Table of Contents
In recent years, flexible solar panels have gained significant attention in the solar industry for their lightweight and convenient features, making them ideal for portable devices and wearable applications. However, for applications that require long-term efficiency and high durability, rigid double-glass solar panels with bifacial power generation technology remain the backbone of solar energy production.
So, which technology will dominate the future solar market? Today, we’ll delve into the unique advantages of these two technologies and their optimal use cases.
What Are Flexible Solar Panels?
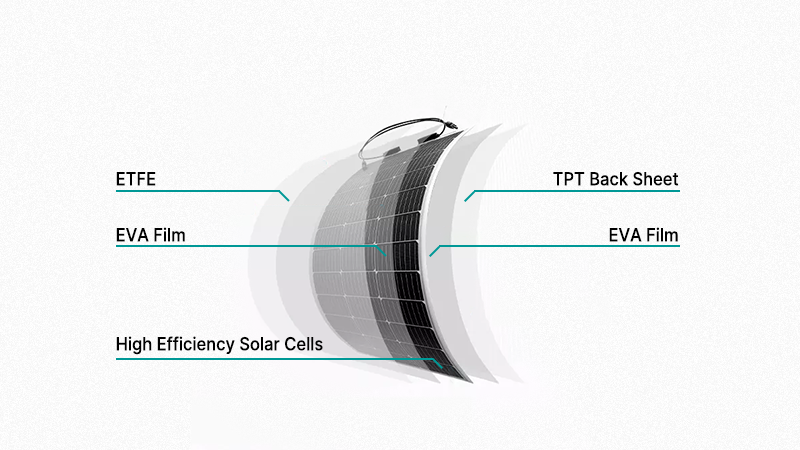
Flexible solar panels operate on the same principles as traditional rigid solar panels, often made with the same types of photovoltaic silicon cells. However, flexible solar panels are over 300 times thinner than traditional ones, making them lightweight and much more versatile.
Unlike conventional panels, flexible solar panels lack a protective glass or metal cover. Instead, they are coated with a polymer called ETFE, which allows easy bending. This design enables the panels to be as thin and lightweight as possible while maintaining flexibility.
The biggest advantage of flexible solar panels is their adaptability, but this comes at a cost. The same design that enhances flexibility also compromises their efficiency and durability compared to traditional solar panels.
Currently, five major types of flexible solar panel technologies dominate the market, with theoretical efficiency rates as follows:
- Organic Photovoltaic Cells:~8% conversion efficiency
- Amorphous Silicon Solar Cells:10%-12% conversion efficiency
- CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Selenide) Solar Cells:14%-18% conversion efficiency
- Cadmium Telluride Solar Cells:16%-18% conversion efficiency
- Gallium Arsenide Solar Cells:28%-31% conversion efficiency
In the following sections, we’ll explore how these technologies compare with rigid double-glass solar panels to help you determine the best fit for your specific requirements.
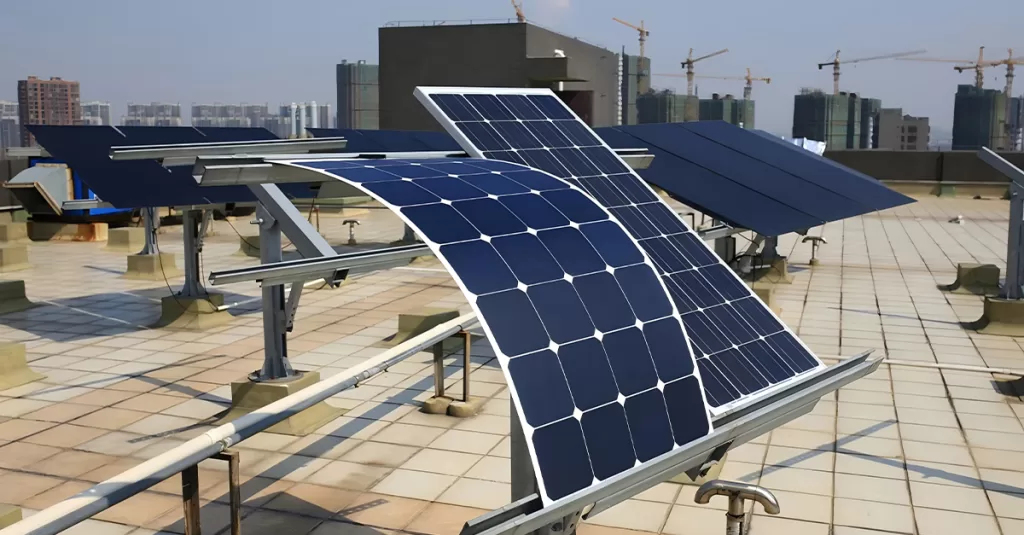
What Are Rigid Double-Glass Solar Panels?
