Introduction
As global attention to renewable energy increases, solar photovoltaic systems have become a popular energy solution. However, an often overlooked but crucial factor when installing solar panels is the optimal distance between them. This article will explore the importance of panel spacing, methods for determining the optimal distance, and related regulations.
Why is the Distance Between Solar Panels Important?
In photovoltaic system design, the spacing between solar panels is a key factor that directly affects system performance, including light reception, heat dissipation, and maintenance convenience. Proper panel spacing not only enhances energy efficiency but also extends the system’s lifespan. The main reasons are as follows:
- Hot Spot Effect and Thermal Management:The hot spot effect can cause localized overheating of photovoltaic (PV) panels, reducing their efficiency and potentially damaging the modules. Recent research from Portland State University and the University of Utah has found that for every 1°C increase in temperature, the efficiency of PV modules can decrease by 0.3% to 0.5%. Therefore, maintaining proper spacing helps facilitate airflow and heat dissipation, effectively reducing the risk of hot spots and improving overall power generation efficiency.

- Preventing Shadows and Obstructions:During sunrise and sunset, the angle of sunlight is lower, and if the spacing between PV panels is insufficient, the front-row panels may cast shadows on the rear-row panels, reducing their power generation efficiency. Properly designed spacing ensures that each panel receives adequate solar radiation, minimizing the negative impact of shadows on power generation and optimizing the overall performance of the system.

- Enhancing System Stability and Safety:Adequate spacing can reduce the risk of physical collisions and damage to PV panels due to wind or other environmental factors. If panels are installed too closely together, it may increase structural stress between panels, affecting the long-term stability and safety of the system. Proper spacing design helps avoid these potential issues, ensuring the stability and safety of the system.

- Maintenance and Cleaning:The spacing between PV panels also affects the ease of cleaning and maintenance. If the spacing is too narrow, dust, leaves, or other contaminants can accumulate between the panels, making cleaning difficult. Proper spacing reduces the accumulation of such debris, simplifying the cleaning process and maintaining the optimal performance of the PV panels.

What Factors Should Be Considered When Installing Solar Panels?
- Panel Size and Configuration:Solar panels come in various sizes and configurations, commonly with 60 or 72 cells. Choosing the right size and configuration should be based on available space and expected energy needs.
- Panel Orientation:To maximize solar radiation, the orientation of the panels is crucial. Ideally, panels should be installed on a south-facing surface. However, geographical latitude, potential shading, and panel tilt angle must also be considered to ensure optimal energy generation.
- Avoiding Shading:Ensuring there is no shading between solar panels is key to stable energy production. A gap of approximately 10-15 cm is recommended to prevent shading issues between panels.
- Panel Tilt Angle:The tilt angle of the panels should be adjusted to capture the maximum solar radiation. This angle depends on the latitude of the installation site. Proper adjustment of the panel tilt angle according to geographic location can enhance energy efficiency.
- Space Planning:In addition to the space required for the panels themselves, the space for other system components such as inverters and storage batteries must be considered. Accurate planning of the overall installation space is necessary to avoid issues during installation.
When designing a solar panel system, besides the five main factors mentioned above, environmental and structural factors should also be considered. These include the impact of wind and wind pressure on the system, snow and rainwater drainage, cable routing, and the stability of the mounting structure, all of which can significantly affect the overall efficiency of the solar panels.

