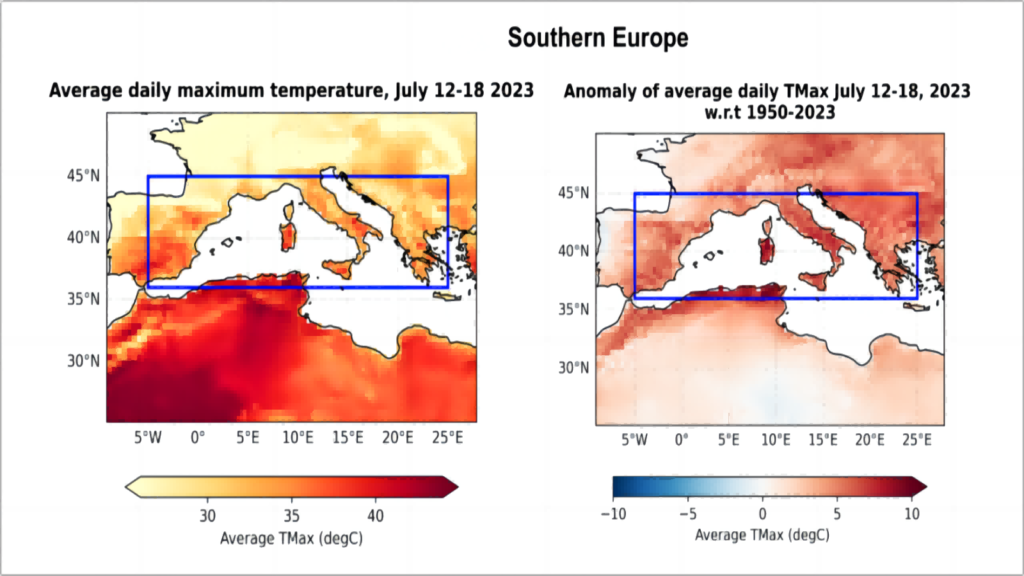
The best time of year to use solar energy is during the summer. For solar inverters, it might also be a difficult period. A heatwave is sweeping across parts of southern Europe, with potential record-breaking temperatures in the coming days. Temperatures are expected to surpass 40C (104F) in parts of Spain, France, Greece, Croatia and Turkey. In Italy, temperatures could reach as high as 48.8C (119.8F). A red alert warning has been issued for 10 cities, including Rome, Bologna and Florence. Experts say periods of exceptionally hot weather are becoming more frequent and climate change means it is now normal to experience record-breaking temperatures (BBC Weather, July 2023). So in this extreme heat, how to keep your solar inverter cool throughout the summer will be covered in this blog post. If you follow these suggestions, you may relax knowing that it will run smoothly all season long!
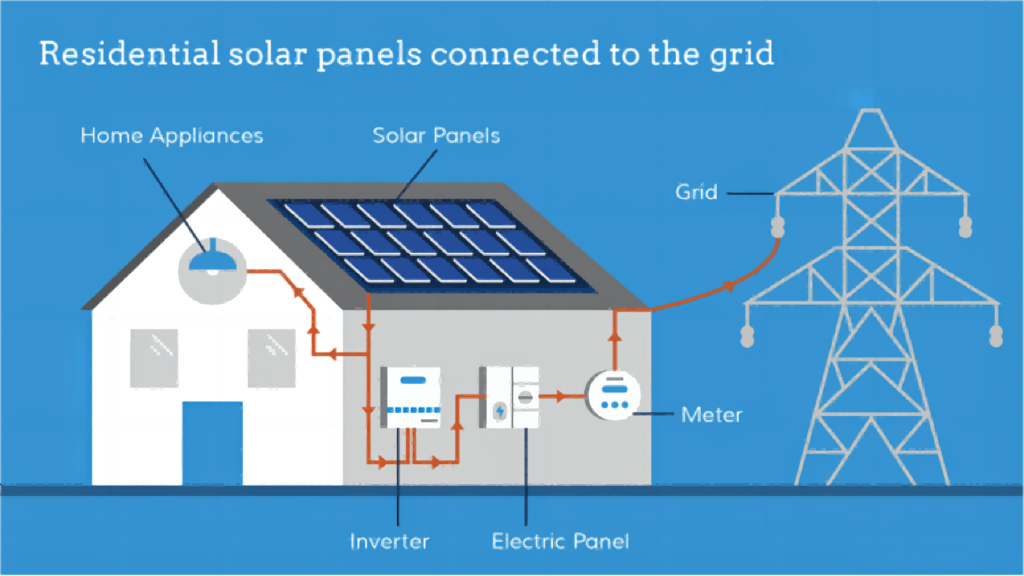
How do inverters work?