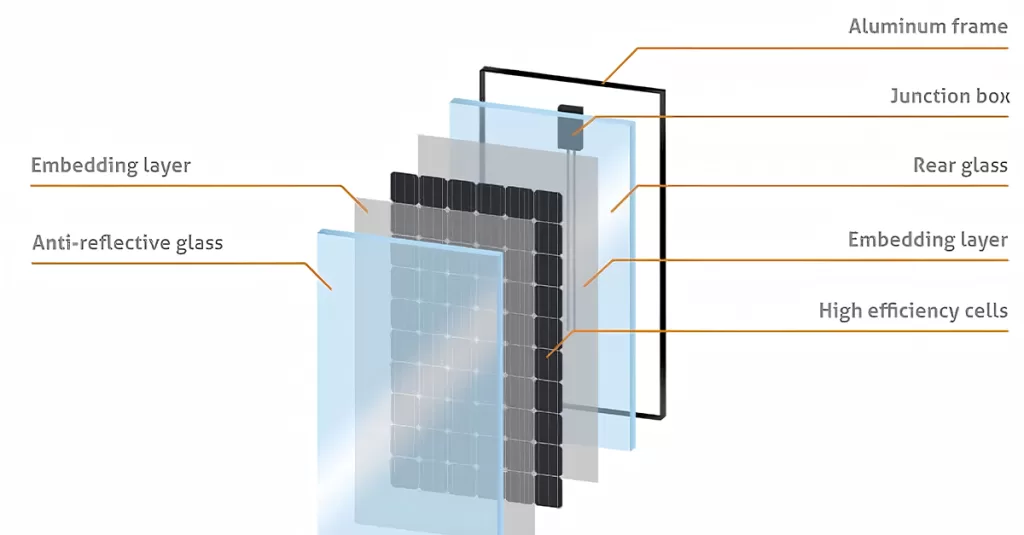
Rigid solar panels are the traditional flat panels most people associate with solar energy. These panels consist of photovoltaic cells made from silicon wafers arranged together and encased in tempered glass and aluminum frames. As an advanced iteration of rigid solar panels, double-glass modules were developed to enhance efficiency, durability, and versatility, making them a standout choice in the solar market.
This design leverages the stability and protective properties of a glass enclosure to deliver higher output power. However, the rigid structure can pose challenges for installations on certain rooftops or unconventional structures.
Which Solar Panel Is Right for Me?
Imagine a family camping outdoors: a lightweight, flexible solar panel can be laid directly on a tent to charge devices. In contrast, a double-glass panel excels in large-scale ground-mounted projects, offering stable performance for over 25 years while withstanding extreme weather conditions. These seemingly distinct scenarios highlight the unique strengths of flexible and rigid solar panels.
Each type of solar panel has its own advantages and ideal applications. Understanding their characteristics can help users make decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Flexible Solar Panels:
The lightweight and flexibility of these panels make them ideal for unconventional installations and easier maintenance. However, their thin materials may require more frequent inspections and upkeep over time.