How to Calculate the Minimum Installation Distance for Solar Panels?
Designing appropriate spacing for inclined or ground-mounted photovoltaic systems can be challenging and even problematic. Ensuring the accuracy of this spacing is crucial to avoid unintended shading from the modules in front of each row, which can lead to poor system performance and customer dissatisfaction. Excessive compensation is also an issue, as it may waste valuable space and reduce the overall efficiency of the system.
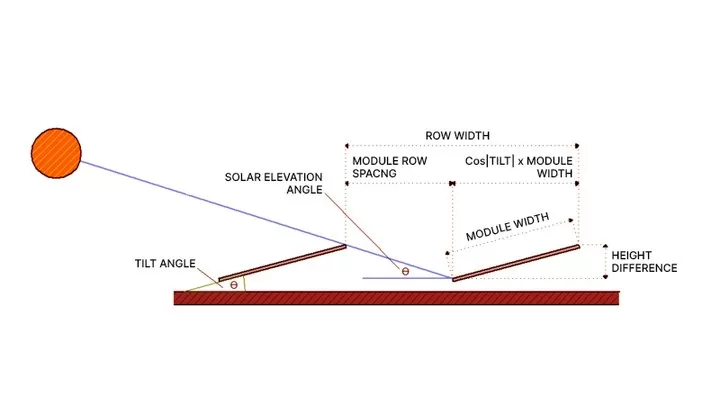
To calculate the row spacing between solar panels, you first need to determine the height difference from the back of the module to the ground. In this example, we use a Maysun Solar module with a width of 39.41 inches and an inclination angle of 15°. Here are the detailed calculation steps:
- Calculate the Height Difference
Calculation formula:
Height Difference = Sin(Inclination Angle) × Module Width
Example:
- Module Width: 39.41 inches
- Inclination Angle: 15°
Calculation:
Height Difference = Sin(15°) × 39.41 ≈ 10.2 inches
Rounded, the Height Difference is 10 inches.
- Calculate the Module Row Spacing
To calculate the module row spacing, you need to use the solar altitude angle, which can be obtained from a solar chart program.
Example:
- Choose the time period from 9 AM to 3 PM during the winter solstice as the worst-case scenario.
- From the solar chart, the solar altitude angle is 17°.
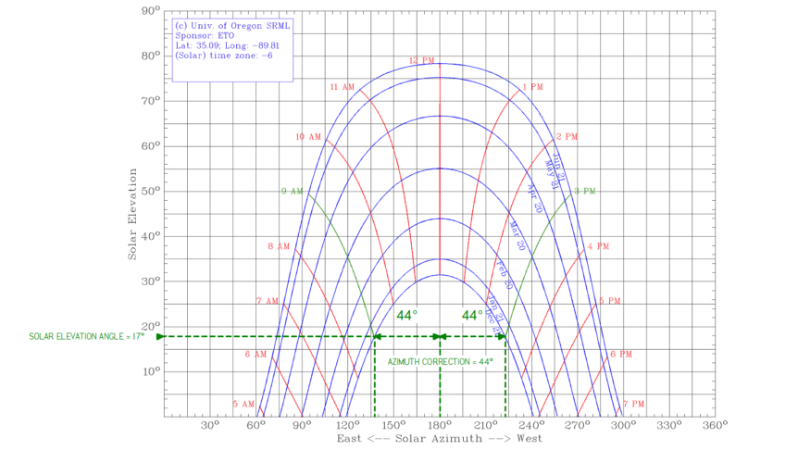
Calculation:
Module Row Spacing = Height Difference / Tan(17°) = 10 / Tan(17°) ≈ 32.7 inches
Rounded, the Module Row Spacing is 33 inches.
- Consider Azimuth Angle Correction
Next, consider the azimuth angle and apply a correction to calculate the minimum module row spacing. Assume the azimuth angle correction is 44°.
Calculation:
Minimum Module Row Spacing = Module Row Spacing × Cos(44°) = 33 × Cos(44°) ≈ 23.7 inches
Rounded, the Minimum Module Row Spacing is 24 inches. This means that in some cases, you can increase the spacing between rows, which may result in significant space savings, potentially increasing the system size by up to 27% in tight rooftop or large commercial systems.
- Calculate the Row Width
The final calculation helps you more easily set up the array in CAD layouts. This calculation determines the distance from the trailing edge of one row to the trailing edge of the next row, i.e., the row width.
Calculation:
Row Width = Minimum Module Row Spacing + Cos(Inclination Angle) × Module Width
= 24 + Cos(15°) × 39.41 ≈ 62 inches
By following these calculation steps, you can effectively determine the optimal row spacing between solar panels, thereby optimizing system layout and space utilization. These calculations will not only help you make more informed decisions during the design phase but also enhance the overall efficiency of the system.
Relevant Laws and Regulations for Solar Panel Boundary Distances
When installing solar panel systems, it is crucial not only to consider the spacing between panels and installation angles but also to comply with local government and regulatory requirements concerning the distance between solar panels and property boundaries.
1. Italy
In Italy, the distance between solar panels and property boundaries is regulated by the Civil Code, particularly Article 889. This law mandates that solar panels must be installed at least two meters away from property boundaries. Additionally, local regulations may vary by region or province, so it is essential to check local laws before installation.
For ground-mounted solar systems, Legislative Decree (DL 17/2022) further specifies suitable areas for such installations. For example, ground-mounted systems can be installed in agricultural areas within 300 meters of industrial, commercial, and quarry zones, as well as within 150 meters of highways. Distance requirements for solar panels from boundaries include:
- A minimum distance of 3 meters between adjacent buildings.
- A minimum distance of 10 meters between opposing building walls and windows (according to Ministerial Decree No. 1444/1968).
- Any necessary pipes must be at least one meter away from the boundary.
2. France
In France, the installation of solar panels is subject to national regulations and local urban planning codes (PLU – Plan Local d’Urbanisme). Specific regulations and distance requirements include:
- Building Permits: Typically, rooftop solar systems do not require a building permit. However, if the system is installed in a protected area (e.g., near historical buildings) or alters the building’s appearance, a permit is required.
- Neighbor Distance: National regulations do not set a uniform distance requirement for solar panels from neighboring properties; this is generally determined by local building codes. It is usually recommended to maintain at least a 3-meter distance to avoid potential shading issues and neighborhood disputes.
- Height Restrictions: In some cases, solar panels installed on rooftops must not exceed 30 centimeters above the roof height. Specific rules vary by local building codes.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: For larger solar projects, especially ground-mounted systems, an environmental impact assessment may be required, along with environmental permits.
3. Germany
In Germany, solar panel installations are regulated by the Federal Building Code (BauGB) as well as state-specific building regulations and the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG). The main distance requirements include:
- Neighbor Distance: According to the Federal Building Code, solar systems on buildings generally do not require special permits but must ensure that the distance between solar panels and neighboring buildings does not cause adverse effects (such as shading issues). Recommended distances generally range from 1.5 to 3 meters, with specific requirements varying by local building codes.
- Building Permits: Rooftop solar systems typically do not need special building permits, but ground-mounted systems may require permits depending on project size and location.
- Height Restrictions: Local building codes specify that the height of solar panels must not exceed a certain range, especially for rooftop installations, generally not more than 30 to 50 centimeters above the roof height.
- Local Regulations: States may have their own rules. For instance, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg have stricter regulations for solar system installations, sometimes requiring special permits in certain situations.
Conclusion
Ensuring the minimum installation distance between solar panels is a crucial step in system design, directly affecting energy efficiency, heat dissipation, and maintenance convenience. Proper spacing design can optimize light absorption and ventilation, reduce shading effects, and minimize potential structural damage risks. Additionally, adhering to local laws and regulations is essential for ensuring the legality and compliance of the system. Therefore, when planning a solar system, it is vital to consider environmental factors, system layout, and local regulations to ensure optimal performance and long-term stability.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has been dedicated to producing high-quality photovoltaic modules. Our range of solar panels, including IBC, HJT, TOPCon panels, and balcony solar stations, are manufactured using advanced technology and offer excellent performance and guaranteed quality. Maysun Solar has successfully established offices and warehouses in many countries and built long-term partnerships with top installers! For the latest quotes on solar panels or any photovoltaic-related inquiries, please contact us. We are committed to serving you, and our products provide reliable assurance.
Reference:
Peloi, V., & Peloi, V. (2024, August 22). Distanza tra pannelli fotovoltaici: qual è la migliore? Otovo Italia | Blog Fotovoltaico in Italia. https://www.otovo.it/blog/distanza-pannelli-fotovoltaici/#ecco-cosa-ha-scoperto-un-gruppo-di-ricercatori
Renewables, G. (2024, March 18). Determining Module Inter-Row spacing. Greentech Renewables. https://www.greentechrenewables.com/article/determining-module-inter-row-spacing
You may also like:

