help build a more sustainable future for future generations.

Switch to solar energy to reduce carbon footprint
A 10 kW solar roof typically reduces carbon emissions by about 4 tons annually. This roughly equates to planting more than 100 trees annually. Larger installations may have a ten-fold greater impact. In reality, the ecosystem is impacted by even one domestic solar installation.
Perhaps it’s time you switched to solar power now that you are fully aware of the carbon impact of solar energy. The main global source of greenhouse gases is the burning of fossil fuels, particularly coal. A portion of your carbon footprints are immediately offset when you choose a green energy source. That is why the use of solar panels is becoming more popular and widespread today. Installing solar panels is a great choice for both cost savings and environmental protection.
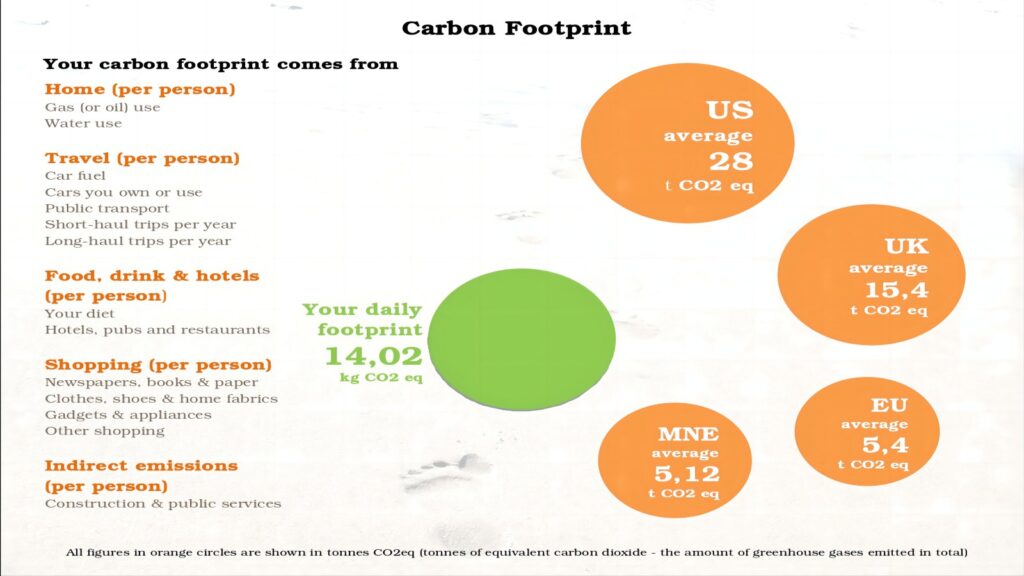
Solar panels not only lessen the harm that burning fossil fuels causes to the environment, but they also provide a steady supply of renewable energy that can be utilised to run almost any appliance or gadget.
Household appliances, home heating and cooling systems, and even electric car charging stations can all be powered by solar panels. Solar panels can offer energy for many years to come with little harm to the environment if they are installed and maintained properly.
It is obvious that purchasing solar panels could be a good strategy to lessen one’s carbon impact while retaining access to contemporary energy sources. We can contribute to protecting the environment for future generations by making investments in clean, renewable energy sources. If you want to install energy-saving, environmentally friendly, high-efficiency and long-lasting solar panels, Maysun is a good choice!


Everyone should take into account their individual environmental effect when deciding how much electricity to use, and solar panels are an excellent method to do so without giving up contemporary conveniences.
Maysun Solar has been specialising in producing high quality photovoltaic modules since 2008. Choose from our wide variety of full black, black frame, silver, and glass-glass solar panels that utilise half-cut, MBB, IBC, and Shingled technologies. These panels offer superior performance and stylish designs that seamlessly blend in with any building. Maysun Solar successfully established offices, warehouses, and long-term relationships with excellent installers in numerous countries! Please contact us for the latest module quotations or any PV-related inquiries. We are excited to assist you.
Reference:
Abundance. (2018, May 23). How much Carbon Dioxide do solar panels save? – Abundance Blog. Medium.
Lawrence, B. (2021). Carbon footprint of solar panel manufacturing. Cool Effect.
Morgan, S., & Wade, A. (2016). Carbon footprint of solar panels under microscope.
Solar panels and their effect on the environment — Environmental protection.
Solar panels have a carbon emissions problem. (n.d.). Michigan Capitol Confidential.
Zimmermann, N. (2021, January 6). How many solar panels do we need to save the climate?

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!