Table of Contents
Solar energy is becoming a more popular option for households and businesses trying to minimize their carbon footprint and save money on energy bills. Solar systems are classified into two types: on-grid and off-grid. Despite their variations, they both provide similar advantages. The suitability of a solar system for your home or company is determined by your individual needs and circumstances. This article will mainly talk about what makes on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid systems different and then you can consider which system is better for you.
What are on-grid system and off-grid solar system?
On-grid solar system
This technique, also known as grid-tied or grid-feed, is the most popular and widely used in both homes and businesses.
An on-grid solar system, as the name implies, is connected to your local utility grid. On-grid solar systems function in tandem with your home’s power source to provide as much energy as feasible. Its clever architecture enables it to detect when power is available and when it is not, allowing it to synchronize power delivery with grid power.
On-grid solar system is made up of the following parts:
(1)On-grid inverter (GTI) or microinverters
(2)Power meter
The system begins with solar panels, which capture and convert sunlight into DC (direct current). The inverter converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), which is then routed through a switchboard to power your home and appliances. Finally, the power meter monitors power in order to compute the amount of electricity generated by both the grid and the solar system. When there is insufficient solar energy, such as at night or on cloudy days, the inverter returns to its grid power source.
On-grid solar systems are also less expensive because you don’t need to purchase an expensive battery backup device to store extra energy.
Off-grid solar system
Off-grid solar systems are fully isolated from the electrical utility grid, relying primarily on sunshine as its primary energy source, and are completely self-sufficient. This system is more sophisticated, and thus more expensive, than on-grid system.
Off-grid solar system is comprised of the following components:
(1)Solar charge controller
(2)Battery bank
(3)Off-grid inverter
(4)DC Disconnect (additional)
(5)Backup generator (optional)
An off-grid solar system operates by transferring energy from solar panels to a solar battery via a charge controller. The charge controller regulates the amount of energy stored in the battery bank and prevents it from overcharging. To provide power to your home, this electricity is converted into alternating current (AC) using an off-grid inverter.
This system, by storing electricity in its battery bank, allows your home to run entirely on solar energy, even at night or on overcast days. If you live somewhere where there isn’t constantly sunlight throughout the year, you’ll need more battery banks to plan for days without solar exposure. Alternatively, you could consider purchasing a backup generator. These generators typically provide alternating current (AC) power that can be used with an inverter.
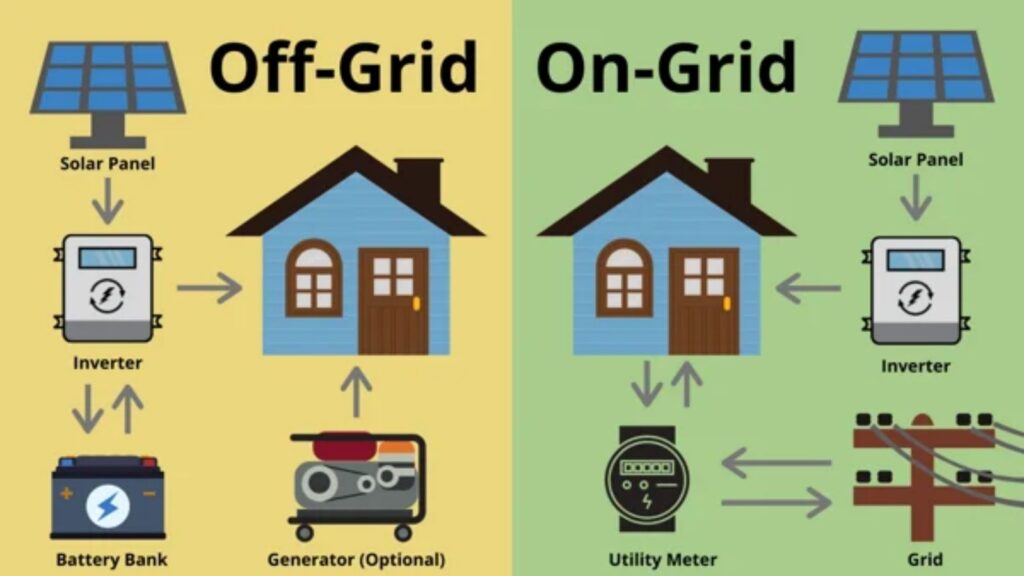
What are the differences between on-grid and off-grid solar systems?
You must carefully analyze your individual demands and circumstances when determining which sort of solar system is best for you. For example, if you live in an area prone to power outages, an off-grid solar system is a great way to maintain a steady supply of electricity. On the other hand, if you want to decrease your carbon footprint while also saving money on electricity, an on-grid solar power system could be a good option. It may allow you to participate in net metering and may also make you feel more safe if you live in a place with dependable electrical infrastructure and little peak sunlight.
Ability to Access Grid Power
On-grid solar systems can both rely on solar energy to produce electricity and use power from the public grid. Off-grid systems have the potential to run out of electricity during extended periods of gloomy weather. On-grid residences can always use the utility company’s electricity as needed.
Power Generation in Excess of Demand
When the system produces more power than you require, on-grid solutions might pay rewards. Sending excess energy back to the grid can earn you money if your utility company enables net metering. For the energy you provide back to the grid, you will normally receive credits on your electric bill. In the same case of an off-grid solar system, the excess power is stored in the battery bank and can be saved for later use.
Grid Power Outage
One of the biggest downsides of on-grid system is that you will not have access to electricity if there is no sunshine and the grid breaks down, resulting in a power outage. Unless, of course, you decide to invest in a battery bank or generator.
Off-grid solar systems give homeowners who live in places prone to power outages or harsh weather peace of mind. They can continue to use electricity even if the power system fails.
Electricity Charges
An on-grid system will still result in minimal charges on your electricity account because it is linked to your local utility grid. A service fee for connecting your solar system to the grid is one of the expenses, as is a demand tax for the higher electric rate you pay for power used during peak demand periods, or when your home uses the most electricity.
One of the benefits of off-grid solar systems is that you do not have to pay electric bills if you generate your own power. Electric bill elimination can be a considerable financial savings for households, particularly in locations with high electricity costs. Producing your own electricity can save you hundreds or even thousands of dollars every year.
Total Cost
The on-grid solution is simple to set up and inexpensive. It allows household and commercial customers to receive passive money from excess energy produced by the systems. According to an Economic Times research, private, commercial, or industrial buildings can benefit from ‘Accelerated Depreciation Benefit’ by installing PV rooftop systems, which is now 80 percent in a year.
While an off-grid solution does not force you to pay electric bills, it does demand a considerable initial expenditure. Fortunately, there are numerous government programs and tax breaks available to assist with the early costs.
Off-grid systems with LFP batteries require little to no maintenance, and solar panels can survive for more than 25 years before needing replacement. Off-grid solar can be a great long-term investment, especially as the cost of traditional electricity sources like fossil fuels continues to grow.
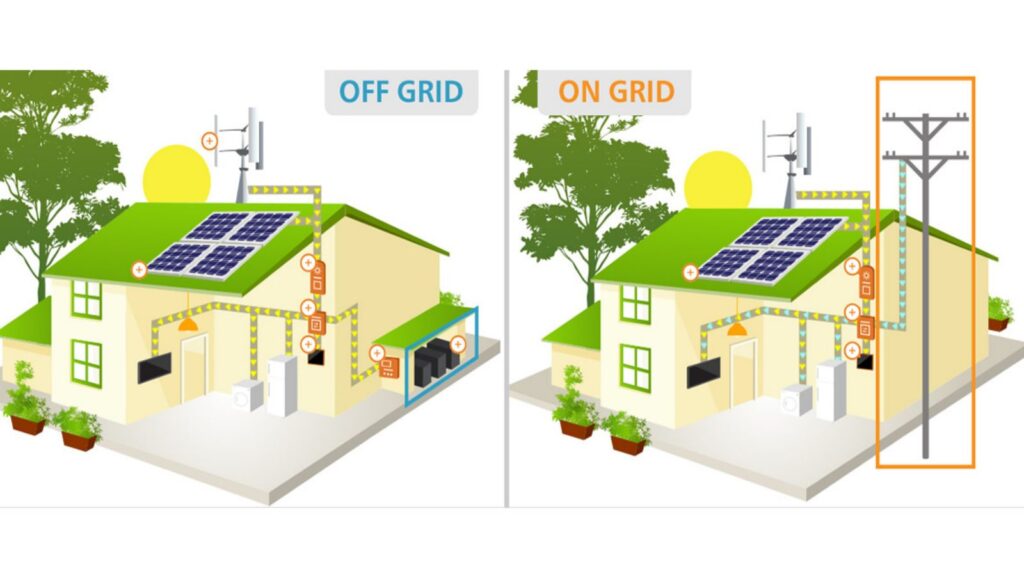

