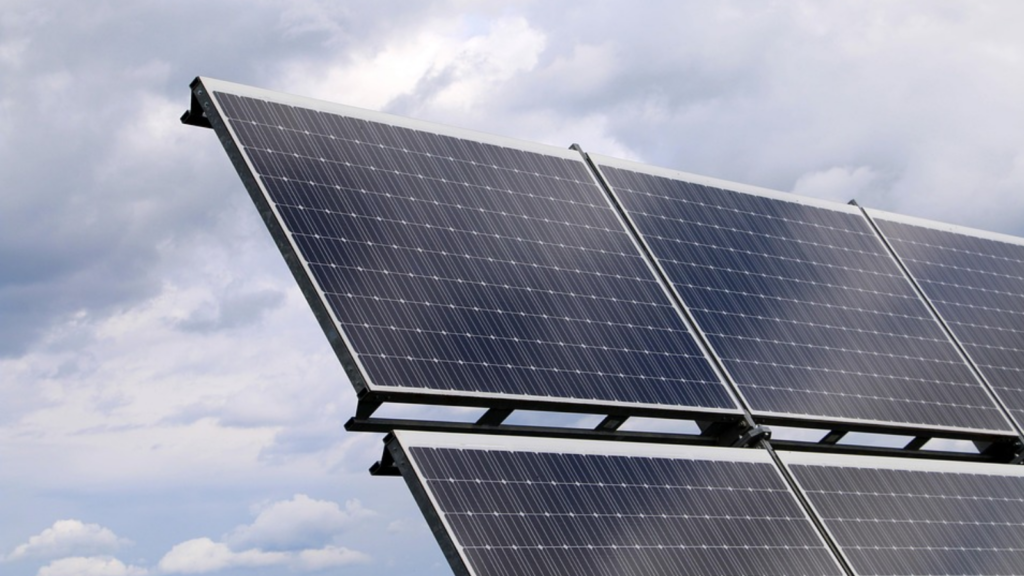
The technology behind solar panels is continuously evolving, and manufacturers are now capable of producing bifacial solar panels. As the name suggests, bifacial solar panels are devices that feature photovoltaic cells on both the front and back sides, designed to capture sunlight from both directions. Unlike traditional monofacial solar panels, bifacial panels can absorb direct sunlight from the front while also utilizing light reflected from the ground or nearby surfaces. This dual absorption capability often results in higher efficiency for bifacial solar panels compared to conventional monofacial panels, significantly enhancing energy generation.
What are the types of bifacial modules?
Bifacial solar panels primarily come in three forms, each with its own advantages and characteristics:
Glass/Glass Panels(most common on the market):
- Structurally stronger, these panels can withstand greater loads.
- Suitable for high-intensity environments, offering enhanced durability and reliability.
Glass/Transparent Backsheet Panels:
- These panels have a glass front and a transparent backsheet.
- Generally more affordable, making them ideal for budget-conscious projects.
Glass/Backsheet Panels:
- Featuring a glass front and a non-transparent backsheet.
- While they have slightly lower reflective performance, they still provide good energy generation efficiency.
Each of these types of bifacial solar panels has unique features, allowing users to choose the most suitable product based on specific needs and environmental conditions.