Photovoltaic Fire Safety Guide: How to Reduce the Risk of Power Plant Fires?
The risk of fire in photovoltaic power plants is on the rise. This article, based on European policy standards, provides a detailed explanation of design optimization, operation and maintenance strategies, and emergency response measures to enhance fire safety levels.

IBC Solar Modules vs. Bifacial Glass-Glass Solar Modules: Which Is More Suitable for Low-Light Conditions?
Discover the performance of Maysun Solar’s IBC full-black solar modules and bifacial glass-glass modules under low-light conditions. Based on real-world test data, this article offers scientific guidance for photovoltaic system selection to help you optimize energy efficiency and investment returns.

How to Design Low Maintenance High Yield Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaic Systems
How to build low-maintenance high-return photovoltaic plants This article analyzes the cost challenges and optimization paths of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe helping enterprises achieve payback within 5–6 years and steadily increase long-term returns

How Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) is Changing the Commercial and Industrial Rooftop Solar Market
BIPV in Europe is reshaping the landscape of commercial and industrial rooftop photovoltaics, integrating building and power generation functions while offering policy incentives, economic returns, and ESG value. This article analyzes the advantages of BIPV in technological innovation, business models, and investment returns, helping enterprises seize the opportunity for green transformation.

How to Effectively Clean and Intelligently Maintain Photovoltaic Systems for Optimal Performance?
Explore how scientific cleaning and intelligent maintenance can ensure the efficient operation of commercial and industrial photovoltaic systems. Practical advice covers module cleaning frequency, monitoring system configuration, and long-term strategies for energy savings and performance enhancement.

2025 European Photovoltaic Policy Map: Deployment Paths and Regional Strategies for Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics
A comprehensive analysis of the 2025 European commercial and industrial photovoltaic policy map, focusing on deployment strategies, incentive comparisons, and zero-investment models to support businesses in achieving an efficient and green transition.



