Table of Contents
Intro:
Inverters are crucial components in solar energy systems, they play a key role in converting the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be used to power homes and industries. Join us for an in-depth look at the functions and importance of inverters.
What is an inverter?
A solar inverter is an electronic device used to convert direct current (DC) electricity collected by solar photovoltaic (PV) panels into alternating current (AC) electricity in order to supply power to a home, industrial equipment, or the electrical grid. The electricity generated by solar solar module is DC, but most power-consuming equipment and grids use AC. Therefore, inverters play a key role in solar power systems by converting DC power into AC power suitable for home use or for injection into the grid.
How Solar Inverters Function?
When sunlight makes contact with solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) cells, constructed from crystalline silicon or gallium arsenide semiconductors, a sophisticated process is set in motion. These semiconductor layers consist of a combination of positive and negative layers interconnected by junctions. Upon contact with sunlight, these semiconductors absorb the solar energy, initiating a flow of energy within the photovoltaic cell. This energy circulates, interacting with free electrons, which shuttle between the positive and negative layers, thereby generating direct current (DC) – an electric current characterized by unidirectional flow. Once produced, this electrical energy can be either stored in a battery for later usage or transmitted directly to an inverter, contingent on the specific type of solar system you’ve implemented.
What are the types of inverters?
1. String Inverters
A ‘string’ refers to an array of solar panels organized in clusters or rows and linked in a series configuration. For a string inverter to operate optimally, it’s imperative that all panels within a given string share identical spacing and orientation.
Notably, multiple strings can be connected to a single inverter. In fact, many string inverters feature 2 or even 3 MPPTs (Maximum Power Point Tracking) to accommodate this. This essentially means that different strings of solar panels can be associated with each MPPT. This configuration is particularly advantageous for scenarios such as East/West installations, where two strings of panels can deliver unparalleled solar power generation.

2. Micro inverters
Micro inverters are a relatively new technology that has become a popular choice for home solar PV systems. Given that a solar panel system on a string inverter can be affected by individual panel failures or shadowing, micro inverter systems solve this problem. This is because in a micro inverter system, each individual solar panel has an inverter of its own, thus isolating any problems. As a result, micro inverters are often considered a way to install more solar panels on a roof. As shaded areas are no longer taboo or the need to mix orientations is no longer an issue. Although a micro inverter system is usually more expensive than a traditional string inverter, it can increase your solar power generation and thus improve your return on investment.

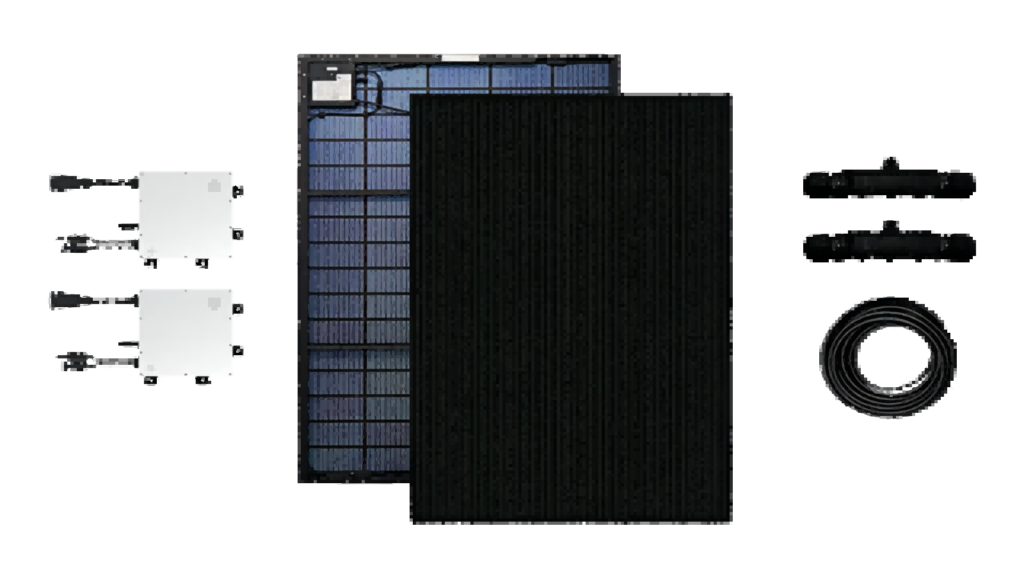
The Maysun Balcony Power Station Mini PV, which contains 2 customized solar panels (390-410W, transparent backsheet) and 2 Hoymiles 400W micro inverters. Micro-inverters enhance the power generation of balcony Balcony Power Station, reducing many potential issues such as the impact of shading, hot spots caused by performance discrepancies between modules, challenges in system scalability, difficulties in monitoring and fault detection, inefficiencies in overall system performance, and safety concerns related to high direct current voltages.
3. Hybrid Solar Inverter
When embarking on the installation of a new solar PV system coupled with energy storage, the concept of a hybrid inverter holds substantial appeal. Given that solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, it is imperative for an inverter to facilitate the conversion of this DC energy into alternating current (AC) for seamless operation of household appliances. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that solar cells inherently store electricity in DC form. Enter the hybrid solar inverter – a versatile solution adept at not only transforming incoming DC power into AC power but also intelligently directing surplus DC power towards the solar cells for storage or potential sale to the grid. This stored energy can subsequently be tapped into and converted back into AC power whenever your home demands it.