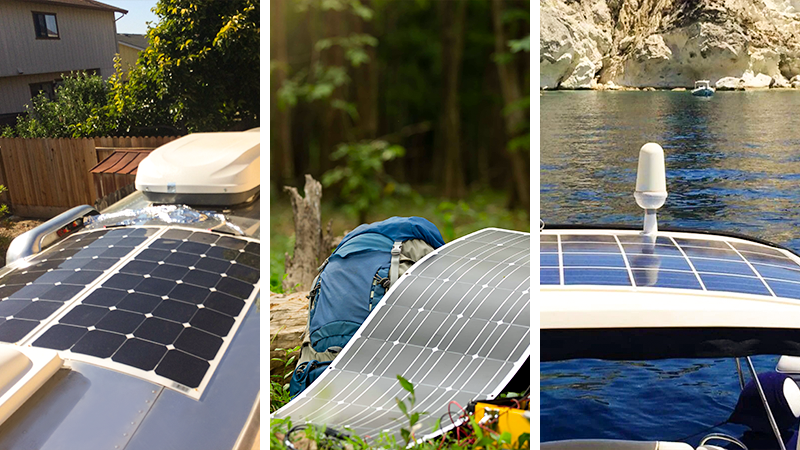
If the installation involves irregular or curved surfaces, or if users seek portable, lightweight solutions, flexible solar panels are an ideal choice. They are especially suited for small rooftops, limited installation spaces, or mobile applications such as RVs, camping, and yachts.

Rigid Solar Panels (Double-Glass):
The glass layers of double-glass panels effectively protect the cells, reducing damage from external factors and ensuring longer maintenance intervals and stable long-term performance. For users prioritizing stability and low maintenance costs, rigid solar panels are the optimal choice.
These panels are particularly suited for long-term solar systems, such as rooftop installations, large-scale power plants, or agrivoltaic projects. Their durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions, such as wind, sand, and high temperatures, make them an excellent solution.

By considering different installation methods, environmental conditions, and usage expectations, users can choose the most suitable type of solar panel to maximize efficiency and economic benefits.
Next, we’ll dive deeper into the specific parameters to analyze the pros and cons of both technologies.
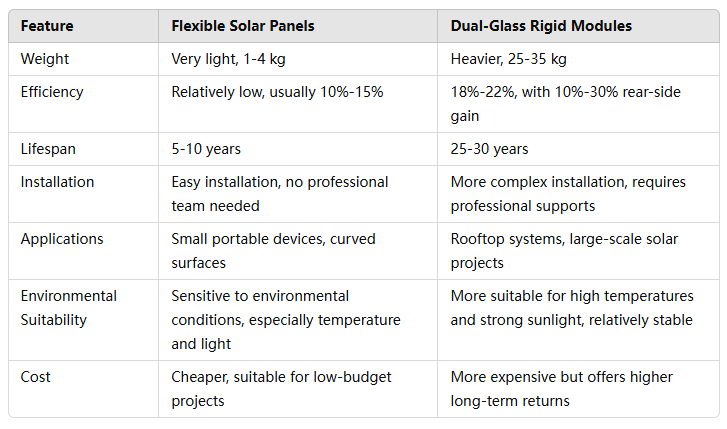
Performance of Flexible and Dual-Glass Solar Panels in Different Environments
1. High-Temperature Environments
High-temperature environments are common in tropical or summer heat-prone regions, such as Middle Eastern deserts or Mediterranean coastal areas. In such conditions, the temperature coefficient of photovoltaic (PV) modules significantly affects their efficiency.
Environmental Characteristics:
- Ambient temperatures often exceed 40°C, with module backsheet temperatures reaching 70°C or higher.
- Frequent thermal cycles can lead to material expansion and contraction.
Flexible Solar Panels:
- Flexible panels typically have a temperature coefficient of -0.40%/°C to -0.45%/°C. This means that for every 1°C increase in temperature, the efficiency drops by approximately 0.4% to 0.45%.
- Under high temperatures, the aging of polymer backsheets and other flexible materials accelerates, leading to a power degradation of 10%-15% within 10 years of operation.
- Flexible panels often exhibit poor thermal management under prolonged high temperatures, resulting in more significant efficiency losses.
Dual-Glass Solar Panels:
- Dual-glass panels feature a dual-layer glass structure with excellent heat dissipation and a lower temperature coefficient (typically -0.30%/°C to -0.35%), ensuring more stable power output in high-temperature conditions.
- The robust glass encapsulation minimizes the risk of microcracks caused by high temperatures, making dual-glass panels ideal for long-term installation in hot climates.
2. High-Humidity Environments
Tropical rainforests, coastal regions, or areas with monsoonal climates present challenges such as high humidity and salt spray, which can significantly affect PV modules.
