When you’re ready to go solar, you first need to consider which PV system to install. There are two types of home PV systems, one is off-grid PV, and other is on-grid PV. Both advantages and disadvantages exist, and you should choose according to your circumstances.
Overview
In simple terms, an off-grid is to store the electricity generated by a photovoltaic system in a battery, which is then converted by an inverter to power household appliances. On-grid means that it is connected to the mains electricity directly converted into the voltage requirements of the national grid through the inverter, and prioritized for household use. The surplus electricity is sold to the state.
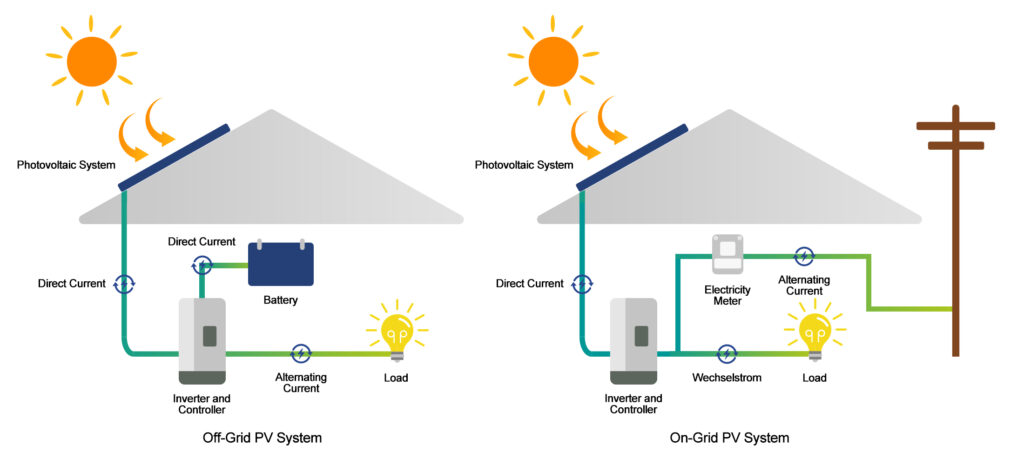
Off-grid PV systems
Advantages of Off-grid PV
1. The great advantage of an off-grid PV system with storage is independence. You can install an off-grid PV system almost anywhere that is off the grid but constantly in need of electricity, such as a mountain hut or a boat.
2. You can use it as an emergency power generator in areas where there are frequent power cuts.
Disadvantages of off-grid PV
Batteries account for 30-50 percent cost. And the service life of the battery is generally 3-5 years, after that, it has to be replaced, which increases the use cost. In Germany, for example, the cost of purchasing a PV system for a typical single-family home is around €8,500 (average 5 kW P system). A 5 kW P system with a 5 kWh battery costs between 14,000 and 16,000 euros.
Another disadvantage of off-grid systems is low power supply security.
If there is not enough generation and storage to get the necessary power from the grid, your house will be left without power.

On-grid PV systems
Advantages of On-grid PV
- It does not need to use batteries, saving costs.
- When the solar system generates more electricity than your appliances can use, the excess is sent to the public grid, where you not only get paid for it but also contribute to the energy transition.
If you have a 10-kilowatt photovoltaic system installed in your home, the EEG 2023 amendment allows you to get 8.6 euro cents per kilowatt-hour for excess electricity that goes into the public grid. Large systems also offer higher rates of return than before. Up to 40 kW (including 40 kW), raised to 7.50 euro cents per KWH. The portion up to 750 KWH still earns 6.20 euro cents per KWH. In an average household, about 35 per cent, or 65 per cent, of the electricity generated is put into the grid and paid for. A rough estimate is that a home PV power station pays for itself in about 10 years.
Disadvantages of On-grid PV
The PV system can’t work when the public grid is cut off. However, the power station can operate normally if the on-grid inverter is replaced by an intelligent micro-grid inverter (on-grid and off-grid hybrid inverter).
At present, many households choose to install on-grid PV systems. But this is not suitable for all families, it depends on specific circumstances and also needs to meet local policies.
Conclusion
Whether off-grid or on-grid, the most important thing about a PV system is choosing the right PV modules. The modules are the key to determining how much return the PV system will get. Maysun Solar, a professional PV module manufacturer for 14 years, click to see all our modules.