What Are the Best Practices to Install Bifacial Solar Panels Effectively?
1. Optimize Panel Height and Clearance
Elevate bifacial panels higher than traditional monofacial panels, ideally at least 1 meter (3.3 feet) above the ground or roof surface. This increased height allows more reflected light to reach the rear of the panels and reduces shading risks at the bottom edge. For sloped roof installations, maintain a clearance of at least 10-15 cm (4-6 inches) between the panel’s back and the roof surface to promote airflow and light reflection.
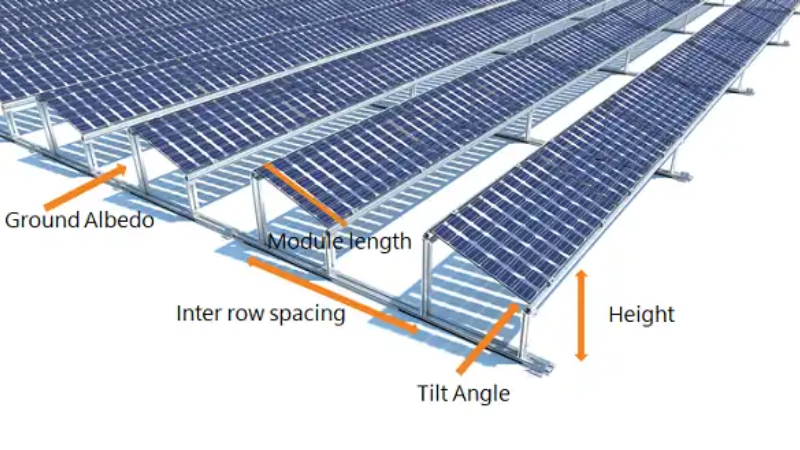
2. Implement Optimal Row Spacing
Ensure adequate spacing between panel rows to allow light to reach the ground and reflect back to the panel’s rear. Start with a row spacing of at least 2.5 meters, with wider gaps preferred to maximize rear light absorption. When designing the layout, consider seasonal changes in solar angles, typically setting the spacing for a ground coverage ratio (GCR) of 0.3 to 0.5.
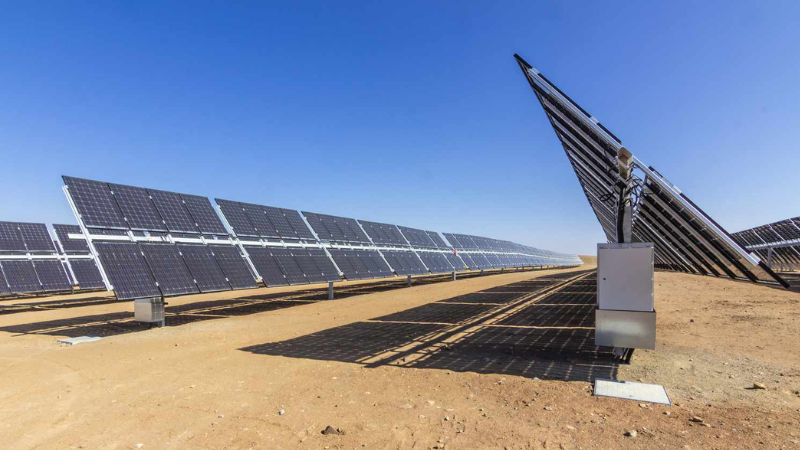

3. Determine Panel Location
The area surrounding the panels should have high-albedo surfaces to reflect light onto the rear of the bifacial panels. Ideal locations include white roofs, low vegetation, asphalt, and bodies of water. Avoid shaded areas and light-absorbing surfaces, such as those obscured by tall buildings or dark soils, as these can reduce rear illumination.
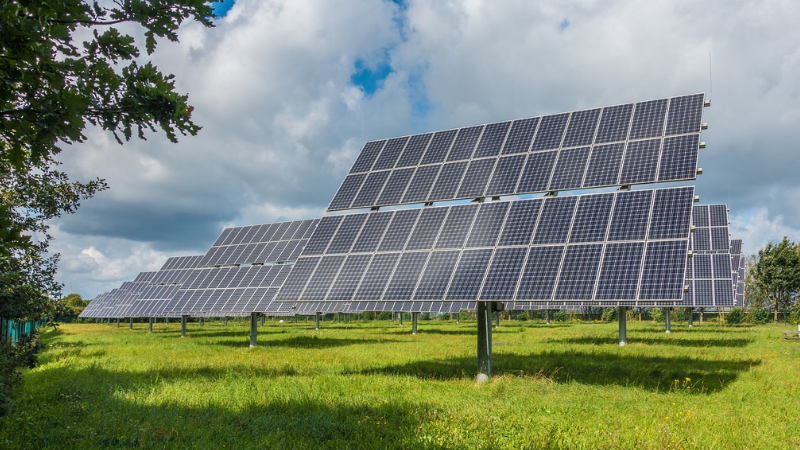

