Government subsidies helped the PV industry establish economies of scale to compete in markets where PV power costs more than grid power. These policies promote energy independence, high-tech jobs, and carbon dioxide reduction.
European countries have issued PV subsidy policies to encourage people to install PV systems and adhere to the concept of saving energy and protecting the environment. Photovoltaic-popular European countries’ policy introductions are below.
Table of Contents
Germany’s most recent PV subsidy policy
1. A tax-free tax credit :
Electricity income is tax-free (German personal income tax in 22 years will be 14% to 45%): From January 2023, photovoltaic systems installed on the roofs of single-family homes and commercial buildings with a maximum capacity of 30 kW will be exempt from power generation income tax; b) For multi-family conjoined buildings, each building unit can have 15 kW, and each taxpayer can have 100 kW.
Household solar-storage system purchases are VAT-free. This includes importing, buying, and installing small rooftop solar and energy storage systems.
2.An increase in the feed-in tariff:
A portion of the grid-connected power price will increase to 8.6 cents/kWh starting on July 30, 2022; b) if the user elects to fully connect to the grid, there will be 4.8 cents/kWh on the basis of 8.6 cents/kWh. The total excess feed-in tariff, which includes the additional subsidy for kWh, is 13.4 cents/kWh.
3.Capacity subsidy policy for energy storage systems:
Some states directly fund energy storage systems based on their capacity. Users who elect to connect all solar energy to the grid will get additional subsidies based on the standard price of grid-connected electricity. The German government wants to encourage people who don’t need solar panels for personal use to install them on their roofs. They also want these people to connect the electricity produced by the panels to the grid.
4. Financial assistance:
The German government offers low-interest loans and financial help for energy storage projects.
The installation, growth, and purchase of renewable energy, including photovoltaics or energy storage systems, are supported by KfW’s low-interest loans for energy-efficient building retrofits (KfW Promotion Program 270), which can cover 100% of the acquisition cost at a loan with a 2.3% interest rate.
5. Lower EEG(Surcharge for renewable energy)costs at the current power price level:
German industrial power costs can be exempted or partially reduced to retain global manufacturing competitiveness. EEG surcharges, electricity taxes, transmission fees, and other surcharges decreased. Industrial consumers can save 95% by following this approach.
Elimination of the green energy surcharge (EEG surcharge) results in a reduction in power usage costs for consumers of 3.72 cents per kilowatt.

France’s most recent PV subsidy policy
Solar system assistance in France is provided by the FIT (Feed-In Tariffs) system. Laws determine the values used in this FIT system. In this approach, either extra energy produced or all of it is sold to the network. This system is supplemented by a more adaptable energy transfer law. Under the law, producers are not obliged to sell the energy they produce.
According to installed power, FIT ratings are likewise divided into categories in France. This classification has limits of 3-9-36-100 kW. Additionally, the sale of any extra or surplus production has an impact on the FIT value. The illustration below depicts this scenario.
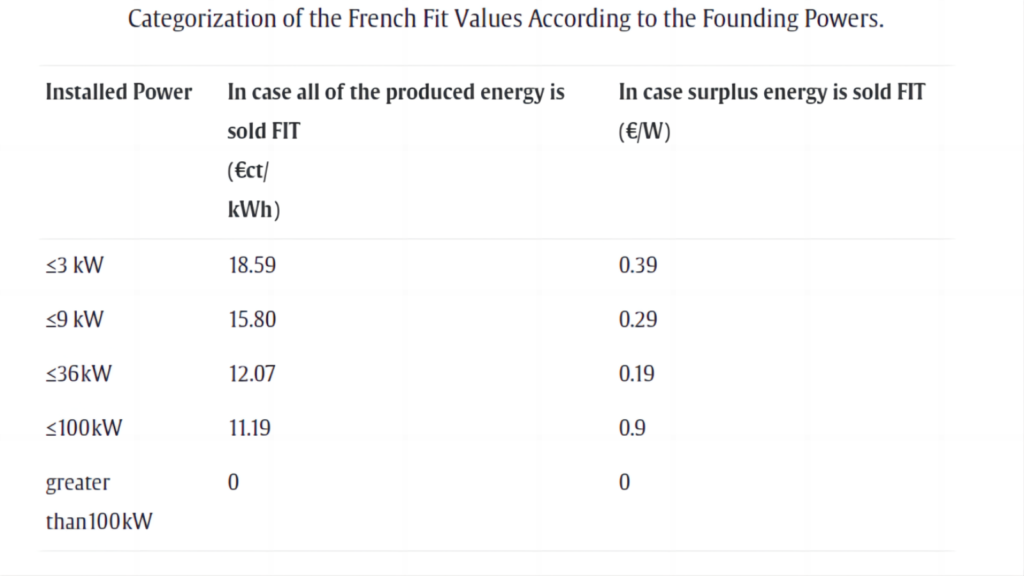
The most recent PV subsidy policy in Spain
- Policies vary from city to city or state to state, but basically they are in the range of 40% to 50% subsidy.
- 2. Installation cost has about 50% subsidy, which is about 3,500€.
- 3.State consumption subsidy:
- Commercial or industrial: 15%. 45% for SMEs with own power equal to or less than 15Kw
- Individuals:40%
- Shared own-use facilities:50%
- Public administration component:70%
- Those with a population of less than 5,000 will receive an additional 5%