Which is better: on-grid or off-grid solar system?
Here are a few crucial points to consider when determining which sort of solar system is ideal for you:
1. Budget
On-grid solar systems are typically the most cost-effective option. You’ll be able to reduce your monthly electricity expenses while also earning money in the form of credits.
Off-grid is more complicated and requires greater upfront costs for additional equipment such as pricey battery banks to be practical.
2. Situation of the environment
If you reside in a city with convenient access to electricity lines, an on-grid system is simple to install in your house.
However, if you reside in a region that is disconnected from the electricity grid, an off-grid system is the ideal method to power your home.
3. Your Energy Requirements
If you have a large family or building with a high level of power demand, an on-grid solar system is an excellent backup option to ensure you never run out of electricity.
Off-grid systems, on the other hand, have the advantage of being able to store power for 24/7 use if you have a smaller home or reside in an area prone to frequent power outages.
For homes wishing to add solar into their energy mix, both on-grid and off-grid solar systems are feasible possibilities.
On-grid solar system may enable you to take advantage of net metering and save money on your electric bill. Off-grid solar system provides complete energy independence from outdated infrastructure as well as security against power interruptions.
Regardless of which option you pick, creating clean, renewable energy, lowering your carbon footprint, and saving money on energy expenditures is a win-win situation. Before deciding on the type of solar system that is best for you, you must carefully analyze your individual demands and circumstances.
Maysun Solar has been specialising in producing high quality photovoltaic modules since 2008. Choose from our wide variety of full black, black frame, silver, and glass-glass solar panels that utilise half-cut, MBB, IBC, and shingled technologies. These panels offer superior performance and stylish designs that seamlessly blend in with any building. Maysun Solar successfully established offices, warehouses, and long-term relationships with excellent installers in numerous countries! Please contact us for the latest module quotations or any PV-related inquiries. We are excited to assist you.
Reference:
Chint. (2023, March 17). Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid Solar: Which is Right for You? CHINT. https://chintglobal.com/blog/grid-tied-solar-vs-off-grid-solar/
Ecoflow. (2023). What are the differences between On-Grid and Off-Grid solar? EcoFlow US Blog. https://blog.ecoflow.com/us/differences-between-on-grid-off-grid-solar-system/
Genus. (2021). Major Differences between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar System. Genus. https://www.genusinnovation.com/blogs/on-grid-and-off-grid-solar-system
https://www.cnbctv18.com. (2022, January 19). Off-grid or on-grid solar power system, which one should you choose? cnbctv18.com. https://www.cnbctv18.com/environment/off-grid-or-on-grid-solar-power-systems-which-one-should-you-choose-12171952.htm
Solar-Admin. (2022, December 29). A guide on the key differences between On-Grid & Off-Grid solar system. Solar Square Blog. https://www.solarsquare.in/blog/on-grid-and-off-grid-solar-system/
Wolf, S. (n.d.). The difference between Off-Grid and On-Grid solar energy. https://www.paradisesolarenergy.com/blog/difference-between-off-grid-and-on-grid-solar-energy