4. Incorporate Diffusers
Strategically place scatter-type “enhancers” around the panels to effectively diffuse and reflect more light onto the rear. Cost-effective options include painting nearby walls or fences white or applying reflective film to barriers, along with placing white gravel around the solar mounts. Adding white or light-colored stones beneath the ground-mounted array can increase reflectivity from 0.2-0.3 to 0.5 or higher. In agricultural settings, certain crops (like specific lettuce varieties) also exhibit high reflectivity. Additionally, painting the mounting structure’s rails white can enhance light reflection beneath the panels.
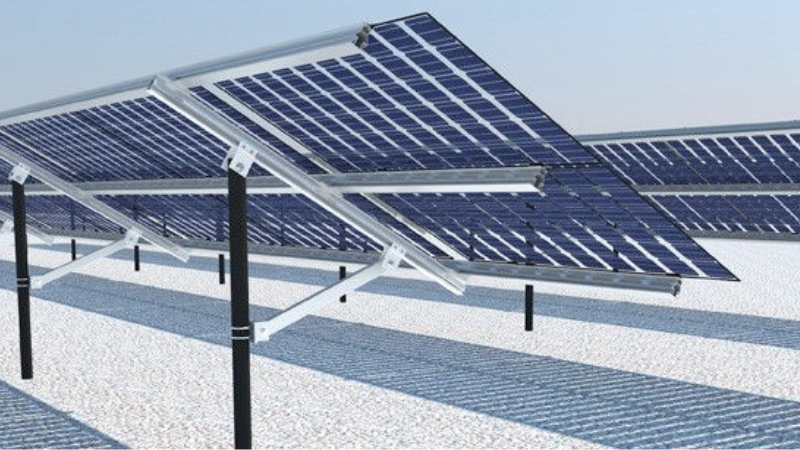

5. Use Transparent or Reflective Mounting Components
Prioritize mounting materials that allow light to pass through or reflect onto the rear of the panels. Using light-colored or reflective materials for rails and supports can significantly increase rear illumination, enhancing energy production efficiency. If windbreaks are necessary, transparent or semi-transparent materials are ideal, as they ensure light penetration while reducing wind effects. Minimize the use of opaque components to avoid casting shadows on the back of the panels, which could hinder light reflection and absorption.
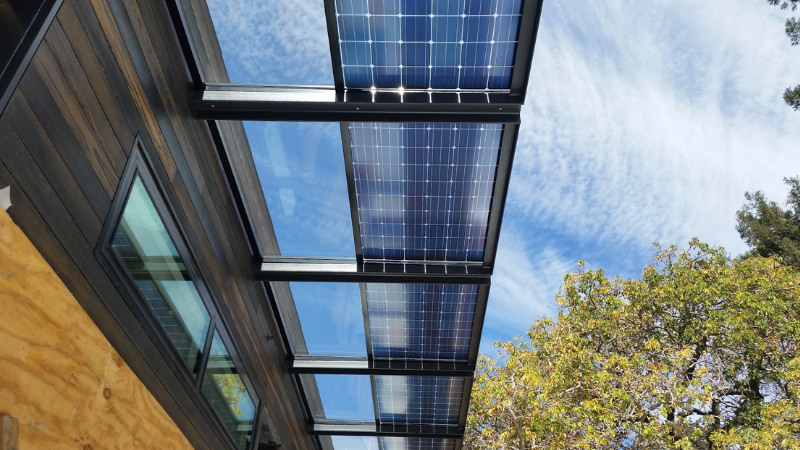