4. Power Inverter
Power inverters offer many of the same benefits as microinverters and are also located on each individual panel. Power inverters, also known as DC power optimizers, provide panel-level optimization and performance monitoring. Unlike a microinverter system, instead of converting DC to AC power directly on the roof, the optimizer transfers DC power to a string inverter. It may be installed next to your battery storage system. Because they are at the module level, they are often a cheaper alternative to microinverters.
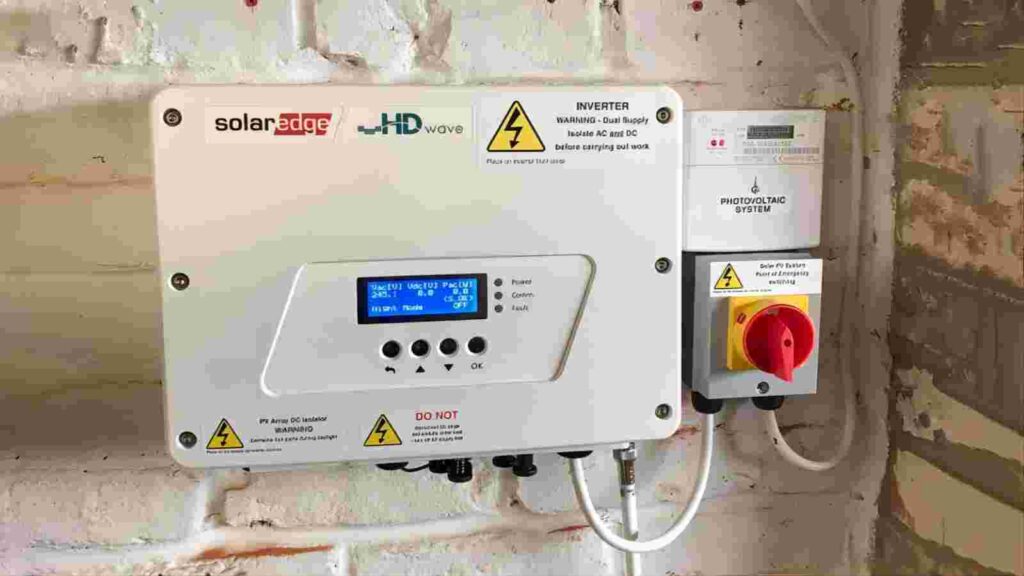

