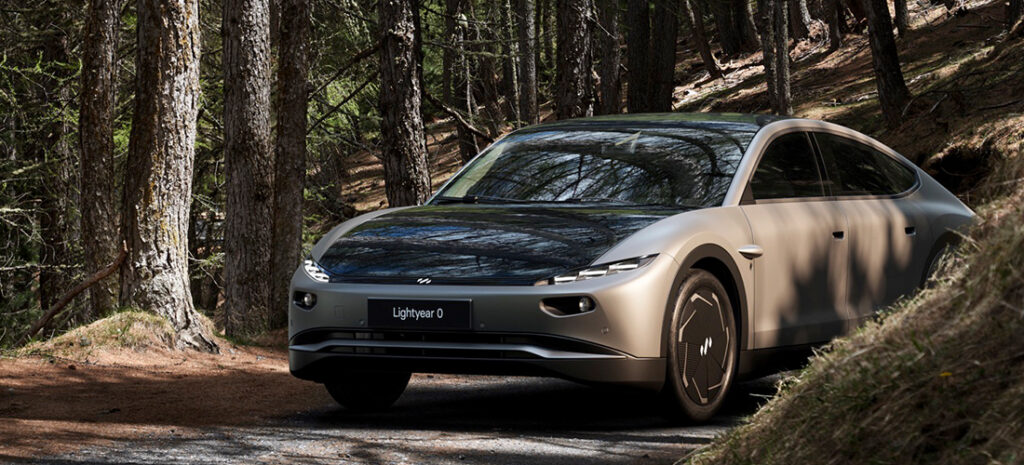
Recently, Dutch electric car startup Lightyear released its solar-powered EV Lightyear 0, priced at a whopping $263,000. Unlike previous solar-powered cars, which are mostly concepts, the company announced that it will deliver the model to customers one by one in November this year, with a total of 946 units.
According to the company, the solar panels will allow the Lightyear 0 to travel about 70 kilometers per day without recharging. With an average commuting distance of about 35 kilometers per day, it can travel for up to two months in cloudy weather conditions before recharging, and even up to seven months at a time in sunny countries.
So, is the Lightyear 0 a pure solar car?

What is a solar car?
Equivalent to an off-grid PV system, a solar car uses solar cells to convert light energy into electricity, which is used to drive the car, and the electricity can also be stored in a battery for backup. The energy required for the car is provided entirely by solar energy, which is considered to be a pure solar car.
As we have seen most “solar cars” are actually a on-grid PV system, where solar energy can provide part of the energy for the car, and in the absence of sunlight or battery power depletion, the car can be powered by connecting to an external power source or adding other fossil fuels.

What forms of solar cars are available?
So far, there are two main technologies for the application of solar energy in automobiles: as a driving force; and as a supplement to the vehicle’s power energy.
One is to use solar energy entirely as the driving force, without using any fossil fuel or external power source. It is very different from the traditional car both in appearance and in operation principle. The solar car has no engine, chassis, drive, transmission and other components, but consists of battery panels, storage appliances and motors. The use of solar panels affixed to the exterior of the car body, the solar energy directly into electricity, and then through the consumption of electricity, drive the vehicle.
Second, solar energy and other energy mixed drive car, that is, the use of solar energy as an auxiliary energy to drive the car. The appearance of the composite energy car is similar to the traditional car, but only on the surface of the car with a part of the solar cells (panels), such as the roof. The limited body area attracts sunlight and produces electricity as a supplementary power source for vehicle use.