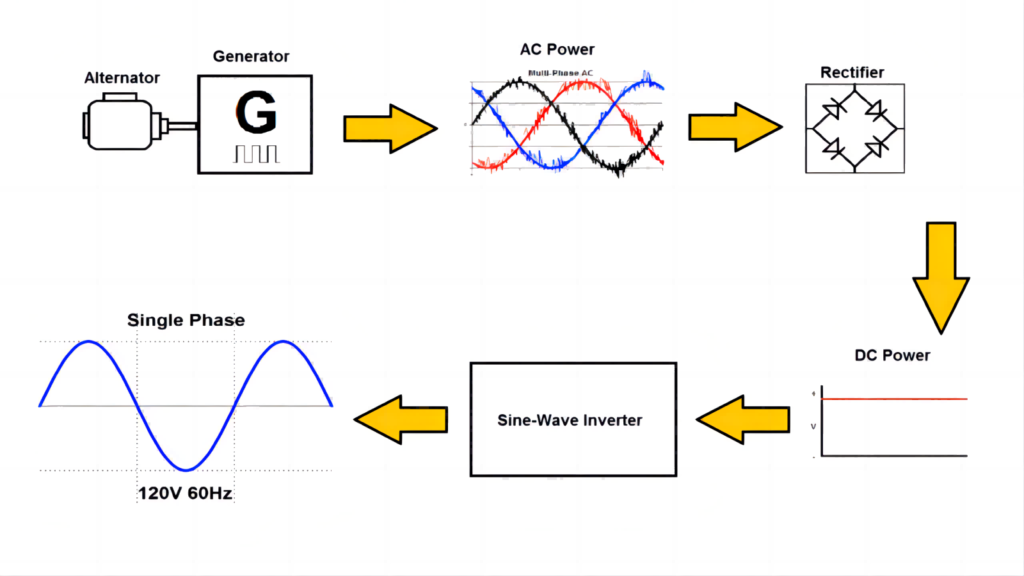
One of the most crucial components of a solar energy system is an inverter. It is a device that transforms solar panels’ produced direct current (DC) electricity into the alternating current (AC) electricity needed by the electrical grid. DC keeps the voltage of the electricity constant in one direction. As the voltage shifts from positive to negative in an AC circuit, electricity moves in both directions. One type of power electronics—a class of devices that control the flow of electrical power—includes inverters.
In essence, an inverter converts a DC input into AC by rapidly flipping the direction of the input. As a result, an AC output is produced from a DC input. A clean, repeating sine wave that fluctuates in voltage and can be injected into the electrical grid can also be created using filters and other electronics. The sine wave is a shape or pattern that the voltage takes over time and is the type of power that the grid may use without causing harm to electrical apparatus that is designed to function at specific frequencies and voltages.
If you have a solar-powered home system, your inverter likely serves numerous purposes. It can monitor the system and act as a communication portal with computer networks in addition to transforming your solar energy into AC electricity. If they are built to do so, solar-plus-battery storage systems rely on cutting-edge inverters to function without assistance from the grid in the event of outages.
High temperature’s effects on solar inverters
1.Solar inverters have a certain operating temperature range, and if this temperature range is exceeded, the efficiency will be affected.