What are the advantages of inverters?
1. Maximize energy production
Solar inverters track the voltage of your solar array to maximize the operating power of your solar panels so you can produce the most, cleanest power possible.
Grid-connected residential solar inverters are known for producing a more pristine sine wave output – a metric that gauges the seamless transition of electrical current. This superior sine wave quality sets them apart from budget-friendly inverters that generate a modified sine wave. The advantage of a purer sine wave is its ability to guarantee the smooth and efficient operation of delicate and sensitive equipment.
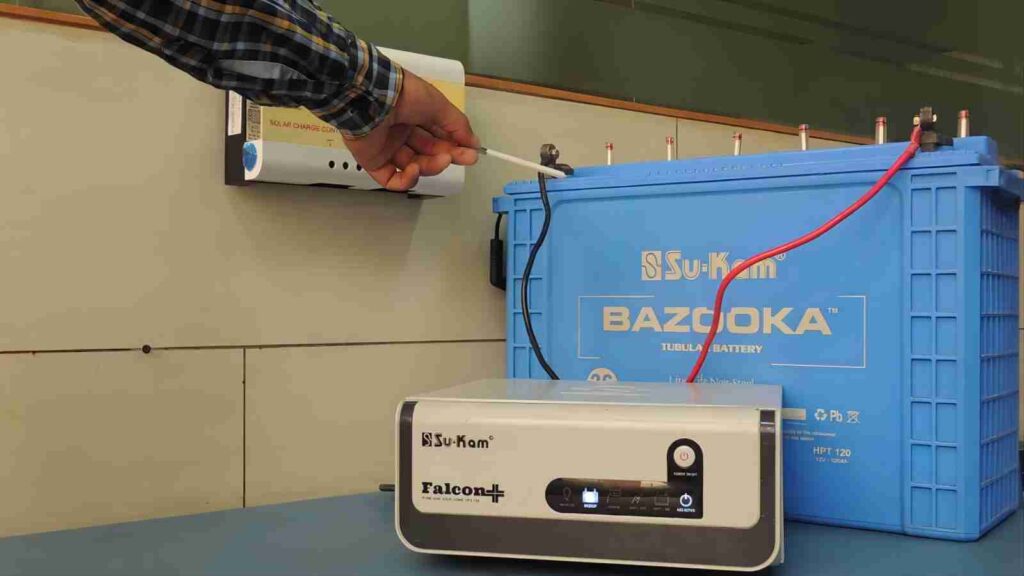

2. Monitor System Output
Observing your solar power system generating thousands of watts during a sunny day is truly exhilarating. As a result, it’s only natural for most homeowners to seek a means of monitoring the performance of their valuable investment.
The majority of solar panel inverters are equipped with built-in mechanisms for displaying real-time energy production. Furthermore, some advanced models offer the convenience of tracking your entire solar system’s performance through a dedicated mobile app or a user-friendly website interface. This enables you to stay connected with your solar system and make the most of your clean energy investment.If something goes wrong, some home inverters will automatically check the performance of your solar system and alert you if they detect a problem with any of the components. You can also use your home inverter’s performance tracking to periodically check how well your system components are working and to make sure they’re producing the right amount of power.
3. Communicate with the utility grid
In the event of a temporary power outage, the solar inverter ensures that power is not transmitted from the panels to external power lines. This way, any line workers who may be inspecting or repairing the grid will be out of harm’s way.
If you have a full solar array, or if your home does not need to generate all of its solar power, the inverter can also feed excess power into the grid to help you generate net energy credits.
What problems are likely to occur with the inverter?
1. Failure or damage to the inverter:
The internal components of the inverter may be damaged, causing it to stop working or degrade in performance. This failure may be caused by aging components, material fatigue, manufacturing defects, or poor operating conditions. Repair may require inverter replacement or repair.
2. MPPT Failure:
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is a key function of the inverter that ensures that the solar panels are working at optimum efficiency. an MPPT failure can be caused by a software problem, a circuit problem, or a faulty sensor. This can result in the solar panels failing to produce their maximum power, thus reducing system efficiency.

