Table of Contents
Introduction
In the field of solar photovoltaics, the efficiency and stability of modules are crucial factors determining the amount of electricity generated. With technological advancements, the design of photovoltaic modules has been continuously optimized. 1/3 cut and half-cut solar panels, due to their different current and voltage characteristics, exhibit significant performance differences in high-temperature environments. This article will explore why 1/3 cut solar panels generate more power than half-cut panels in such conditions.
Photovoltaic modules convert solar energy into electrical energy through the photoelectric effect. In this process, the current in the module affects its operating temperature. The higher the current, the greater the resistance losses, leading to a more significant increase in the module’s operating temperature. Additionally, the operating temperature of the module affects its power output losses. Generally, the higher the operating temperature of a photovoltaic module, the greater its power losses. Therefore, the current of the module has a significant impact on its power output, with higher current leading to greater power losses.
Performance Comparison of 1/3 Cut and Half-Cut Solar Panels in High-Temperature Environments
1. Current and Voltage Characteristics:
- 1/3 Cut Solar Panels: These panels have lower current and higher voltage. For instance, Twisun Pro (TOPCon) 1/3 cut panel with a power output of 430W has a current of 9.96A and a voltage of 43.2V.
- Half-Cut Solar Panels: These panels have higher current and lower voltage. For example, the other TOPCon half-cut panels on the market with a power output of 430W have a current of 13.49A and a voltage of 31.88V.
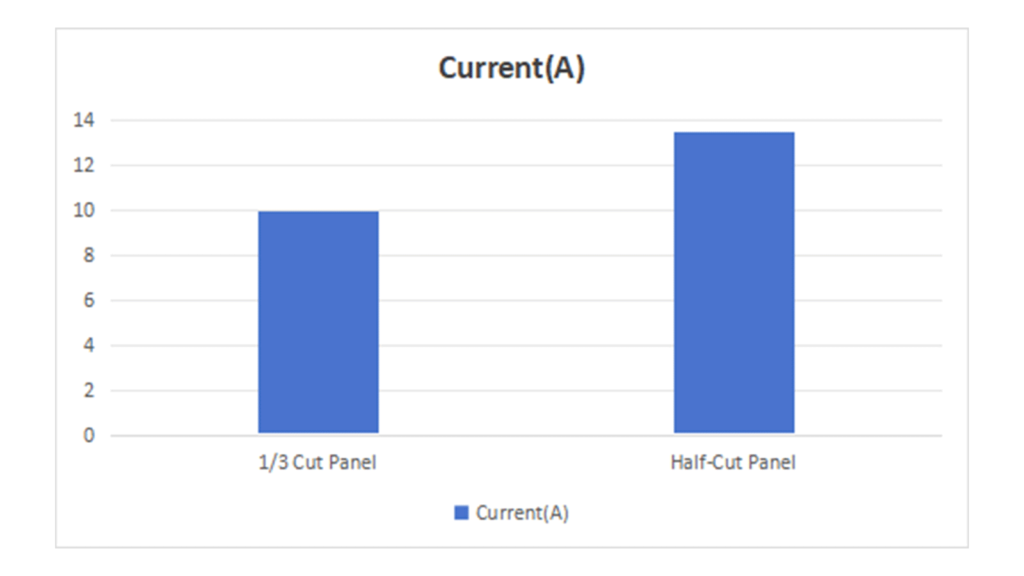
2. Resistance Losses:
Higher current results in greater heat loss due to resistance. Resistance loss Pres can be calculated using the formula Pres=I2×R
Assuming the resistance R is the same for both types of panels, the current in half-cut panels (13.49A) is higher than that in 1/3 cut panels (9.96A), leading to greater resistance loss.
Resistance Loss Calculation:
- 1/3 Cut Panel:
Current I=9.96A
Resistance Loss Pres=I2×R=9.962×R=99.2R
- Half-Cut Panel:
Current I=13.49A
Resistance Loss Pres=I2×R=13.492×R=181.98R