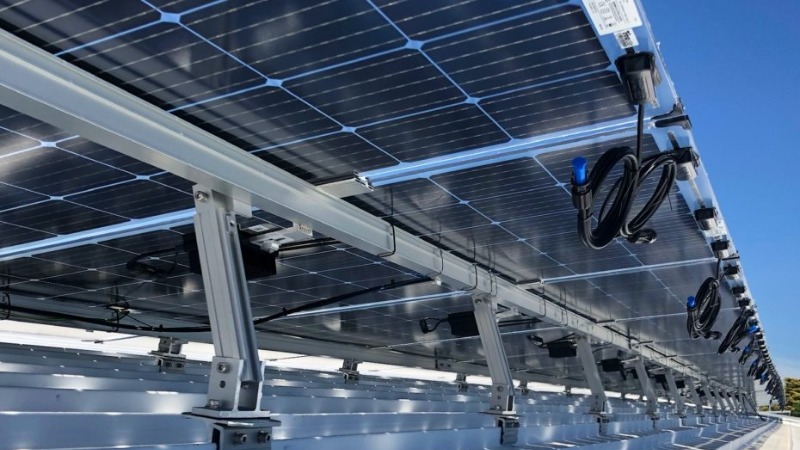
6. Plan for Cable Management
Route cables along the sides of the bifacial solar panels or mounting components to minimize shading on the rear. Use transparent or light-colored cable ties and conduits to optimize lighting conditions. Additionally, pre-planning cable paths, employing dedicated cable management solutions, and regularly checking the cable condition for wear or aging are critical measures to maintain system efficiency.

Conclusion
In the quest for cleaner and more efficient energy, bifacial solar panels have emerged as a promising solution. Not only do bifacial solar panels enhance energy generation efficiency, but they also contribute to the broader adoption of sustainable energy. Through proper design and installation, users can maximize their return on investment while supporting environmental sustainability. These panels will play a significant role in advancing the green energy transition and the future development of renewable energy.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has focused on producing high-quality photovoltaic modules, particularly bifacial photovoltaic modules. Our HJT and TOPCon bifacial solar panels, designed with lightweight materials, offer exceptional dual-sided energy generation performance, maximizing sunlight utilization and improving efficiency. Additionally, our balcony solar power stations provide users with flexible application options. Maysun Solar has successfully established sales offices and warehouses in multiple EU countries and has developed long-term partnerships with excellent installers. For the latest solar panel quotes or any photovoltaic-related inquiries, please contact us. We are committed to assisting you in making optimal choices regarding the design, installation, and selection of photovoltaic modules.
Reference:
Heltsley, K. (2024, June 30). Best practices for installing bifacial solar panels | explained. ItekEnergy. https://www.itekenergy.com/solar-panels/best-practices-for-installing-bifacial-solar-panels/
9 Tips and Tricks for deploying bifacial solar panels. (n.d.). Waaree Energies Limited. https://shop.waaree.com/blog/9-tips-and-tricks-for-deploying-bifacial-solar-panels/?srsltid=AfmBOoqdaA1bhATCHPqFaA2YzrBgD5OQwzWb2WUQs5UVUsOQOZIEozGa
You may also like:

How to Effectively Clean and Intelligently Maintain Photovoltaic Systems for Optimal Performance?
Explore how scientific cleaning and intelligent maintenance can ensure the efficient operation of commercial and industrial photovoltaic systems. Practical advice covers module cleaning frequency, monitoring system configuration, and long-term strategies for energy savings and performance enhancement.

2025 European Photovoltaic Policy Map: Deployment Paths and Regional Strategies for Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics
A comprehensive analysis of the 2025 European commercial and industrial photovoltaic policy map, focusing on deployment strategies, incentive comparisons, and zero-investment models to support businesses in achieving an efficient and green transition.

Empowering Factories with Solar Energy A Strategic Tool for Controlling Production Electricity Costs
Commercial and industrial solar is becoming a key solution for factories to reduce electricity costs and hedge against price fluctuations. This article systematically analyzes its deployment models, cost advantages, and sustainable value pathways.

How Businesses Can Offset Carbon Taxes with Solar Power
This article analyzes the latest carbon tax policies and photovoltaic deduction strategies, helping European businesses legally reduce taxes, increase profits through solar investment, and achieve a win-win situation for both economy and environment.

Forecast and Response: Seizing the Next Decade’s Growth Dividend in Europe’s Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics Market
Maysun Solar analyzes the growth trends of commercial and industrial photovoltaics in Europe over the next ten years, from policies and ESG to technological innovation, helping companies seize the initiative in the energy transition.

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.



