Table of Contents
Freight Expenses Approach Pre-Pandemic Levels, Impacting Solar Module Costs
Freight container shipping rates have surged to their highest levels since 2022, as reported by Xeneta, a leading Norwegian ocean and freight rate benchmarking platform.
Xeneta revealed that by the end of May, the market average spot rates from the Far East to the US West Coast were projected to soar to $5,170 per forty-foot equivalent unit (FEU) by June 1st. This marks a staggering 57% increase from May and the highest point in 640 days, surpassing the peak seen during the Red Sea crisis earlier this year. Spot rates are anticipated to peak at $6,250/FEU on the Far East to US West Coast route in June, closely approaching the Red Sea crisis peak ($6,260).
Similarly, on the Far East to North Europe trade route, spot rates are expected to surpass the Red Sea crisis peak, reaching $5,280/FEU, compared to $4,839/FEU on Jan. 16. This represents the highest rate on this route in 596 days and reflects a 63% increase since April 29th.
Xeneta also highlighted a similar trend on the Far East to Mediterranean trade route, where spot rates are projected to exceed the Red Sea crisis peak of $5,985/FEU, reaching $6,175/FEU. This signifies a 46% increase from May and the highest rates recorded on this route in 610 days.
Given that freight costs typically account for around 4% of a solar panel’s total costs, the surge in spot rates is expected to impact PV module prices.
Xeneta attributed the market upheaval to ongoing conflicts in the Red Sea, port congestion, and shippers’ decisions to accelerate imports ahead of the third quarter, traditionally the peak season. Despite the recent surge in spot rates, Peter Sand, Xeneta’s chief analyst, noted a slightly slower pace of growth compared to May, suggesting a potential easing in the situation.
However, Sand cautioned that shippers are already experiencing cargo delays, even for containers under recently signed long-term contracts. He emphasized that carriers prioritize shipments from those paying higher rates, leaving cargo from lower-rate contracts vulnerable to being left at ports, a scenario reminiscent of the challenges faced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Sand further explained that freight forwarders are grappling with additional surcharges and are compelled to opt for premium services to secure ship space, inevitably passing these costs on to their shipper customers. He warned that carriers will continue to push for higher freight rates, potentially exacerbating the situation for shippers in the near term.