Electronic equipment like inverters, which include a significant number of common electronic components, integrated circuits, and high-power switching transistors, is used in photovoltaic power plants. Most civilian-grade electrical components can operate in a temperature range of -35°C to 70°C, and most solar inverters can operate in a temperature range of -30°C to 60°C. Beyond this working range, both regular electronic circuits and integrated circuits will enter an unstable condition. This state is mild and will cause circuit equipment to go offline, while serious circuit logic will cause equipment damage.
2.Capacitors in solar inverters are very sensitive to temperature, and high temperatures can even cause them to fail.
There are a lot of electrolytic capacitors in solar inverters, and in order to stabilize the voltage of the PV input and prevent interference, there are typically a variety of large-capacity electrolytic capacitors. These capacitors are very sensitive to high temperatures because they cause the internal electrolyte to gradually evaporate, which can reduce capacitance or even cause the capacitor to fail.
3. Excessive temperature will cause thesolarinverter’s high-power thyristor to burn.
The solar inverter’s high power thyristor is a highly temperature-sensitive component. The correct operation and service life of the high power thyristor will be impacted by excessive temperature, and excessive temperature will cause the high power thyristor to burn.
4. Excessive temperature can lead to damage to the materials of the solar inverter and a significant reduction in efficiency.
To a certain extent, the semiconductors used in solar inverters are quite robust and can withstand high temperatures. The ambient temperature of the inverter enclosure is increased by the heat produced by an inverter as it converts DC power to AC power. Fans and/or heat sinks in the inverter enclosure dissipate the heat, which is then increased. Heat levels shouldn’t be too high because doing so would cause the inverter’s materials to degrade. Metal parts in capacitors may become fatigued, solder may expand and crack, and insulation will become brittle. The inverter will cease producing power or scale back its output by “derating” once the temperature reaches preset thresholds in order to maintain a moderate level of heat.

Cooling types of inverters
First of all, we need to understand that the inverter cooling system mainly includes materials such as radiators, cooling fans, and thermal grease. There are currently two main methods of cooling solar inverters: passive cooling and active cooling. Active cooling refers to the realization of heat dissipation from local heating devices to the surrounding environment to achieve temperature control without using any external auxiliary energy. Passive cooling is mainly a method of forcing the surrounding air to flow around the device by means of fans, etc., so as to take away the heat emitted by the device.
Active Cooling
The inverter’s cooling fins disperse heat naturally or passively, without the aid of a fan. The solar inverter’s lifespan is shortened by the hotspots of warm air caused by the absence of air movement. These usually include three main heat transfer modes of heat conduction, convection and radiation, among which convection is dominated by natural convection.
Active cooling is often suitable for low-power devices and components that do not require high temperature control, and the heat flux density of the device is not large, and devices that are sealed or densely assembled are not suitable for other cooling technologies.
Passive Cooling
Utilizing passive cooling is the second option after active cooling. Passive cooling reduces hot spots by efficiently cooling all of the electrical parts and heat sinks, which lowers the temperature. By lowering component strain, the lifespan of solar inverter components is increased. Since the efficiency of heat dissipation affects power generation, the inverter’s cooling fan is essential.
This method is a heat dissipation method with simple operation and obvious effect. This method of cooling can be used as much as possible if the space between components within the part is suitable for air flow or for the installation of local heat sinks or fans for cooling.