Will Agrivoltaics Affect Crop Growth?
Agrivoltaics combines solar energy and agriculture to reduce up to 700 tons of CO₂ per MW, improve water use, and boost crop growth for sustainable farming.

6.5 Billion Loss Hits Photovoltaics: Reshaping or Elimination?
In 2025, the photovoltaic market may see a turnaround as some companies take early action. A €6.5 billion loss is driving businesses to explore new growth areas like energy storage and hydrogen. Which giants will break through? Industry transformation is accelerating!

What’s New in Solar Energy (March 2025)
March’s solar news highlights include rooftop solar meeting two-thirds of global demand, China’s market reforms potentially boosting solar demand and module prices, France revising solar targets in PPE 3, and challenges in Europe with declining capture rates and price volatility.

Zero-Investment Solar Projects: How to Earn Passive Income Through Rooftop Leasing?
Monetize your idle rooftop and earn stable annual rent! With the photovoltaic rooftop leasing model, businesses can generate long-term revenue without investment, reduce operating costs, and achieve a green transition.

How to Optimize Photovoltaic Power Plant Operations with AI and Big Data
This article explores three methods of using AI to enhance power generation revenue and reduce operation and maintenance costs in intelligent photovoltaic operations.

Solar Module Costs May Rise by 10% in 2026! In-Depth Analysis of CBAM’s Impact on the Industry
Table of Contents Introduction to CBAM 1. Why Did the EU Introduce CBAM? As the challenges posed by global climate change intensify, governments worldwide are accelerating their efforts to achieve carbon neutrality. The European Union, a leader in global carbon reduction initiatives, introduced



