Table of Contents
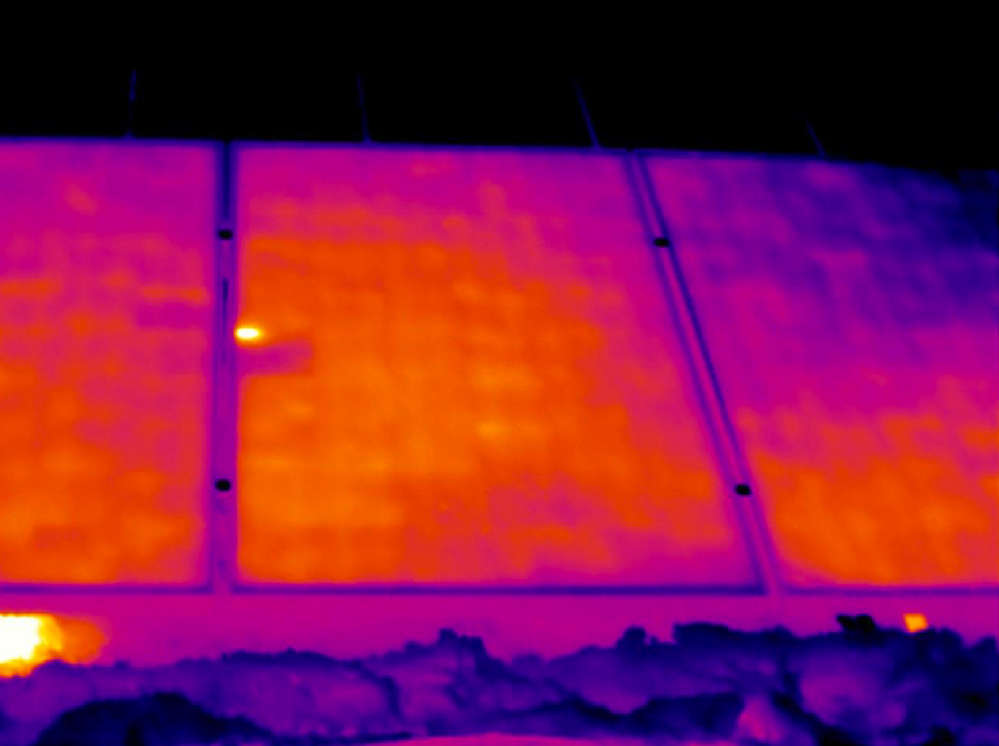
What Are Hot Spot Effects?
The hot spot effect within the realm of solar panels denotes the occurrence of concentrated overheating on the surface of an individual solar cell. This occurrence is usually triggered by the uneven distribution of sunlight across the solar panel, a scenario that arises when a specific section of the panel is shaded or receives less sunlight in comparison to the surrounding areas.
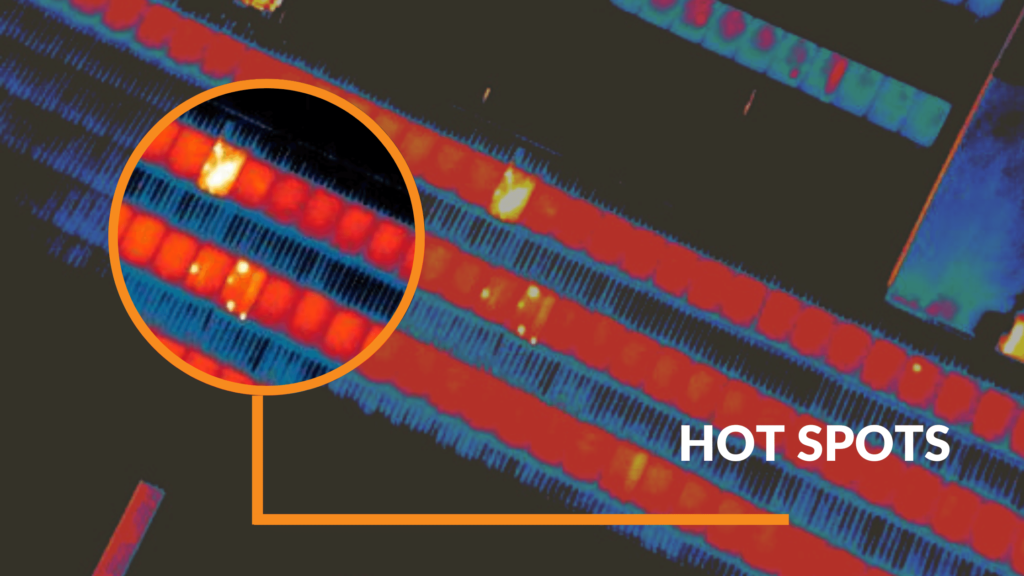
How Do Hot Spot Effect Affect Solar Panels?