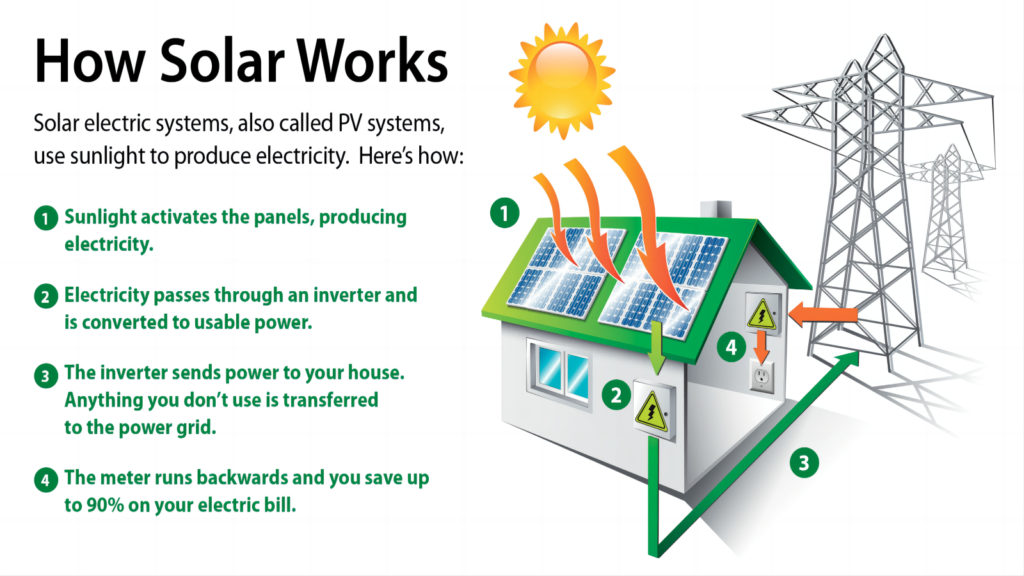
What can we do to keep solar inverter cool throughout the hot days?
1. Install inverters in cool areas (on a wall that is shaded as opposed to the roof).
Make sure your solar inverter is first and foremost mounted in a cool, shaded location. This will aid in lowering the inverter’s temperature and preventing it from overheating.
Some installers surround the inverter with enough computer cooling fans to maintain the proper temperature.
Check your solar inverter’s temperature. If it gets too hot, chill it. Solar fans can help. Solar fans cool the inverter by circulating air. Without a solar fan, aim a regular fan at the inverter. Avoid blowing solar panel trash onto the inverter to avoid overheating it.
2. Select areas with adequate air circulation. Assure when further ventilation is required.
You must make sure that the area around your solar inverter has enough airflow. If the inverter is set up in a small area, the temperature may rise and the solar inverter may sustain damage.
To ensure optimal ventilation, leave at least 30 cm of space on all sides of the solar inverter. Additionally, make sure the solar inverter is not situated close to any heat-producing devices, such as stoves or dryers.
Inverters typically feature vents on the bottom or sides to let hot air out. To ensure efficient operation of the solar inverter, these must be kept free.
It is especially crucial to make sure your solar inverter has excellent ventilation if you reside in a hot climate.
Enhancing airflow involves:
- Installing a solar inverter in an open space, such as next to a window or door or on a wall
- Making cross ventilation with a desk fan
- Letting in cool air by opening windows and doors
3.Avoid placing inverters in the sun’s direct beams. Use existing inverter shadows or covers for outdoor installations.
Many individuals are unaware that installing their inverter in direct sunlight is a bad idea. You’ll find that many manufacturers recommend installing the inverter “where it is not exposed to direct sunlight” in the instruction manual. You should always take steps to avoid direct sun exposure and excessive temperatures, whether it’s the morning sun or the afternoon heat.