History of solar cars
In 1978, the world’s first solar car was successfully developed in the UK, with a speed of 13 kilometers per hour. Later, Mexico developed a three-wheeled new energy vehicle with solar panels on the roof. Although it can reach a speed of 40 kilometers per hour, the electric energy it obtains is only enough to drive for 40 minutes a day, and it cannot travel long distances.
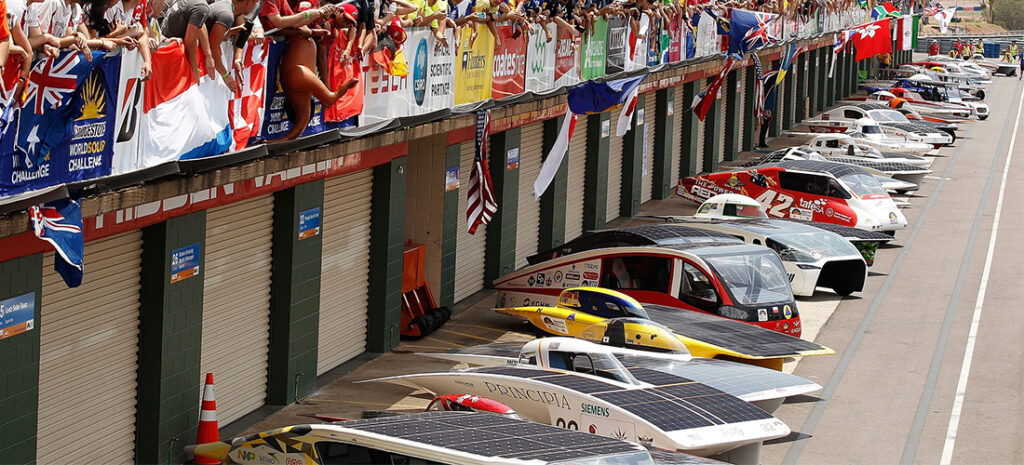
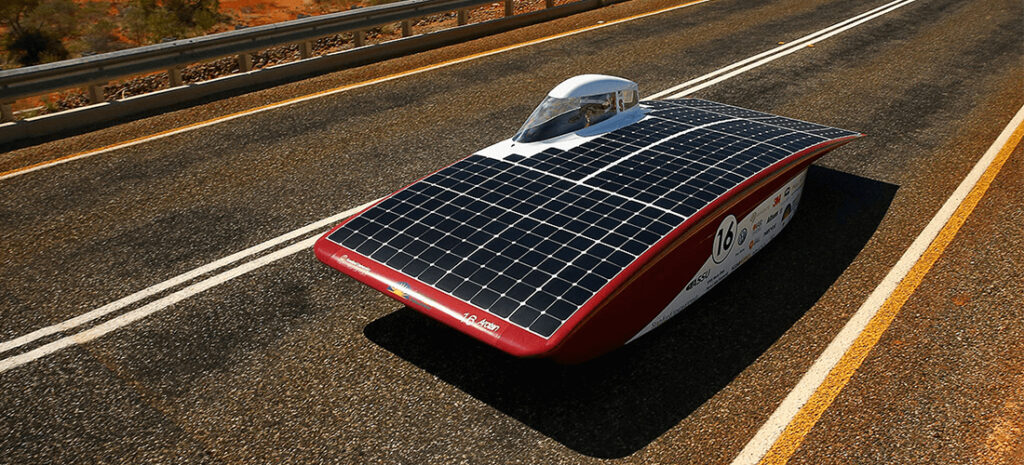
In 1982, Australia built a solar-powered car called “The Quiet Achiever”. The roof of the car is equipped with a device that absorbs solar energy and charges two batteries, which in turn provide power to the engine. The two inventors drove the car across Australia. After that, since 1987, Australia has held a solar energy challenge every two years. The participating teams drive solar cars from Darwin in northern Australia, and drive more than 3,000 kilometers to the end in Adelaide. During the process, only solar power can be used. .
In 2003, in the Australian solar car competition, the “Nuna II” solar car made by the Netherlands won the championship. It ran a distance of 3010 kilometers in 30 hours and 54 minutes, creating a new world record for a solar car with a maximum speed of 170 kilometers per hour.

What kind of solar car is the Lightyear 0?
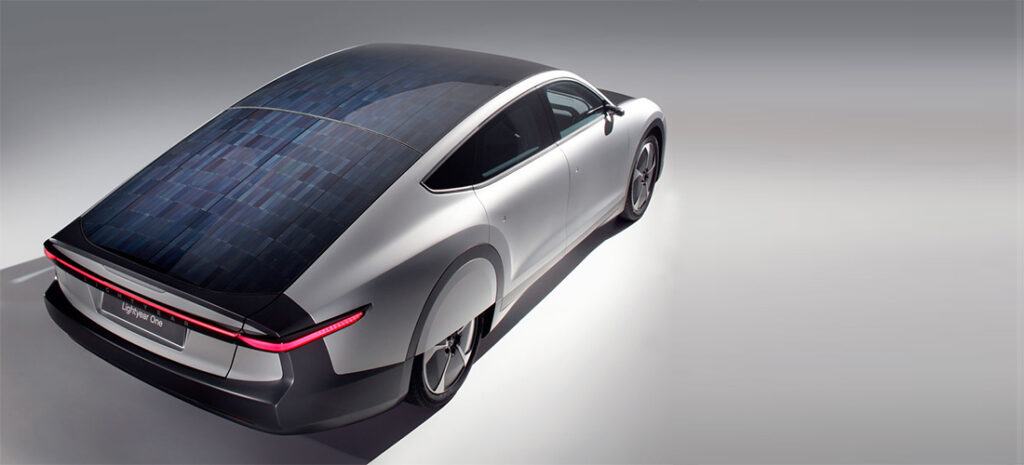
Lightyear, a Dutch company that has been researching solar power for many years and participating in the World Solar Challenge, won first place in the Cruiser class in 2013 and has been developing solar cars ever since. lightyear produced its first prototype in 2019. Three years later, after many tests, iterations and designs, the Lightyear 0 finally went into mass production.
Technically speaking, Lightyear 0 is nothing more than an electric car with solar panels. lightyear 0 has 782 IBC monocrystalline solar cells on the hood, roof, and exterior of the rear hatch, divided into 28 different individual groups and covered with a total of 5 square meters of solar panels.
Although the Lightyear 0 is not considered a pure solar car, it is the world’s first mass-produced car with solar charging capabilities. The highly efficient IBC cells give the Lightyear 0 a pure solar range of 70.8 kilometers per day, which is already a big improvement.

Conclusion
Solar panels have not been an important feature of cars because they can only use a limited surface area for charging. Musk tried to integrate solar panels into the Tesla Model 3, but eventually abandoned the attempt due to inefficient use, saying “the most inefficient area to use solar energy is in cars. If car companies can not solve the conversion efficiency, production costs and design problems, pure solar cars may still be a long way off.
However, as solar cell technology continues to advance (the National Renewable Energy Laboratory has developed a six-junction III-V cell with a photovoltaic conversion efficiency of 47.1% by 2020), the future is still very much in our imagination. Contact us today for more information on our PV products.