Solar panels have been touted around the world as an important weapon in reducing carbon emissions, but they degrade and gradually become less efficient. After about 25–30 years, it is often more cost-effective to replace them with new ones.
Experts say that billions of panels will eventually need to be disposed of and replaced.
How many solar panels need to be recycled?
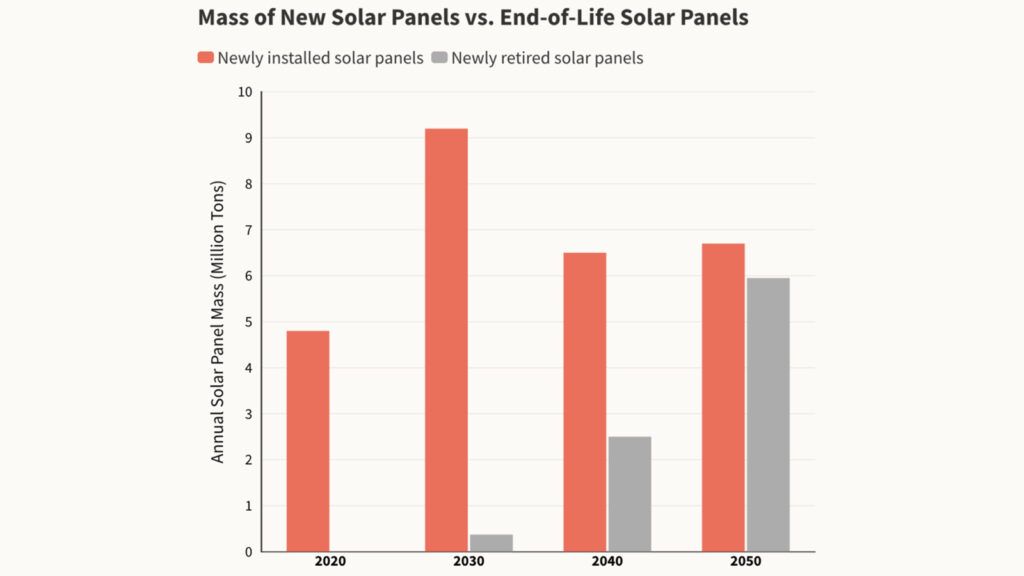
In 2016, the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) predicted that by the early 2030s, the number of retired photovoltaic panels globally would equal about 4% of the number of panels installed. By the 2050s, the amount of solar panel waste will increase to at least 5 million tons per year, the agency said. The cumulative global value of raw materials that could technically be recovered from PV panels could reach $450 million (in 2016 terms), roughly equivalent to the cost of raw materials needed to produce about 60 million new panels or 18 GW of generating capacity. By 2050, the cumulative recoverable value could exceed $15 billion, according to the report.
Energy experts are calling on governments to take urgent action to prevent a looming global environmental disaster.
Ute Collier, deputy director of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), says: “By 2050, this will be a mountain of garbage unless we set up recycling chains now.”
“We’re producing more and more solar panels – which is great – but what will we do with the waste?”
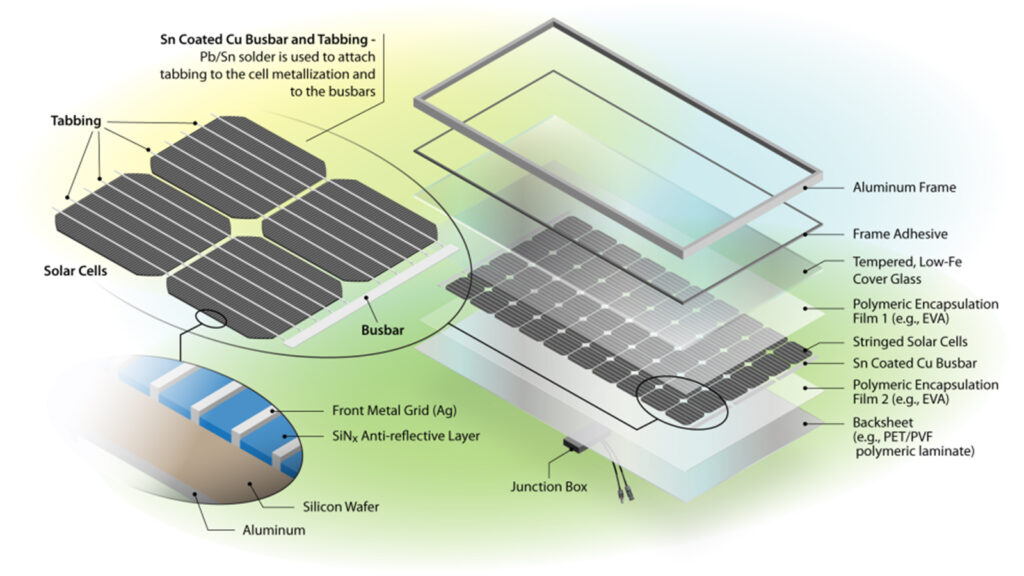
What are solar panel made of?
The solar panels are like sandwiches.
- The solar cell is at the center. About 90% of commercial solar panels use silicon as a semiconductor to convert light energy into electricity. Thin metal strips (usually silver) cross the surface of the silicon crystals in each cell and carry the current into the panel’s copper wiring.
- The solar cell is encapsulated in a protective barrier, usually an encapsulating material of transparent plastic called EVA. The top is covered with another layer of glass, and the back is covered with EVA,too. The whole thing is surrounded by an aluminum frame.