3. Communication issues:
Inverters typically communicate with monitoring systems or remote monitoring platforms for remote monitoring and troubleshooting. Communication problems can be caused by network issues, communication module failures, setup errors, or software issues. This may result in the monitoring system not being able to acquire real-time data or perform telemetry operations.
4. Overheating Problems:
High temperature environments may cause the inverter to overheat. Proper heat dissipation measures and location of the inverter are critical to ensure that the inverter can dissipate heat effectively and not overheat. Overheating may cause the inverter to degrade in performance or damage the internal electronics.
How to maintain the inverter?
1. Cleaning and Inspection:
Clean the inverter housing regularly to ensure there is no accumulation of dust, dirt or debris. Use a dry, soft cloth or brush for cleaning and avoid using water or chemical solvents to prevent water ingress or damage to the electronic components. Check for the entry of cobwebs, insects or other small animals as this may affect heat dissipation or cause short circuits.
2. Check Cable Connections:
Periodically check the inverter’s cable connections to make sure they are tight and secure and not loose or oxidized. Loose connections may lead to increased resistance, which can cause overheating problems.
3. Ambient temperature monitoring:
Inverters operating in hot environments require extra attention. Ensure that the inverter is installed in a well-ventilated, shaded location to minimize the risk of overheating. Monitor the operating temperature of the inverter to ensure that it does not overheat.
4.Maintain the cooling system:
Inverters often have built-in cooling systems, such as fans or heat sinks. Ensure that these cooling systems are kept clean and not blocked so that the inverter can dissipate heat effectively.