Electricity Prices Decline Across Most European Markets
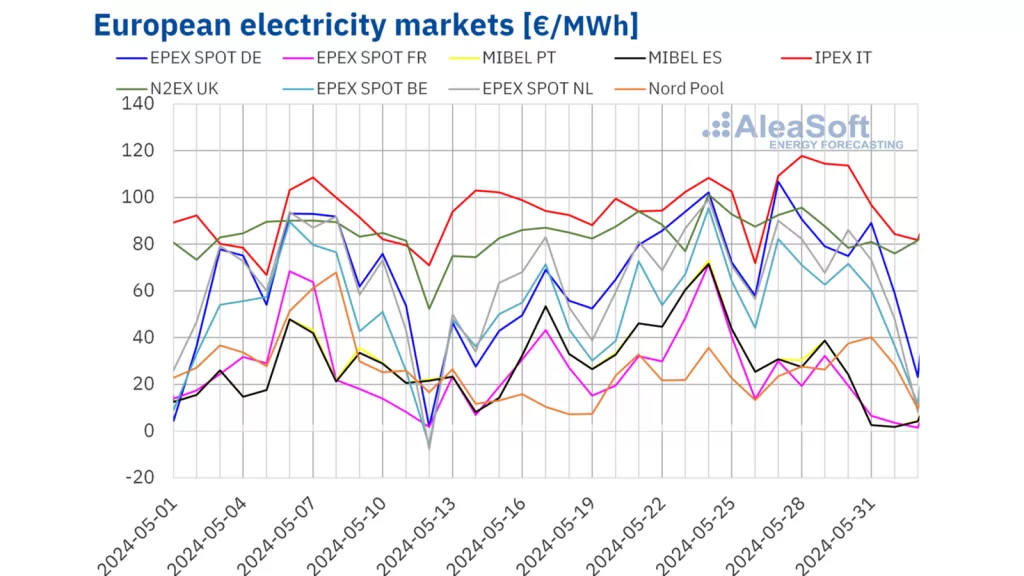
According to analysis from AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, average electricity prices experienced a decline in most major European markets during the final week of May.
Compared to the previous week, prices saw reductions in the Belgian, British, Dutch, German, French, Spanish, and Portuguese markets. The exceptions were the Italian and Nordic markets, where prices rose by 6.7% and 12%, respectively. Notably, France, Spain, and Portugal witnessed the most significant decreases, with declines of 56%, 59%, and 60%, respectively.
During the last week of May, weekly averages surpassed €55 ($59.82)/MWh in all markets except for France, Spain, Portugal, and the Nordic countries. France reported the lowest weekly price, at €16.13/MWh, while Italy had the highest, at €102.60/MWh.
With the exception of the British and Italian markets, all analyzed markets recorded negative electricity prices at least once during the week. The Dutch market notably maintained its streak of recording the lowest price for the sixth consecutive week, hitting -€81.00/MWh on June 2nd between 15:00 and 16:00.
AleaSoft Energy Forecasting attributed the downward trend in electricity prices during the last week of May to higher wind energy production and reduced electricity demand in some markets. Additionally, increased solar production in the Iberian Peninsula contributed to the price decrease in Portugal and Spain.
Looking ahead to the first week of June, AleaSoft forecasts an increase in electricity prices across most markets, driven by anticipated decreases in wind energy production and, in many markets, an uptick in electricity demand.
While solar energy production decreased in most major markets during the final week of May, Germany experienced the largest drop, at 20%. However, Portugal saw a notable week-on-week increase of 9.5% and achieved a new daily photovoltaic energy production record for the second consecutive week, reaching 21 GWh on May 27th.
AleaSoft anticipates a decline in solar production in Spain and Italy during the first week of June, but predicts an increase in Germany.
Austria Introduces “Made in Europe” Bonus for Photovoltaic Systems Over 35 Kilowatts
The Austrian government announced on Thursday the introduction of a “Made in Europe” bonus. “This government decision strengthens the economic location, creates jobs, and supports the energy transition,” stated Vice Chancellor Werner Kogler, Climate Protection Minister Leonore Gewessler, and Labor and Economic Affairs Minister Martin Kocher.
According to the Federal Association Photovoltaic Austria, the increased funding will be available as part of the EAG investment subsidy from autumn. It applies to photovoltaic systems with a capacity of at least 35 kilowatts. The government resolution stipulates that up to 20% more funding will be granted depending on the proportion of European components used. This includes all components, from solar modules to photovoltaic inverters to mounting structures.
While the resilience bonus, which the German government has not yet agreed upon in the recent EEG amendment, has not yet been decided, the Austrian Ministerial Council is expected to approve it next week. The government needs a two-thirds majority in Parliament to introduce the “Made in Europe” bonus.
PV Austria supports the introduction. “This measure is an important signal for both the Austrian industry and the public, indicating that high quality from domestic production is being promoted and the strong price pressure is being mitigated,” said Vera Immitzer, Managing Director of PV Austria.
Given the intensified competitive situation, the Austrian photovoltaic company Fronius confirmed the reduction of 350 jobs this week. Other companies in the sector are also suffering from strong competitive pressure, with components for photovoltaic systems primarily coming from China.
“Those who genuinely want to strengthen European environmental technologies must also set the corresponding investment incentives. Therefore, the ‘Made in Europe’ principle should be a key element of Austria’s funding culture,” explained Vice Chancellor Werner Kogler. Climate Protection Minister Leonore Gewessler agreed, stating: “With this bonus, we support companies in Austria and Europe, thus promoting domestic value creation. This is good for our economy and simultaneously creates future-proof and climate-friendly jobs.”
“Europe must not be naive,” said Labor and Economic Affairs Minister Martin Kocher. Other countries are taking targeted measures to gain a strategic advantage, especially in climate protection technologies. With the ‘Made in Europe’ bonus, we guarantee fair competition and enable Austrian and European manufacturers to compete on a level playing field. We continue to advocate for a fair, rules-based, multilateral world trade order at the EU level,” Kocher concluded.

First Solar Panels Connected in France in 1992 Still Produce 79.5% of Their Initial Power
The first photovoltaic installation connected to the French electrical grid, Phébus 1, was commissioned by the association Hespul in 1992. In 2023, the 10 square meters of panels, with less than 1 kWc of power, were dismantled and tested in a laboratory according to international standards. For this test, the photovoltaic modules were placed in a dark chamber with controlled temperature and subjected to a flash of light with an intensity of 1000 W/m2, and their maximum instantaneous power was measured. This value was then compared to the one measured at the time of their manufacturing. These tests were made possible by the corporate sponsorship of the certification body Certisolis and the company Isowatt, which respectively carried out the panel flashing and dismantling-remounting.
The results show that the modules still produce an average of 79.5% of their initial power after 31 years of operation. This same operation was conducted at the 20-year mark of the installation, with the panels producing 91.7% of their initial power. “This result exceeds the performance commitments of manufacturers, who usually guarantee a power retention of 80% after 25 years,” Hespul noted with satisfaction.
In detail, the performance decline is on average 20.5%, or 0.66% per year over 31 years, and 1.11% per year over the last 11 years. For the same series of modules, two categories were observed: one part with a significant performance decline after 20 years (one-third of the installed modules), averaging 33.9% over 31 years, or 1.09% per year. The other part maintained a performance decline consistent with the 2012 tests, averaging 13% over 31 years, or 0.42% per year. After 31 years, the modules produced 20,366 kWh for 882 Wc, or 745 kWh/kWc/year.
“These results confirm those of various scientific studies on the subject,” continued the association. Tests were also conducted on a more than 40-year-old installation, Tiso, in Switzerland. The observed performance decline of the modules was in line with the guarantees announced, ranging from -0.2% to -0.7% per year. The study showed that the differences in performance decline between modules were mainly due to differences in additives in the encapsulant composition from three different manufacturers.
Another, more recent study was conducted on 1,700 sites in the United States totaling 7.2 GW of power, showing a median degradation of about -0.75% per year. The distribution of results was quite wide, with fairly heterogeneous populations. Finally, a research on 4,300 residential installations in operation in Europe used various data processing methodologies. Depending on the methods, a median loss of -0.36% to -0.67% per year was obtained.

