Over time, the performance of solar panels gradually decreases, a phenomenon known as degradation. Understanding solar panel degradation is crucial for assessing the long-term benefits and reliability of solar power systems.
Types of Solar Panel Degradation: Initial and Long-Term Degradation
Solar panel degradation can be classified into two types: initial degradation and long-term degradation.
Initial Degradation: This typically occurs within the first few months after the solar panels are installed, and the degradation rate is relatively high. Initial degradation mainly results from unstable factors during manufacturing and the initial operating phase after installation. Generally, the initial degradation rate ranges from 1% to 3%.
For example, if a solar panel has an initial power output of 300 watts, and the degradation rate is 2%, its output could drop to 294 watts.
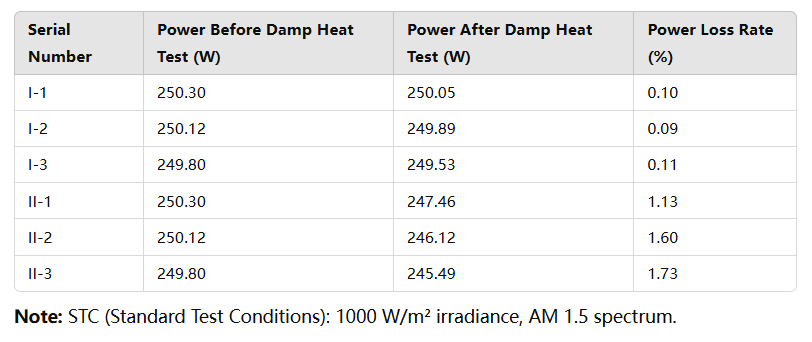
Long-Term Degradation: After a few years of use, the degradation rate slows down. Long-term degradation is influenced by various factors, including the material quality, manufacturing process, environmental conditions (such as temperature, humidity, and sunlight intensity), and daily maintenance.
Under normal operating conditions, the average annual long-term degradation rate for crystalline silicon solar panels typically ranges from 0.5% to 0.8%. For instance, if a solar panel has an initial power output of 300 watts and a long-term degradation rate of 0.7%, after 10 years, its power output would be approximately 207 watts.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Degradation
Environmental factors play a significant role in solar panel degradation. Some common factors include:
- High Temperature: High temperatures accelerate solar panel degradation. If solar panels operate in environments that exceed the standard working temperature (usually 25°C), the degradation rate may increase by 0.03% to 0.05% per degree Celsius. For example, if the solar panel operates in an environment of 50°C (a 25°C increase), the degradation rate could rise to approximately 1.45% per year.
- Humidity: In high-humidity environments, moisture may penetrate the solar panel, leading to the aging of encapsulation materials and the corrosion of cells, which can accelerate degradation. In environments with humidity above 80%, the degradation rate may increase by 0.2% to 0.3% annually.
Dust and Dirt: Accumulation of dust and dirt can reduce the amount of sunlight the solar panels receive, leading to a decrease in power output. If the solar panel surface is 20% covered with dust, the output could drop by 30% to 40%.

How to Delay Solar Panel Degradation
To reduce solar panel degradation, the following measures can be taken:
- Regular Cleaning: Ensure that the solar panel surface is free from dust and dirt to maintain its light absorption efficiency.
- Optimize Installation Location: Avoid installing solar panels in high-temperature or high-humidity environments. Choose an appropriate location to minimize environmental factors that contribute to degradation.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Periodically check the condition of the solar panels and address any potential degradation issues promptly to maintain the system’s high efficiency.
Conclusion
Solar panel degradation is a complex process influenced by a variety of factors. When designing and installing a solar power system, it is essential to consider these factors thoroughly. Selecting high-quality, reliable solar panels and ensuring regular maintenance and cleaning can slow down the degradation rate, extend the lifespan of the solar panels, and maintain high power output efficiency.
Since 2008, Maysun Solar has been dedicated to producing high-quality photovoltaic modules that contribute to combating climate change. Our advanced technology in IBC, HJT, TOPCon panels, and balcony solar stations ensures exceptional performance and reliability, capable of withstanding harsh weather conditions for long-term operation. We have established offices and warehouses in multiple countries and built lasting partnerships with top installers to provide comprehensive support. For the latest quotes or any inquiries related to photovoltaics, feel free to reach out to us—we’re here to help!

A Detailed Introduction to Solar Panel Degradation
The performance of solar panels gradually declines over time, a phenomenon known as degradation. Understanding solar panel degradation is critical to assessing the long-term benefits and reliability of a solar energy system.

What’s New in Solar Energy (January 2025)
Discover the latest in solar energy updates for January 2025. Highlights include Germany’s new ZEREZ registration requirements for PV systems, Italy’s enhanced incentives for EU-made solar modules, Hungary’s solar measures for apartment buildings, and insights on the European solar market growth slowdown.

Russia-Ukraine Gas Cut: Who’s Taking the Hit?
As Russia halts gas supplies, Europe’s energy prices are soaring. Discover how solar energy can help mitigate rising electricity costs, enhance energy security, and support sustainability goals.

Solar and Nuclear Energy: 6 Key Questions You Need to Know
Discover the future of clean energy with a comparison of solar and nuclear power. Explore the investment, efficiency, environmental impacts, and safety risks of both energy sources. Learn why a balanced energy mix of solar and nuclear is crucial for a sustainable, low-carbon future.

2025 Trends in the Photovoltaic Industry Development
This article analyzes key trends and growth drivers in the photovoltaic industry by 2025, highlighting opportunities amid the global energy transition.

Energy at Christmas – How Much Electricity is Used During Christmas?
Explore the major sources of energy consumption during Christmas, from festive lighting to fireplaces. Learn practical tips to reduce electricity use and celebrate the holidays sustainably.