The resistance loss in half-cut panels is approximately 1.83 times that of 1/3 cut panels.
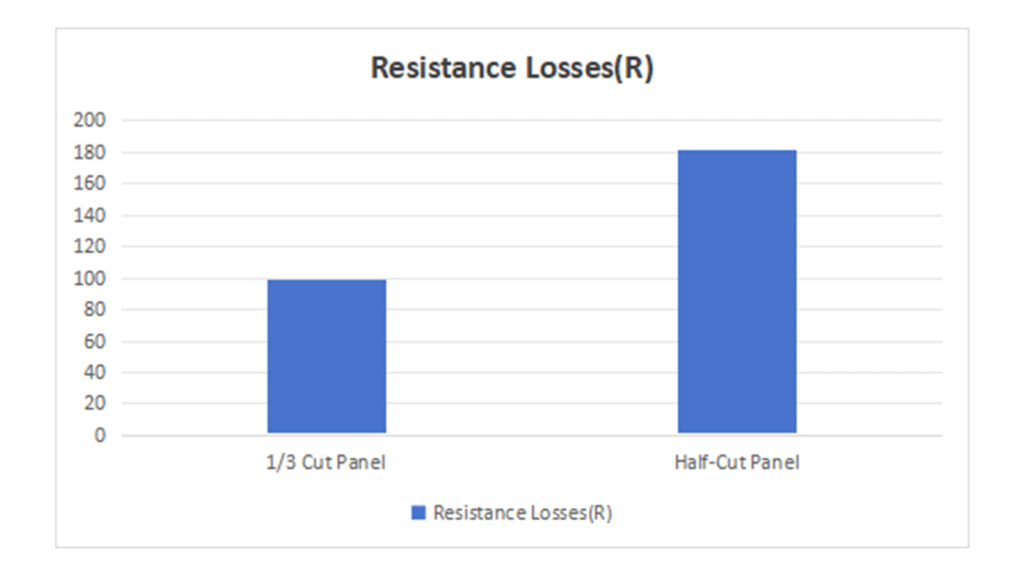
3.Temperature Rise
The temperature rise is proportional to resistance loss. If other conditions are assumed to be the same, the temperature rise in half-cut panels will be 1.83 times that of 1/3 cut panels.
Due to the higher current in half-cut panels, the resistance loss is greater, resulting in a more significant temperature rise.
Assuming an ambient temperature of 30°C and an operating temperature of 60°C for 1/3 cut panels:
- 1/3 Cut Panel:
Temperature rise =60°C−30°C=30°C
- Half-Cut Panel:
Temperature rise =30°C×1.83=54.9°C
Operating temperature =30°C+54.9°C=84.9°C
Therefore, in a 30°C environment, the operating temperature of a half-cut panel would be approximately 84.9°C, which is 24.9°C higher than that of a 1/3 cut panel.
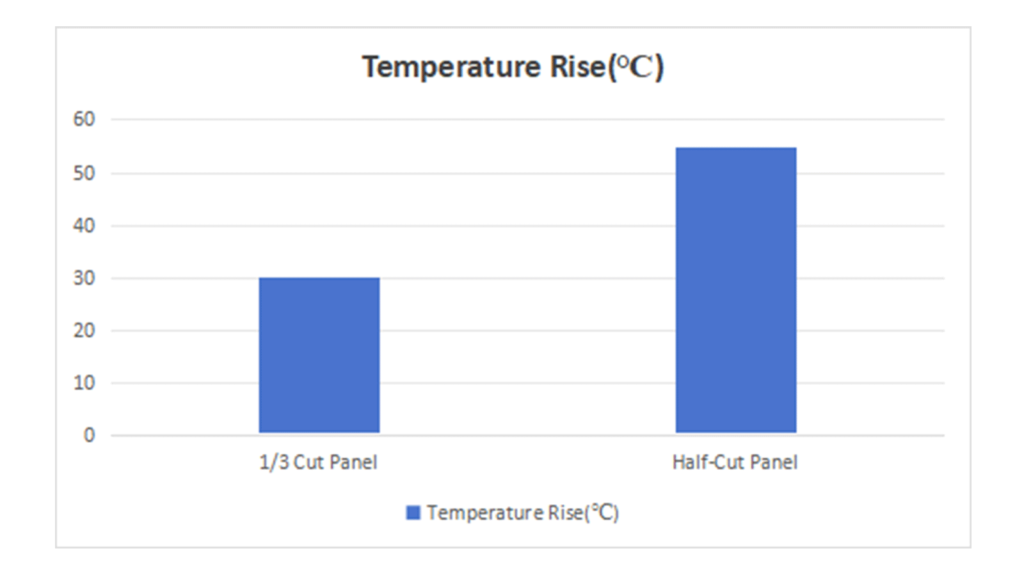
4.Power Loss
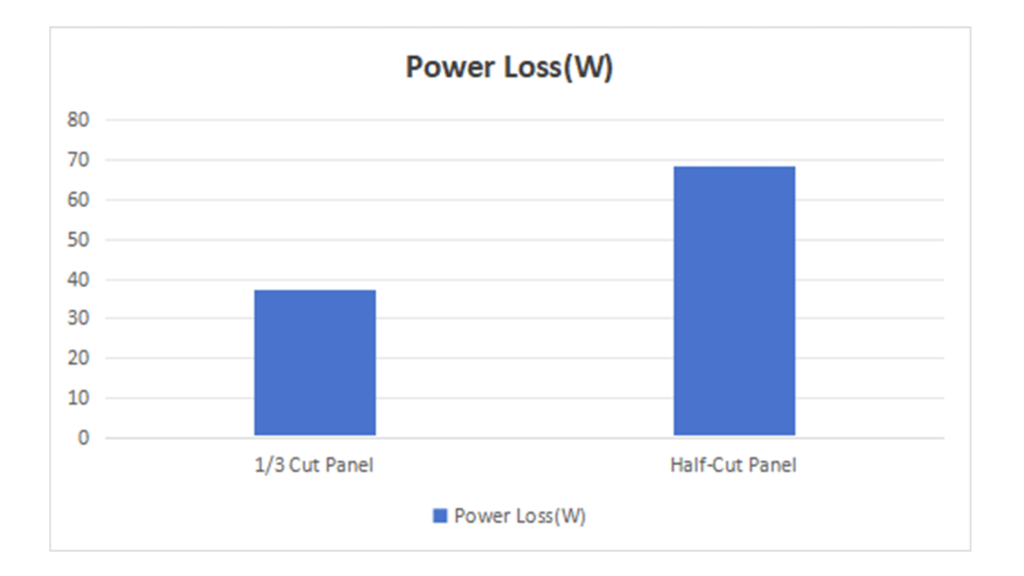
Assuming a power temperature coefficient of -0.29%/°C for TOPCon solar panels:
Power Loss Percentage:
- 1/3 Cut Panel:
Power loss percentage =−0.29%/°C×30°C=−8.7%
- Half-Cut Panel:
Power loss percentage =−0.29%/°C×54.9°C=−15.92%
With a nominal power of 430W:
- 1/3 Cut Panel:
Power loss =430W×(−8.7%)=−37.41W
- Half-Cut Panel:
Power loss =430W×(−15.92%)=−68.456W
The half-cut panel loses about 31.046W more power than the 1/3 cut panel.
Percentage Power Loss Difference:
- Percentage difference =(456W−37.41W)/430W×100%=7.22%
Due to the higher current (13.49A) in half-cut panels, which leads to a higher temperature rise (54.9°C), they experience greater power loss. According to the calculations, half-cut solar panels lose approximately 31.046W more power than 1/3 cut solar panels, which equates to an additional 7.22% power loss.
5.Annual Power Generation Loss
Assuming a 10kW TOPCon photovoltaic system with an average sunlight duration of 4 hours/day, system efficiency of 85%, and 365 days/year:
The additional power loss for half-cut panels compared to 1/3 cut panels is 31.046 watts.
Annual Power Generation Loss Calculation:
Annual power generation loss =31.046W×4 hours/day×365 days×0.001 kWh/W=45.33 kWh
The annual loss of approximately 45.33 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity generation is equivalent to the energy consumed by a typical household using a microwave oven daily for an entire year.