Environmental Characteristics:
- Prolonged high humidity (humidity >90%) leads to vapor infiltration.
- Coastal regions have high salt spray levels, which can corrode backsheets and cells.
Flexible Solar Panels:
- Flexible panels, often made with polymer backsheets and thin-film materials, are more susceptible to water vapor and salt spray. In high-humidity environments, the durability of polymer backsheets decreases, potentially causing encapsulation failure.
- Tests show that in humid environments, flexible panels experience a power degradation rate of 1%-2% per year, which can be higher in coastal regions.
- Environmental factors significantly impact the performance of flexible panels, especially in high-humidity and salt-spray conditions.
Dual-Glass Solar Panels:
- Dual-glass panels, with glass encapsulation, are highly resistant to water vapor penetration. Their strong corrosion resistance makes them well-suited for high-humidity and salt-spray environments.
- By reducing potential-induced degradation (PID), dual-glass panels maintain long-term stability. International test data indicate a power degradation rate below 0.5%-1% per year in humid environments, making them ideal for coastal and humid regions.
3. Wind-Sand and Desert Environments
In desert regions, wind-blown sand impacts the mechanical performance and light transmission of PV modules. Such environments also feature high radiation and large temperature differences between day and night.
Environmental Characteristics:
- Windblown sand erodes module surfaces, reducing light transmittance.
- Large temperature variations may cause material fatigue and cracking.
Flexible Solar Panels:
- Flexible panel surfaces are more prone to erosion from sand due to their softer polymer materials. Prolonged exposure to wind-sand abrasion can decrease transparency, reducing light transmission.
- Tests in sandy regions show that flexible panel transparency can decrease by 5%-10%, leading to efficiency losses.
- In harsh desert conditions, flexible panels exhibit poor long-term stability, with power degradation rates reaching 15%-20%.
Dual-Glass Solar Panels:
- The tempered glass surface of dual-glass panels is more resistant to wind-sand erosion. Their scratch-resistant and wear-resistant properties ensure better light transmittance over time.
- Studies show that dual-glass panels experience minimal efficiency losses in desert environments, with transparency degradation below 3% and annual power degradation rates generally between 1%-2%.
4. High-Altitude Environments
High-altitude areas, such as the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau or the Alps, present challenges including intense ultraviolet (UV) radiation and large temperature fluctuations.
Environmental Characteristics:
- Intense UV radiation accelerates material aging.
- Large temperature variations between day and night lead to frequent thermal expansion and contraction.
Flexible Solar Panels:
- UV radiation at high altitudes is typically 1.5 times stronger than at lower altitudes. Flexible panels, with thinner materials, are more prone to UV-induced degradation of backsheets and cells.
- Tests show that in high-altitude environments, flexible panels exhibit annual degradation rates of 2%-3%, compared to 1%-1.5% in lower altitudes.
- Prolonged UV exposure weakens polymer materials, leading to a rapid decline in efficiency.
Dual-Glass Solar Panels:
- Dual-glass panels have strong UV resistance, minimizing material degradation caused by UV exposure. This makes them well-suited for high-altitude regions.
- Verified data shows that dual-glass panels maintain annual degradation rates below 1.5% in high-altitude environments, providing greater stability under intense UV radiation.

Comparison of the Installation Convenience and Maintenance Requirements of Flexible and Bifacial Solar Panels
Installation Convenience Comparison
Flexible Solar Panels:
- Lightweight:The biggest feature of flexible solar panels is their lightweight and flexibility, allowing them to adapt to various non-flat installation surfaces, such as roofs, car roofs, tents, etc. This makes the installation process simpler and suitable for areas with limited space or irregular surface shapes.
- Simplified Installation Process:Flexible solar panels typically do not require complex frame supports and can be directly glued or fixed onto surfaces, reducing installation time and costs. This installation method is especially suitable for temporary installations or mobile photovoltaic systems, such as RVs and boats.
- Tool Requirements:Due to the lightweight and flexibility of the panels, the tool requirements during installation are minimal. In most cases, basic tools such as adhesive, brackets, or simple supporting materials are sufficient.