The hot spot effect can cause solar panels to overheat locally, reducing their efficiency and potentially causing damage. Details are as follows:
1.Efficiency degradation: When hot spots occur in solar panels, the local temperature rises, which usually leads to a decrease in the performance of the solar cell as the temperature rises. At high temperatures, the electronic conductivity of the photovoltaic cell is weakened, thus affecting the cell’s power generation efficiency.
2.Thermal Expansion and Contraction: Solar panels are subject to solarisation and thermal expansion due to prolonged exposure to sunlight. This surface thermal expansion and contraction may cause fatigue and stress in the panel material, which increases the risk of cracks or other structural problems in the panel.
3.Component Damage: Hot spots may cause damage to electronic components inside the solar panel from high temperatures, such as battery connectors, wires, etc. Damage to these components may degrade the overall performance of the panel.
4.Lifespan affected by thermal stress: When exposed to high temperatures for extended periods of time, solar panels may be subjected to frequent thermal stress. This thermal stress may shorten the life of the panel, thereby reducing its reliability in a solar power system.
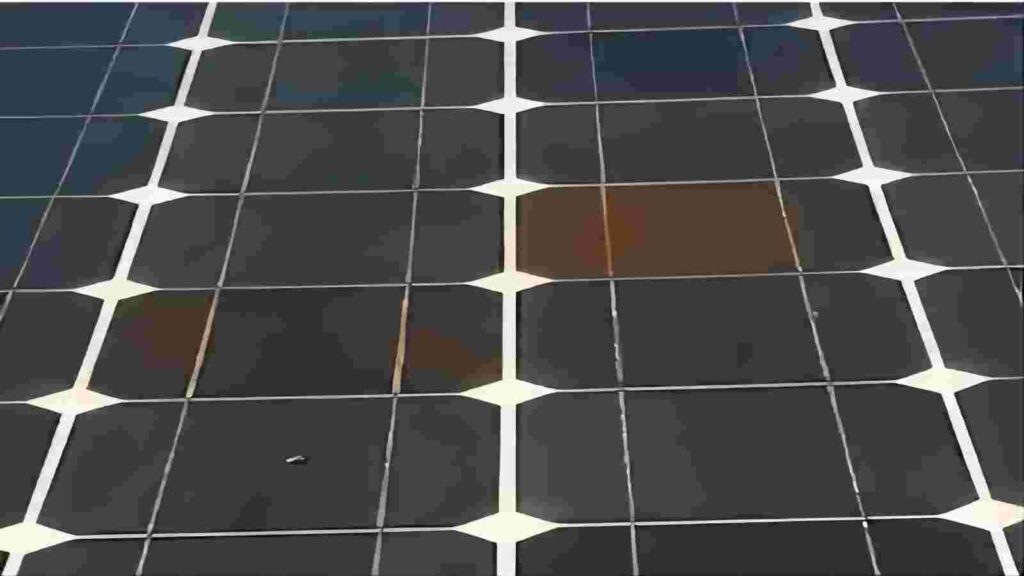
Causes for Hot Spot Effects
Causes of the hot spot effect may include shadowing, module defects, or uneven aging of the cell, which results in localised uneven light, overheating certain areas. Specific causes are listed below:
1.Partial Cell Aging:Over time, individual solar cells within a panel may age differently due to various factors like uneven exposure to sunlight, leading to an imbalance in cell performance. This can contribute to the formation of hot spots as some cells degrade faster than others, affecting the overall efficiency of the solar panel.