Conclusion
In conclusion, 1/3 cut solar panels demonstrate significant advantages over half-cut solar panels in high-temperature environments. This is primarily due to their lower current, which results in reduced resistance loss and temperature rise. Conversely, half-cut panels, with their higher current, experience greater resistance loss and temperature rise, thereby increasing power losses and ultimately impacting overall electricity generation efficiency. In practical applications, especially in high-temperature conditions, opting for 1/3 cut solar panels can significantly enhance the overall electricity generation and stability of the system. Therefore, for photovoltaic systems operating in high-temperature conditions, 1/3 cut solar panels are undoubtedly the more ideal choice.
It is worth noting that Maysun Solar’s Twisun Pro is an outstanding performer among 1/3 cut panels. Twisun Pro features excellent characteristics with a low current of 10A, showcasing exceptional electricity generation performance even in high-temperature environments, while minimizing power thermal losses to the maximum extent. Additionally, the low current helps mitigate potential risks such as fire hazards due to excessive temperature rise. Choosing Twisun Pro ensures that your photovoltaic system operates efficiently and reliably under various climatic conditions. This choice not only enhances overall electricity generation efficiency but also provides longer-term reliability and safety for your energy system.


Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!

What’s New in Solar Energy (March 2025)
March’s solar news highlights include rooftop solar meeting two-thirds of global demand, China’s market reforms potentially boosting solar demand and module prices, France revising solar targets in PPE 3, and challenges in Europe with declining capture rates and price volatility.

Zero-Investment Solar Projects: How to Earn Passive Income Through Rooftop Leasing?
Monetize your idle rooftop and earn stable annual rent! With the photovoltaic rooftop leasing model, businesses can generate long-term revenue without investment, reduce operating costs, and achieve a green transition.

How to Optimize Photovoltaic Power Plant Operations with AI and Big Data
This article explores three methods of using AI to enhance power generation revenue and reduce operation and maintenance costs in intelligent photovoltaic operations.

Solar Module Costs May Rise by 10% in 2026! In-Depth Analysis of CBAM’s Impact on the Industry
Table of Contents Introduction to CBAM 1. Why Did the EU Introduce CBAM? As the challenges posed by global climate change intensify, governments worldwide are accelerating their efforts to achieve carbon neutrality. The European Union, a leader in global carbon reduction initiatives, introduced