Italy’s most recent PV subsidy policy
The Italian government authorized five Conto Energia subsidy schemes between 2005 and 2012, and GSE, a state-owned energy service provider, was in charge of their issuance, verification, and regulation. The proposal allows Conto Energia to provide subsidies for electricity generated by grid-connected new energy power plants, with a typical 20-year subsidy tenure. Since the maximum amount set aside by the Italian government for Conto Energia subsidies has been achieved, new electric power plants are no longer eligible to receive new Conto Energia subsidies as of July 6, 2013.
The Italian government announced the FER 1 subsidy scheme in 2019, which covers four different types of new energy generating plants, including rooftop photovoltaics. By enrolling in the public system run by GSE or taking part in open bidding, new energy generation plants must get FER 1 subsidies. The installed capacity that can receive subsidies under the subsidy plan has an upper limit requirement; installed capacity that is higher than the upper limit is not eligible for subsidies.
In addition, Italy recently introduced a new subsidy policy, providing 90% of the installed cost subsidy for the newly installed photovoltaic capacity for agricultural purposes, in order to support agricultural, aquaculture, and agro-industrial companies to invest in expanding photovoltaic power generation. The subsidy is estimated to cost 1.2 billion euros, and it will be in effect until June 30, 2026.

England’s most recent PV subsidy policy
1. Modification of related standards to promote the installation of photovoltaic systems in buildings
Residential solar PV demand has increased significantly as a result of the energy price crisis and the conflict in Ukraine. Additionally, new residential building regulations in England and Wales now require rooftop PV systems for all new homes, and more households are likely to purchase energy storage systems that can maximize usage time tariffs.
Rooftop PV license development rights in the UK were last modified in 2015, when the barrier for rooftop PV license development was increased from 50kW to 1MW. The UK government will also change performance criteria to require photovoltaic systems to be installed in all new homes and structures.
2. Abolition of VAT on household PV systems
The strategy is already boosting the technology, as seen by the UK’s recent elimination of VAT on household solar systems.
The UK government will consult on revisions to planning regulations for the installation of large-scale solar systems to enhance policies that support development on unprotected land. This includes fighting to safeguard the environment and making sure the community continues to have a say in initiatives.
Projected impact of UK photovoltaic subsidy policy:
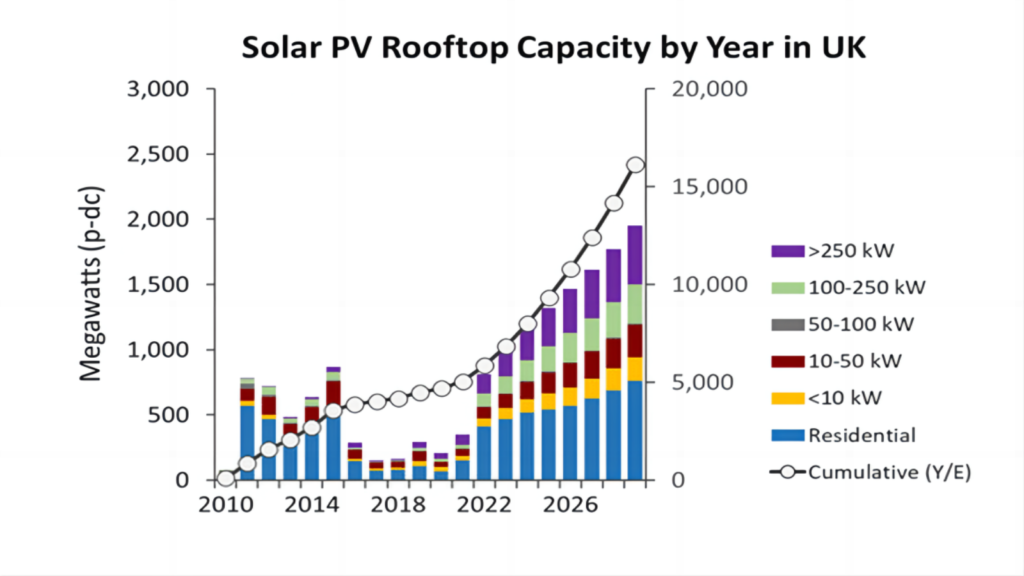
The British solar Association applauded the strategy’s publication and predicted that by 2035, installed solar systems in the UK will increase from their present installed capacity of 14 GW to 70 GW, resulting in a five-fold increase in installed capacity and the creation of additional jobs.
“The UK government’s plan to increase the installed capacity of photovoltaic systems by 5 times by 2035 shows that it now has the same goal as the UK photovoltaic industry,” said Chris Hewett, chief executive of the British solar Association. The UK government has publicly announced plans that could accelerate solar system installation. These plans include CFD auctions and potential changes to affordable financing.
The implementation of these plans could also create many jobs and reduce energy expenses. Additionally, it would enhance the UK’s energy security.
Austria’s most recent PV subsidy policy
Subsidies for investments in photovoltaic (PV) systems and power storage.
PV classification is divided into four categories: A → D, the four categories do not make a special distinction between the presence or absence of power storage equipment
Class A: PV systems ≤ 10kWp
Class B: 10≤PV system≤20kWp
Class C: 20≤PV system≤100kWp
Category D: 100 ≤ PV system ≤ 1,000kWp
Subsidy costs:
PV category A: €285/kWp (max.)
PV category B: €250/kWp (max.)
Photovoltaic category C: €180/kWp (max.)
Photovoltaic category D: €170/kWp (max.)
Electricity storage: €200/kWp (only subsidised for storage equipment combined with new or extended photovoltaic systems).