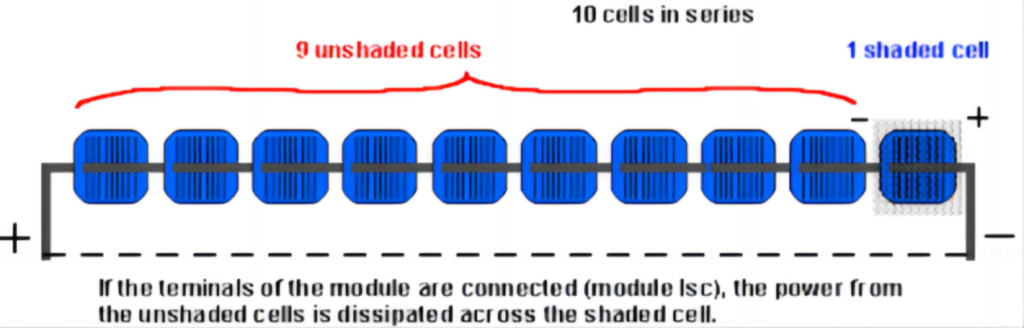
2.Mismatched Panels in Series:In solar panel installations where panels are connected in series, a mismatch in panel specifications or conditions can lead to uneven power production. This imbalance can cause certain panels to operate at lower currents, making them susceptible to hot spot formation, particularly during periods of high solar irradiance.
3.Faulty Bypass Diodes:Bypass diodes are crucial components that help mitigate the impact of shading on solar panels. If these diodes fail to function properly due to manufacturing defects or wear and tear, it can result in ineffective shading mitigation, promoting the occurrence of hot spots in the shaded areas of the panel.
4.Inadequate Ventilation:Poor ventilation around solar panels can contribute to heat buildup, especially in warmer climates. Inadequate airflow can hinder the dissipation of heat generated during energy conversion, exacerbating the hot spot effect. Proper design considerations for ventilation are essential to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
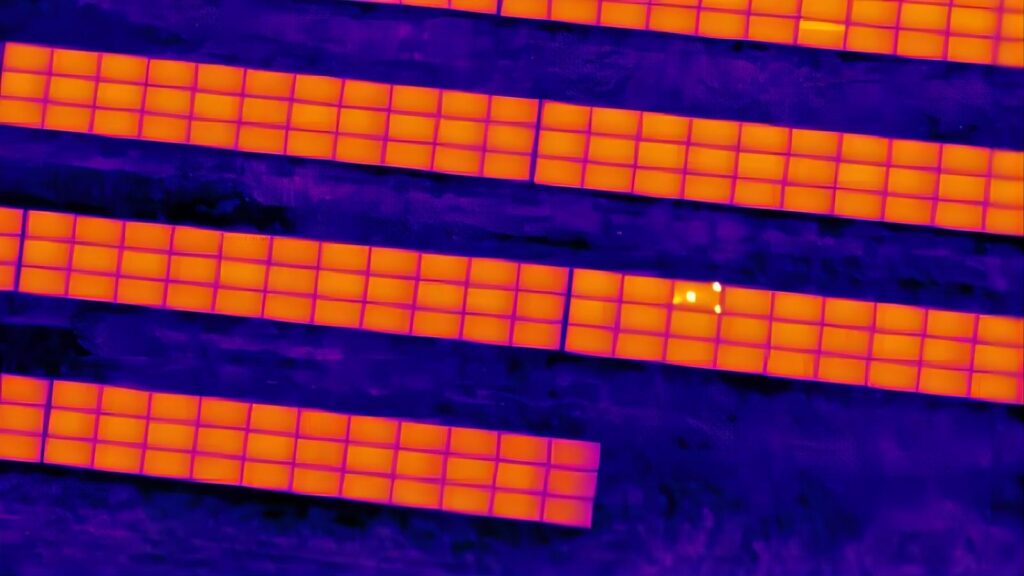

5.Installation Errors: Errors during the installation process, such as improper tilt or orientation, can impact the uniformity of sunlight exposure across the solar panel array. This non-uniform exposure may lead to localized overheating, emphasizing the importance of precise installation practices to prevent hot spot formation.