How to adapt solar inverter to solar module?
There are many inverter brands on the market today, such as Huawei, Homer, Growat, SMA, and many more. Don’t worry, these inverters are all compatible with Maysun solar panels.
1.Power Rating Matching:
The solar inverter should have sufficient power rating to handle the output power of the connected solar module. The power rating of the inverter should be slightly higher than the maximum output power of the solar module to ensure that the solar module are able to perform at their maximum potential. When selecting an inverter, make sure its power rating is appropriate for the total capacity of the solar module.
2.Input current matching:
The inverter must also adapt to the output current of the solar module. The output current varies according to light conditions and temperature, and the inverter must be able to handle this variation.
3.Input connection method:
solar module are usually connected to the inverter in series or parallel. Series connections increase the voltage of the system, while parallel connections increase the current of the system. The inverter must support your specific connection method.
1. MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) function:
Many modern solar inverters have an MPPT function, which tracks the current maximum power point of the solar module to ensure optimal energy conversion efficiency. Make sure your inverter has this feature and configure it to maximize energy use.
Examples:
Maysun Balcony Power Station MiniPV :How do the solar panels adapt to the inverter?
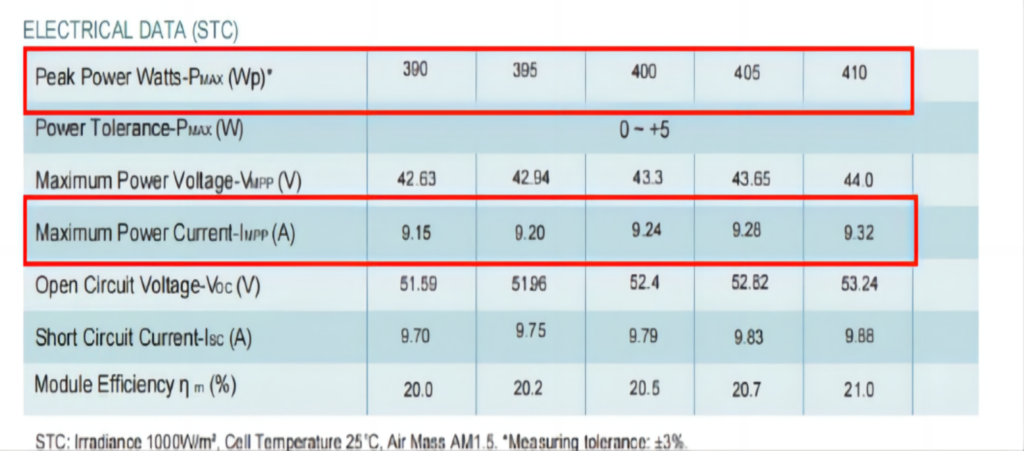
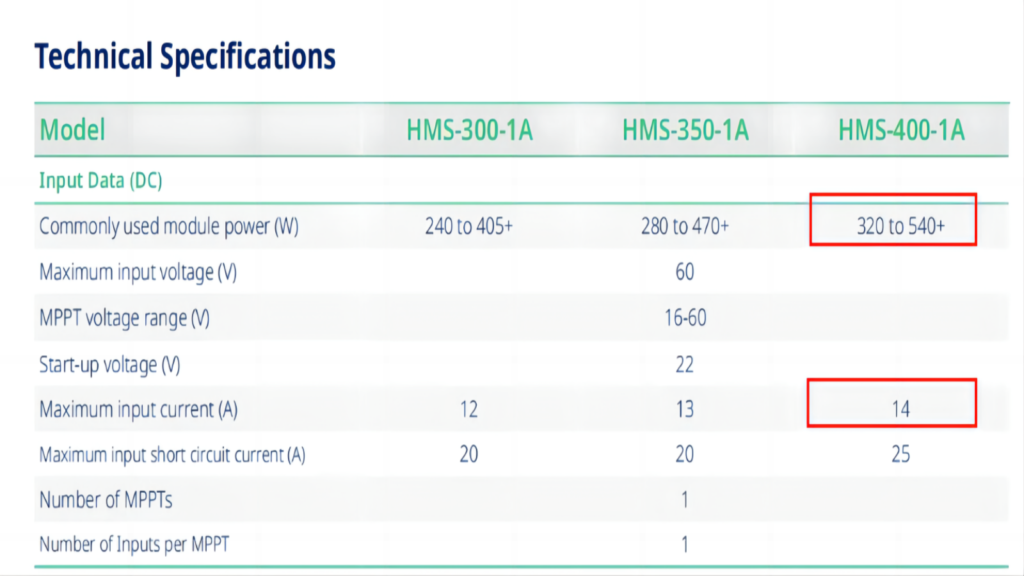
The Maysun Balcony Power Station MiniPV pairs the Venusun S solar panel, with its power range of 390W-410W and a Maximum Power Current of 9.32A, and the Hoymiles inverter HMS-400-1A, designed for a module power range of 320W-540W+ and a Maximum input current of 14A. Their matching power range and maximum current specifications ensure they are perfectly compatible, guaranteeing they will work together efficiently and effectively.
What is MPPT of solar inverter?
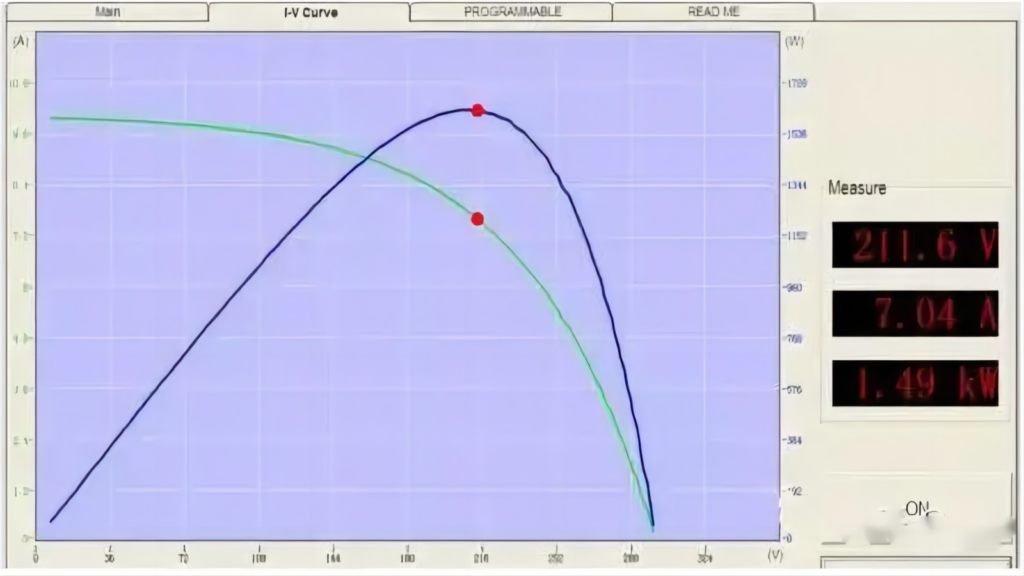
The performance of a photovoltaic (PV) module hinges on its output voltage and current, which adhere to the I-V curve (depicted in green) and the P-V curve (illustrated in blue). To ensure your inverter harnesses the utmost power output, it’s crucial to maintain the DC voltage at the specific point marked by the red dot – this point is known as the maximum power point. For instance, if the maximum power point corresponds to 500V, the power output at this voltage level reaches 200 watts. In contrast, operating at 480V yields around 190 watts, while 530V only produces approximately 185 watts. Clearly, neither of these alternatives match the efficiency of the 500V setting. Neglecting to track 500V leads to a decline in power generation.