Siemens Installs Photovoltaic Parking and 60 Electric Charging Stations
At its Milan headquarters on Via Ponte Nuovo, Siemens has installed a new photovoltaic system, adding to the existing rooftop photovoltaic systems on two of its corporate buildings. “Together, they produce 930 MWh annually, significantly contributing to the reduction of the Milan headquarters’ carbon footprint across a total area of over 5,500 square meters,” the company stated in a press release.
This new installation is part of Siemens’ journey toward carbon neutrality by 2030 and has led to the reopening of the corporate parking lot, transforming it into a photovoltaic park with a total generation capacity of 456 MWh per year.
Additionally, 60 new VersiCharge electric charging stations have been installed, bringing the total number of electric vehicle charging points to 120, each with a power capacity of 11 kW.
“The expansion of the photovoltaic system and the availability of charging stations demonstrate how digitalization and sustainability are inseparable in the company’s DNA,” Siemens stated.
The installation of these charging stations in the new parking area enhances the existing availability of charging stations at the headquarters, serving both company and guest vehicles. Today, there are nearly 140 charging points throughout Casa Siemens.
“With photovoltaics, we improve our energy autonomy and our services to customers and partners, while the new charging stations help us electrify our entire fleet,” said Floriano Masoero, President and CEO of Siemens Italy.
In terms of the photovoltaic parking area, about a year ago, ENVIarea snc completed a study on the glare hazards for the photovoltaic installation on canopies in the parking lot on Via Werner Von Siemens in Milan, serving Siemens’ employees. The study focused on glare risks for pilots and control tower operators at Linate Airport, nearby building occupants, and public road users.
Lastly, around 12 months ago, Pradella Sistemi publicly announced the installation of its new EBS2k photovoltaic rack at the Siemens Industry site in Milan. This pilot project, initiated thanks to A2A, showcases the potential of photovoltaic glass by GruppoSTG – The Italian Photovoltaic Factory.

Maysun Solar has been specialising in producing high quality photovoltaic modules since 2008. In addition to the Balcony Solar Power Station, Maysun Solar offers wide variety of full black, black frame, silver, and glass-glass solar panels that utilise half-cut, MBB, IBC, and HJT technologies. These panels offer superior performance and stylish designs that seamlessly blend in with any building. Maysun Solar successfully established offices, warehouses, and long-term relationships with excellent installers in numerous countries! Please contact us for the latest module quotations or any PV-related inquiries. We are excited to assist you.
Reference:
Jowett, P. (2024b, June 5). Freight costs edge toward pandemic levels, hitting solar module costs. Pv Magazine International. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2024/06/05/freight-costs-edge-toward-pandemic-levels-hitting-solar-module-costs/
Jowett, P. (2024b, June 5). Electricity prices falling in most European markets. Pv Magazine International. https://www.pv-magazine.com/2024/06/05/electricity-prices-falling-in-most-european-markets/
Enkhardt, S. (2024, June 7). Österreich führt „Made in Europe“-Bonus für Photovoltaik-Anlagen ab 35 Kilowatt ein. Pv Magazine Deutschland. https://www.pv-magazine.de/2024/06/07/oesterreich-fuehrt-made-in-europe-bonus-fuer-photovoltaik-anlagen-ab-35-kilowatt-ein/
Deboutte, G. (2024, June 7). Les premiers panneaux solaires raccordés en France en 1992 produisent encore 79,5 % de leur puissance initiale. Pv Magazine France. https://www.pv-magazine.fr/2024/06/07/les-premiers-panneaux-solaires-raccordes-en-france-en-1992-produisent-encore-795-de-leur-puissance-initiale/
Yjofsjqptq. (2024, June 10). Siemens installa un parcheggio fotovoltaico e 60 colonnine di ricarica elettrica. Pv Magazine Italia. https://www.pv-magazine.it/2024/06/10/siemens-installa-un-parcheggio-fotovoltaico-e-60-colonnine-di-ricarica-elettrica/
Recommend Reading:

How to Calculate Solar System ROI and Optimize Long-Term Returns?
Solar power is becoming a key solution for businesses to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Accurately calculating ROI and optimizing long-term returns are essential to maximizing investment value.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!

What’s New in Solar Energy (March 2025)
March’s solar news highlights include rooftop solar meeting two-thirds of global demand, China’s market reforms potentially boosting solar demand and module prices, France revising solar targets in PPE 3, and challenges in Europe with declining capture rates and price volatility.

Zero-Investment Solar Projects: How to Earn Passive Income Through Rooftop Leasing?
Monetize your idle rooftop and earn stable annual rent! With the photovoltaic rooftop leasing model, businesses can generate long-term revenue without investment, reduce operating costs, and achieve a green transition.

How to Optimize Photovoltaic Power Plant Operations with AI and Big Data
This article explores three methods of using AI to enhance power generation revenue and reduce operation and maintenance costs in intelligent photovoltaic operations.