6.Shadow masking: One of the primary reasons for hotspots on solar panels is shading. When a portion of the panel is shaded, a significant reverse bias voltage can develop across the shaded cells due to the series connection of cells. This can lead to heat accumulation, temperature rise, and the formation of hotspots. Additionally, shading can reduce the overall efficiency of the panel because the shaded cells cannot generate electricity at the same rate as the rest of the panel. Another factor contributing to hotspots is the accumulation of dirt and debris. Dirt and dust on the panel’s surface can block some of the incoming sunlight, resulting in reduced performance and increased temperatures. Debris can also disrupt the panel’s heat dissipation and airflow.
7.Extreme weather.During hot weather conditions, the overall temperature of the solar panel increases, making areas where mismatches or partial shadows exist more susceptible to hot spots. This is because high temperatures increase the overall temperature of the solar panel, which exacerbates the likelihood of the hot spot effect; in cold environments, panels may be exposed to snow and ice coverage or icing, resulting in partially shaded and mismatched cells being more susceptible, and the reduced sunlight exposure may cause the cells to produce more heat than electricity; and strong winds and windborne sand may accumulate particulate matter on the surface of the panels, creating a localised shading and triggering the hot spot effect.
How To Avoid Hot Spot Effects ?
1.Choose high-performance solar panels. Firstly, high-efficiency solar panels can more effectively convert solar radiation into electrical energy, reducing energy loss and thus mitigating the severity of the hot spot effect. Second, high-performance solar panels typically have lower temperature sensitivity, which allows them to maintain high energy conversion efficiencies in high-temperature environments, mitigating the negative impact of the hot-spot effect on performance. That’s why it’s important to choose a solar panel with excellent performance, such as IBC panels.
IBC solar panels reduce the likelihood of hot spots on the panel surface, thus improving system safety. When the solar panel is shaded, the unique full back contact technology ensures that the positive and negative metal electrodes on the back continue to flow properly. This eliminates frontal resistance, thus reducing the possibility of hot spots on the solar panel and the hazards associated with power plant operation.
The IBC solar panels provided by Maysun have been sold to various European countries and have received good reviews! . Customers have reported that they are impressed by the performance and reliability of Maysun’s IBC panels.
Besides that, Using solar panels with built-in bypass diodes also help avoid hot spot effects. This measure prevents the formation of hotspot effects as it allows the current to bypass the affected area in the event of defects or shadows, thus maintaining system performance. All of Maysun’s solar panels are equipped with internal bypass diodes.
2.Optimal orientation and mounting of the solar system: Ensuring that the solar modules are aligned and tilted in an optimal manner is essential to ensure that the sun’s rays are evenly directed at the solar cells to prevent hotspot problems. By carefully adjusting the orientation and tilt angle of the solar modules, the energy capture efficiency of the solar system can be maximised. Such an optimised design helps to ensure that the light energy is evenly distributed across the entire surface of the solar cell, avoiding shadow masking to prevent preventing overheating in certain areas and thus improving the overall performance and stability of the system.
3.Cooling by air circulation. Hot spots do not occur for no reason, but are due to heat build-up and can be the result of a number of factors. However, hot spot effects are more likely to occur if the airflow in the solar panel system is restricted (e.g. through a protective cover). To ensure good system operation, adequate ventilation and air circulation must be ensured to prevent the panels from overheating. Installing power optimisers is one of the best preventative measures, as they automatically reduce power generation when needed, ensuring stable production levels.
4.Clean solar panels regularly. Dirty or dusty panels are more prone to the hot spot effect. It is also necessary to ensure that trees, leaves and other debris do not block direct sunlight from reaching the solar panels to ensure that light energy is fully utilised. Through the combined application of these methods, solar panel systems can be effectively prevented from developing hotspot effects and their stable and reliable performance can be guaranteed.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has been dedicated to producing high-quality photovoltaic modules that contribute to combating climate change. Our advanced technology in IBC, HJT, TOPCon, and balcony solar panels ensures exceptional performance and reliability, capable of withstanding harsh weather conditions for long-term operation. We have established offices and warehouses in multiple countries and built lasting partnerships with top installers to provide comprehensive support. For the latest quotes or any inquiries related to photovoltaics, feel free to reach out to us—we’re here to help!

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!