Bifacial Solar Panels:
- Installation Difficulty: Bifacial solar panels, due to their double-glass encapsulation, are generally heavier and sturdier than traditional single-glass panels. Installation requires more robust support structures and greater precision. For large-scale photovoltaic installations, the installation process may be more complex and require specialized installation personnel.
- Installation Method:Bifacial solar panels usually require traditional frame systems for support, and these frames have strict size and installation requirements, making the installation process more tool-intensive and time-consuming.
Maintenance Requirements
Flexible Solar Panels:
- Durability:Although flexible solar panels offer greater installation flexibility, their materials (such as polymers or thin films) are generally softer and less durable than traditional glass panels. Exposure to harsh weather conditions (like strong winds, dust, and UV radiation) may cause surface damage or aging over time.
- Maintenance Difficulty:Since the panel material is thinner and more susceptible to physical impacts, extra caution is needed during maintenance to avoid scratches or damage. When cleaning or repairing, it is important to avoid using overly hard tools or harsh cleaning agents to minimize damage to the surface.
- Regular Inspections:Flexible solar panels are more likely to experience performance degradation in humid environments, so it is recommended to regularly inspect the connections of the wiring and cells, especially when used in high-humidity or high-temperature areas.
Bifacial Solar Panels:
- Durability:Due to the double-glass encapsulation, bifacial solar panels can effectively reduce damage from external factors (such as rain, wind, and sand) and have higher UV resistance, making them less prone to aging. This results in longer maintenance intervals.
- Maintenance Difficulty: The surface of bifacial solar panels is more durable, and cleaning and maintenance are relatively easier. Even under extreme weather conditions, cleaning the glass surface is simple and can be done with standard cleaning tools.
- Regular Inspections: Although bifacial solar panels have lower maintenance needs, it is still necessary to regularly check the backsheet and connections, particularly in harsh climates, to ensure there are no microcracks or poor contact issues. Regular cleaning of the glass surface helps maintain maximum light absorption.
Choosing the Right Investment as a Photovoltaic Industry Professional
As a photovoltaic industry professional, when selecting solar modules for investment, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the project’s characteristics and customer needs. Below are several key considerations:
Project Scale and Type:
- Small Portable Projects: Flexible solar panels are suitable, such as for outdoor travel, mobile power sources, or photovoltaic devices on RVs and boats.
- Small to Medium Roof-top Photovoltaic Projects: Rigid panels, especially bifacial ones, are ideal for installation on roofs of factories, warehouses, or commercial buildings due to their high efficiency and durability.
- Large Ground-mounted Stations: Rigid panels are preferable due to their high efficiency and bifacial generation capabilities, meeting high power generation requirements and optimizing land use.
Comprehensive Indicators:
- Cost and Return:Flexible solar panels are significantly less expensive than rigid panels, but rigid panels provide a much higher long-term return on investment. Bifacial panels, due to their long lifespan and lower levelized cost of energy (LCOE), are the preferred choice for clients seeking long-term returns.
- Aesthetic Requirements:All-black bifacial panels are more popular in the European high-end residential market, catering to customers’ dual demands for aesthetics and performance.
- Durability Needs:For extreme climates or harsh environments (e.g., high temperature, humidity, and sandy areas), bifacial panels offer better weather resistance and stability.
- Installation and Maintenance Convenience:Flexible solar panels are lightweight, making them suitable for non-professional installation or complex surfaces, thus reducing initial investment costs. Rigid solar panels, although requiring higher initial installation, have lower long-term maintenance costs and are more suitable for long-term projects.

Policy Support:
Large-scale photovoltaic stations and commercial photovoltaic projects can receive more policy subsidies and financial support. As an industry professional, selecting more advanced and stable bifacial panels can better respond to future market demands and policy directions.
FAQ
Can flexible solar panels be used on roofs?
The application of flexible solar panels on roofs is limited for the following reasons:
- Load-bearing and Installation Stability: Flexible solar panels are designed to be lightweight and adaptable to flat or slightly curved surfaces. Most traditional roofs, especially sloped ones, require strong fixation and professional support. Flexible solar panels may not provide adequate stability in these environments and are more susceptible to wind and external impacts.