PV subsidy policy in Sweden
In October 2022, the Swedish Ministry of Finance issued a new regulation to increase the tax deduction for the installation of PV system from 15 per cent to 20 per cent; the total amount is estimated at SEK 280 million, effective 1 January 2023.
1. For private residences
The limit of tax-free liability is raised from the previous 255 kW to 500 kW of installed power.
- Solar panels from installations of 500 kW or more are subject to the full energy tax.
- Solar electricity from installations with less than 500 kW of their own power – but where the owner has solar panels totalling more than 500 kW in different installations – can be taxed through a reduced energy tax. The reduced energy tax/solar tax is currently 0.6 öre/kWh.
- Anyone with solar panels installed totalling less than 500 kW (equivalent to approximately 2,500 square metres) is completely exempt from the energy tax.
2. Installation tax breaks
Green Technology Tax Deduction 15% tax deduction for installation of grid-connected PV systems.
A 50% tax reduction for the installation of self-produced electrical energy storage systems.
50% tax relief for the installation of electric vehicle charging posts.
Tax deduction for work and material costs, capped at SEK 50,000.
3. Tax reduction for electricity fed into the grid
Tax reduction of 60 kEUR/kWh for excess electricity fed into the grid.
Maysun Solar will continue to update the blog about PV policy subsidies in various countries, welcome to subscribe!
Maysun Solar has focused on creating premium photovoltaic modules since 2008. We use half-cut, MBB, IBC, and Shingled technologies in a variety of solar panels, including those that are all-black, black frame, silver, and glass-to-glass. These solar panels provide exceptional performance and chic looks that fit nicely with any architecture. Maysun Solar has effectively created warehouses and offices in numerous nations, and it has developed enduring connections with top installers! Contact us if you have any questions about PV or would want the most recent module quotes. We will be delighted to assist you.
Source:
https://www.pv-magazine.com/2023/01/13/austria-allocates-650-million-for-solar-incentives-in-2023/
https://guangfu.bjx.com.cn/news/20220412/1217012.shtml
https://www.pv-magazine.com/2022/05/14/the-weekend-read-european-pv-subsidies-a-divisive-topic/
https://xueqiu.com/8431271718/239509788
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Financial_incentives_for_photovoltaics

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!

What’s New in Solar Energy (March 2025)
March’s solar news highlights include rooftop solar meeting two-thirds of global demand, China’s market reforms potentially boosting solar demand and module prices, France revising solar targets in PPE 3, and challenges in Europe with declining capture rates and price volatility.




Pingback: What is the difference between solar thermal and Solar PV(Photovoltaic)? - Maysun Solar-Professional Solar Panel Supplier For 15 Years