Now, you might wonder why it’s imperative to continually track this optimal point. The rationale behind this practice lies in the inherent variability of the PV module’s performance, influenced by factors such as light intensity, temperature, and shading. Consequently, the location of the maximum power point shifts throughout the day – it might be 530V in the morning, 500V at noon, and 520V in the afternoon. As a result, the controller must consistently seek out the maximum power point, employing a technique known as Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). This approach ensures the PV panel maximizes its energy output throughout the day, minimizing the wastage of valuable solar resources.
As the PV module responds to fluctuations in light intensity and external environmental variables, its power output fluctuates accordingly. In situations of intensified sunlight, MPPT-equipped inverters are instrumental in capitalizing on the PV module’s full potential, enabling it to consistently operate at the maximum power point. In essence, under stable solar radiation conditions, the power output post-MPPT surpasses that achieved before employing MPPT, underscoring the significance of this technology.
Maysun does not manufacture inverters, but works closely with a number of well-known inverter manufacturers. When you choose to purchase our photovoltaic panels, you will also benefit from the cooperation with high quality inverter manufacturers that we offer you. Our goal is to provide you with a comprehensive solar solution that ensures your solar power system runs smoothly and excels in energy efficiency and reliability. Whether it’s photovoltaic panels or inverters, we are committed to providing you with the best products and services for your green energy needs.

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!

What’s New in Solar Energy (March 2025)
March’s solar news highlights include rooftop solar meeting two-thirds of global demand, China’s market reforms potentially boosting solar demand and module prices, France revising solar targets in PPE 3, and challenges in Europe with declining capture rates and price volatility.

Zero-Investment Solar Projects: How to Earn Passive Income Through Rooftop Leasing?
Monetize your idle rooftop and earn stable annual rent! With the photovoltaic rooftop leasing model, businesses can generate long-term revenue without investment, reduce operating costs, and achieve a green transition.

How to Optimize Photovoltaic Power Plant Operations with AI and Big Data
This article explores three methods of using AI to enhance power generation revenue and reduce operation and maintenance costs in intelligent photovoltaic operations.

Solar Module Costs May Rise by 10% in 2026! In-Depth Analysis of CBAM’s Impact on the Industry
Table of Contents Introduction to CBAM 1. Why Did the EU Introduce CBAM? As the challenges posed by global climate change intensify, governments worldwide are accelerating their efforts to achieve carbon neutrality. The European Union, a leader in global carbon reduction initiatives, introduced