- Long-term Durability: Flexible solar panels typically use lighter materials such as film or polymer, which, while durable under specific conditions, have lower weather resistance, UV protection, and water penetration resistance compared to traditional rigid panels. Therefore, their stability and safety are compromised in long-term outdoor environments.
- Efficiency and Power Output: Flexible solar panels generally have lower conversion efficiency (typically 15%-20%) than rigid panels. Therefore, in areas with limited roof space, flexible panels may not meet the energy output requirements.
However, in certain roof scenarios, such as those with special shapes, flexible solar panels may still serve as a temporary solution due to their lightweight and easy installation features. For most long-term rooftop projects requiring high efficiency and stability, rigid solar panels (such as double-glass modules) are the preferred choice because they provide higher power output and greater durability.
Do flexible solar panels overheat?
Although flexible solar panels are designed to be lightweight and adaptable, they do face overheating issues in high-temperature environments, which can affect their efficiency and lifespan. If flexible solar panels are planned for use in warm or hot regions, it is recommended to choose products with better heat management capabilities and ensure that the installation environment is well-ventilated. Rigid solar panels, especially double-glass modules, typically offer better heat dissipation performance and stability for long-term, reliable energy production.
Which is better, single-glass or double-glass solar panels?
Overall, double-glass solar panels outperform single-glass panels in terms of efficiency, durability, and long-term returns, making them ideal for large-scale investments and long-term projects. If the budget and project scale allow, double-glass modules are a more prudent choice. However, for small or short-term projects, single-glass panels, with their lower cost and sufficient power output, are still a good option. For more information, please read our blog post, A Guide to Selecting Solar Panels for Various Environments.
How do double-glass solar panels perform in cloudy or low-light environments?
A significant advantage of double-glass solar panels is that they can capture reflected light from the rear side. For example, on smooth rooftops or white walls, reflected light increases the amount of sunlight reaching the back side of the panels, improving energy conversion efficiency. In cloudy or low-light conditions, double-glass panels can still benefit from this reflected light, resulting in better performance compared to single-glass panels.
Do double-glass solar panels have high maintenance costs?
Double-glass solar panels have lower maintenance costs. Their glass surface is more resistant to corrosion and scratching, and their encapsulation design is more durable than single-glass panels, reducing the frequency of common repairs and replacements. Additionally, their superior UV resistance helps prevent material aging, leading to lower overall maintenance costs. They also perform better in humid and sandy environments, reducing performance degradation due to environmental factors.
What double-glass products does MAYSUN offer?
- Twisun Pro, 420-435W N-TOPCon
- 560-580W N-TOPCon
- HJT Series Solar Modules
Conclusion:
Flexible and double-glass solar panels represent two different directions in the solar industry—one focuses on flexibility and adaptability, while the other emphasizes high efficiency and stability. On the path to energy transformation, each technology has its unique value. By understanding the characteristics of both, you can find the best solution for your project’s needs. This is why, even though we don’t produce flexible modules, we are still eager to share insights about this technology.
Contact us for the best products and services, whether your needs are for small rooftop systems or large-scale long-term energy projects. Together, we can contribute to a greener future!

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!

What’s New in Solar Energy (March 2025)
March’s solar news highlights include rooftop solar meeting two-thirds of global demand, China’s market reforms potentially boosting solar demand and module prices, France revising solar targets in PPE 3, and challenges in Europe with declining capture rates and price volatility.

Zero-Investment Solar Projects: How to Earn Passive Income Through Rooftop Leasing?
Monetize your idle rooftop and earn stable annual rent! With the photovoltaic rooftop leasing model, businesses can generate long-term revenue without investment, reduce operating costs, and achieve a green transition.

How to Optimize Photovoltaic Power Plant Operations with AI and Big Data
This article explores three methods of using AI to enhance power generation revenue and reduce operation and maintenance costs in intelligent photovoltaic operations.

Solar Module Costs May Rise by 10% in 2026! In-Depth Analysis of CBAM’s Impact on the Industry
Table of Contents Introduction to CBAM 1. Why Did the EU Introduce CBAM? As the challenges posed by global climate change intensify, governments worldwide are accelerating their efforts to achieve carbon neutrality. The European Union, a leader in global carbon reduction initiatives, introduced