This layered structure protects the cells from natural elements while allowing sunlight to pass through, but may be difficult to deconstruct when the panels reach the end of their useful life.
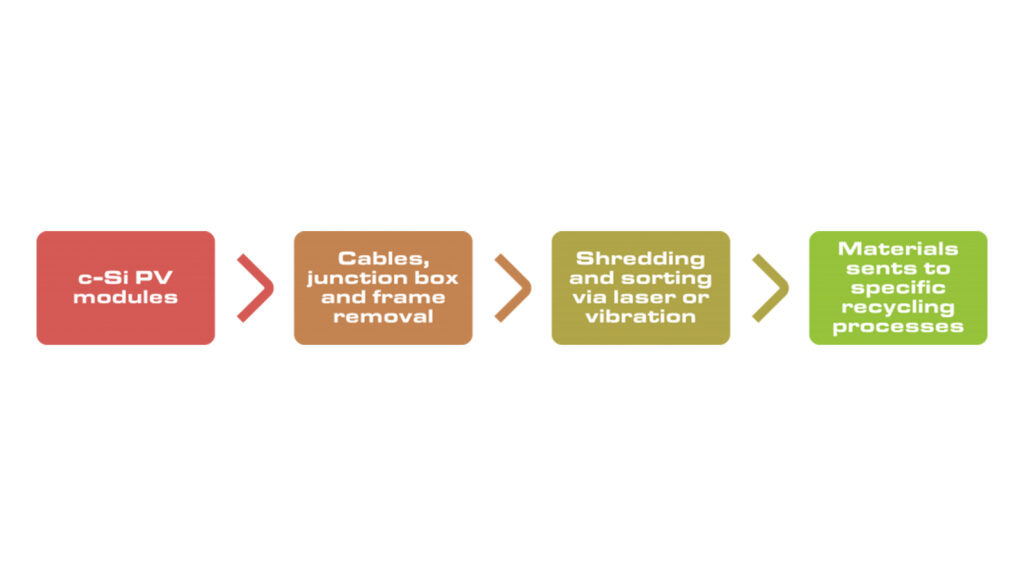
Which parts of a solar panel can be recycled?
Recycling Overview:
- Crystalline silicon solar technology accounts for most of the market share of solar panels. This type of panel consists of an aluminum frame, glass, copper wires, a polymer layer and backsheet, silicon solar cells, and a plastic junction box. The polymer layer seals the panel from the weather, but can make recycling and panel removal difficult, as high temperatures are usually required to loosen the adhesive.
- Many components can be recycled. In a typical crystalline solar module, there are components such as glass, polymers, the solar cell itself, copper, aluminum, and trace amounts of other metals. The largest contributor to the total weight is glass at 75%, followed by polymers at 10% and aluminum at 8%. Trace amounts of silver, lead, and tin are present.
- Other materials located within the solar cell may be more difficult to recycle. Silver and internal copper are valuable components, but panels typically contain very small amounts of these materials. Toxic metals such as lead and cadmium may also be present in solar panels.
- Solar panels may containcritical materials, including aluminum, tin, tellurium, and antimony, as well as gallium and indium in some thin-film modules.
- Other components of a solar power system may include inverters, racking, and battery backup systems, which can also be recycled. Inverters can be recycled with e-waste, and racks can be recycled with similar scrap metal.
Recycling process of solar panels:
Photovoltaic recycling is divided into three main stages: (1) stratification, (2) material separation, and (3) material extraction and purification. Solar panels are recycled primarily through chemical, thermal, and mechanical processes. The process begins with the removal of junction boxes, wires, and frames. The modules are then shredded, sorted, and separated. The separation of materials allows them to be sent to the specific recycling process associated with each material. The above process is applicable to crystalline silicon panels.
The methods described are only a few of many. A number of other methods are currently under investigation. The main problem or concern with the recycling process is the level of impurities. For example, high-temperature heat treatments and mechanical processes can generate impurities. In addition, low-temperature processes that utilize specific mechanical or chemical steps can also generate impurities. Therefore, the desired result can only be achieved through a combination of thermal, chemical, or metallurgical steps. Once these materials can be recycled without impurities, they will have a higher value in the marketplace, which is one of the main obstacles in the PV recycling industry.
What are the future benefits of solar panel recycling?
- The establishment of more solar panel recycling infrastructure,and they will effectively stimulate economic development.A proper solar panel recycling infrastructure needs to be put in place to manage the large number of solar panels that will be disposed of in the near future. Once in place, we will witness a number of positives and new opportunities in the economy.
- Recycling solar panels will create more jobs and save more raw materials.By 2050, PV recycling will not only create more green jobs but also have a recyclable value of around £11 billion.This means that around 630 GW of energy could be produced just by reusing previously used materials.
- Constantly discounted price.As the price of solar energy continues to fall, more and more households and businesses are choosing to invest in solar power systems. As a result, constantly discounted prices mean more households will be able to afford solar power systems.
Maysun works with a number of national suppliers and has assisted many customers with the installation of solar panels.
Maysun Solar has been specializing in the production of high quality solar panels since 2008. We have a wide range of products, including monocrystalline and glas-glas solar panels in addition to roof tiles, with half-cut, MBB and IBC technologies, which provide superior performance and stylish design to blend in perfectly with any building. Maysun Solar has successfully set up offices and warehouses in many countries and has established long-term relationships with excellent installers! For the latest module quotation or any PV related inquiries, please feel free to contact us.

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!