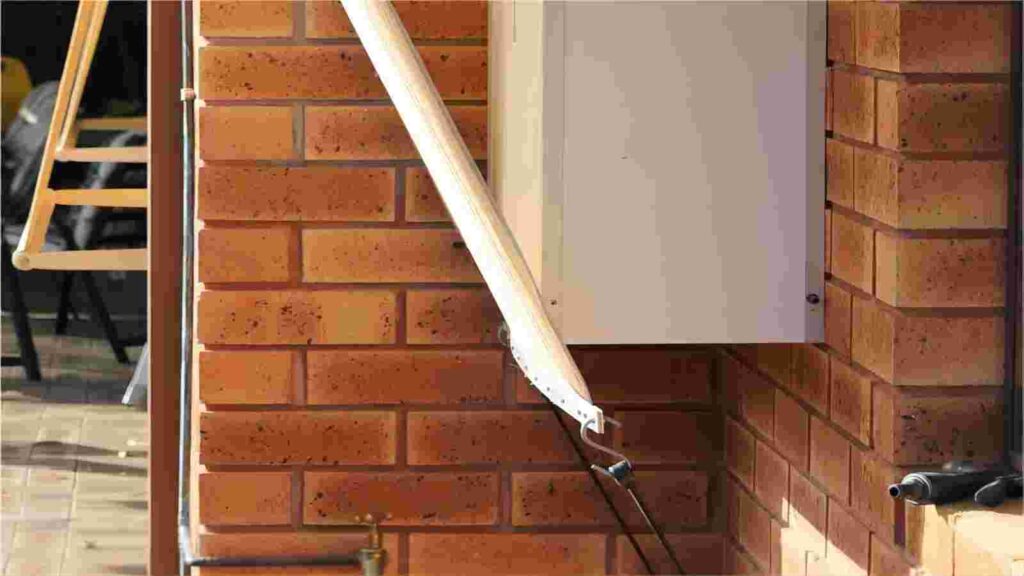
You may also create your own shade cloth box that fits over the inverter and anchors to your wall if your house or place of business lacks a suitable shaded space and you are a skilled do-it-yourselfer.
Installing some shade fabric to make an awning-style cover, as seen in the example image below, is an additional option.

4.Retain the installation guide’s recommended minimum distance from other inverters or nearby objects.
Make sure there is enough room between inverters if there are several of them.
Make sure that the placement of several inverters prevents heat transfer between them. Offset passively cooled inverters enable the upward escape of heat from the heat sinks.
When it is anticipated that the installation site could experience higher temperatures, increase the clearance.
5. Following inverter installation, it’s important to pay attention to ongoing maintenance.
Maintain the heat dissipation and cooling of the inverter by routinely cleaning the fan, fan cover, or heat sink. Typically, the inverter uses sophisticated air-cooling technology to dissipate heat, and the fan will intelligently vary its speed in response to the inverter’s internal temperature. While running steadily, the inverter can also extend the service life of the fan. Additionally, the inverter has a fan failure alarm function, allowing operation and maintenance staff to receive alarm information in the monitoring background, locate the fault quickly and accurately, and help the operation and maintenance staff fix the fan failure in a timely manner so as to minimize power generation loss and ensure power generation revenue.
Due to global warming in recent years, there have been more heat waves and extreme high temperatures in Europe. Your solar power system’s inverter or inverters may occasionally experience stress due to the sun’s higher temperatures on a hot day. These suggestions can help you keep your solar inverter cool and operating normally all summer long. Use solar energy to power your home today to take advantage of the sun’s energy.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has focused on creating premium solar panels. Choose from our extensive selection of solar panels that use half-cut, MBB, IBC, and Shingled technologies in full black, black frame, silver, and glass-glass finishes. These panels provide exceptional performance and fashionable designs that easily fit into any building. In several nations, Maysun Solar has developed offices, warehouses, and enduring partnerships with top installers. Maysun has cooperative installation experts in various European countries. If you have any questions about PV or would want the most recent module quotes, please contact us. If you need photovoltaic system installation consultation, you can also contact Maysun for help. We are eager to help you.

How to Effectively Clean and Intelligently Maintain Photovoltaic Systems for Optimal Performance?
Explore how scientific cleaning and intelligent maintenance can ensure the efficient operation of commercial and industrial photovoltaic systems. Practical advice covers module cleaning frequency, monitoring system configuration, and long-term strategies for energy savings and performance enhancement.

2025 European Photovoltaic Policy Map: Deployment Paths and Regional Strategies for Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics
A comprehensive analysis of the 2025 European commercial and industrial photovoltaic policy map, focusing on deployment strategies, incentive comparisons, and zero-investment models to support businesses in achieving an efficient and green transition.

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.